Math Is Fun Forum
You are not logged in.
- Topics: Active | Unanswered
- Index
- » This is Cool
- » Plasids
Pages: 1
#1 2025-04-16 19:45:27
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,571
Plasids
Plastids
Gist
A plastid is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. Plastids are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. Plant cells with visible chloroplasts.
Plastids are double-membrane bound organelles found in plant cells, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are responsible for various functions, including photosynthesis, pigment storage, and food storage. Plastids are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria.
Summary
Plastids are double-membrane organelles which are found in the cells of plants and algae. Plastids are responsible for manufacturing and storing of food. These often contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis and different types of pigments that can change the colour of the cell.
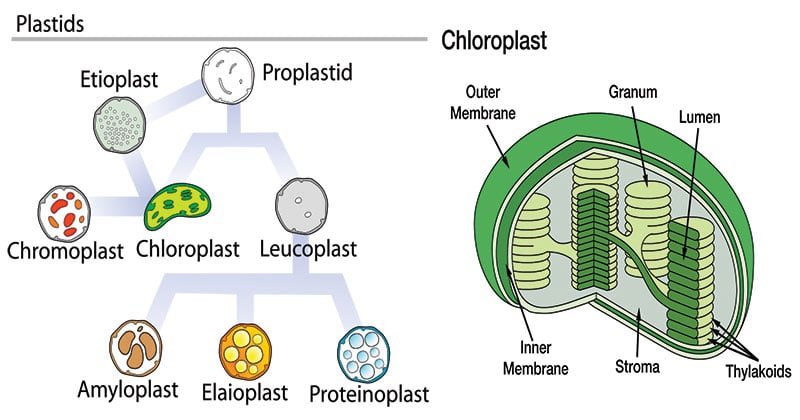
There are different types of plastids with their specialized functions. Among them, a few are mainly classified based on the presence or absence of the Biological pigments and their stages of development.
* Chloroplasts
* Chromoplasts
* Gerontoplasts
* Leucoplasts
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are biconvex shaped, semi-porous, double membraned, cell organelle found within the mesophyll of the plant cell. They are the sites for synthesizing food by the process of photosynthesis.
Chromoplasts
Chromoplasts is the name given to an area for all the pigments to be kept and synthesized in the plant. These can be usually found in flowering plants, ageing leaves and fruits. Chloroplasts convert into chromoplasts. Chromoplasts have carotenoid pigments that allow different colours that you see in leaves and fruits. The main reason for its different colour is for attracting pollinators.
Gerontoplasts
These are basically chloroplasts that go with the ageing process. Geronoplasts refer to the chloroplasts of the leaves that help to convert into different other organelles when the leaf is no longer using photosynthesis usually in an autumn month.
Leucoplasts
These are the non-pigmented organelles which are colourless. Leucoplasts are usually found in most of the non-photosynthetic parts of the plant like roots. They act as a storage sheds for starches, lipids, and proteins depending on the need of the plants. They are mostly used for converting amino acids and fatty acids.
Leucoplasts are of three types:
Amyloplasts – Amyloplasts are greatest among all three and they store and synthesize starch.
Proteinoplasts – Proteinoplasts help in storing the proteins that a plant needs and can be typically found in seeds.
Elaioplasts -Elaioplast helps in storing fats and oils that are needed by the plant.
Inheritance of Plastids
There are many plants which are inherited from the plastids from just a single parent. Angiosperms inherit plastids from the female gamete while there are many gymnosperms that inherit plastids from the male pollen. Algae inherit plastids from one parent only. The inheritance of the plastids-DNA seems to be 100% uniparental. In hybridisation, the inheritance of plastid seems to be more erratic.
Details
A plastid is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. Plastids are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria.
Examples of plastids include chloroplasts (used for photosynthesis); chromoplasts (used for synthesis and storage of pigments); leucoplasts (non-pigmented plastids, some of which can differentiate); and apicoplasts (non-photosynthetic plastids of apicomplexa derived from secondary endosymbiosis).
A permanent primary endosymbiosis event occurred about 1.5 billion years ago in the Archaeplastida clade—land plants, red algae, green algae and glaucophytes—probably with a cyanobiont, a symbiotic cyanobacteria related to the genus Gloeomargarita. Another primary endosymbiosis event occurred later, between 140 and 90 million years ago, in the photosynthetic plastids Paulinella amoeboids of the cyanobacteria genera Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus, or the "PS-clade". Secondary and tertiary endosymbiosis events have also occurred in a wide variety of organisms; and some organisms developed the capacity to sequester ingested plastids—a process known as kleptoplasty.
A. F. W. Schimper[6][a] was the first to name, describe, and provide a clear definition of plastids, which possess a double-stranded DNA molecule that long has been thought of as circular in shape, like that of the circular chromosome of prokaryotic cells—but now, perhaps not; (see "..a linear shape"). Plastids are sites for manufacturing and storing pigments and other important chemical compounds used by the cells of autotrophic eukaryotes. Some contain biological pigments such as used in photosynthesis or which determine a cell's color. Plastids in organisms that have lost their photosynthetic properties are highly useful for manufacturing molecules like the isoprenoids.
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are biconvex shaped, semi-porous, double membraned, cell organelle found within the mesophyll of the plant cell. They are the sites for synthesizing food by the process of photosynthesis.
Chromoplasts
Chromoplasts is the name given to an area for all the pigments to be kept and synthesized in the plant. These can be usually found in flowering plants, ageing leaves and fruits. Chloroplasts convert into chromoplasts. Chromoplasts have carotenoid pigments that allow different colours that you see in leaves and fruits. The main reason for its different colour is for attracting pollinators.
Gerontoplasts
These are basically chloroplasts that go with the ageing process. Geronoplasts refer to the chloroplasts of the leaves that help to convert into different other organelles when the leaf is no longer using photosynthesis usually in an autumn month.
Leucoplasts
These are the non-pigmented organelles which are colourless. Leucoplasts are usually found in most of the non-photosynthetic parts of the plant like roots. They act as a storage sheds for starches, lipids, and proteins depending on the need of the plants. They are mostly used for converting amino acids and fatty acids.
Leucoplasts are of three types:
* Amyloplasts – Amyloplasts are greatest among all three and they store and synthesize starch.
* Proteinoplasts – Proteinoplasts help in storing the proteins that a plant needs and can be typically found in seeds.
* Elaioplasts -Elaioplast helps in storing fats and oils that are needed by the plant.
Inheritance of Plastids
There are many plants which are inherited from the plastids from just a single parent. Angiosperms inherit plastids from the female gamete while there are many gymnosperms that inherit plastids from the male pollen. Algae inherit plastids from one parent only. The inheritance of the plastids-DNA seems to be 100% uniparental. In hybridisation, the inheritance of plastid seems to be more erratic.
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
Pages: 1
- Index
- » This is Cool
- » Plasids