Math Is Fun Forum
You are not logged in.
- Topics: Active | Unanswered
Pages: 1
#1 Yesterday 17:44:35
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,225
Balanced Diet
Balanced Diet
Gist
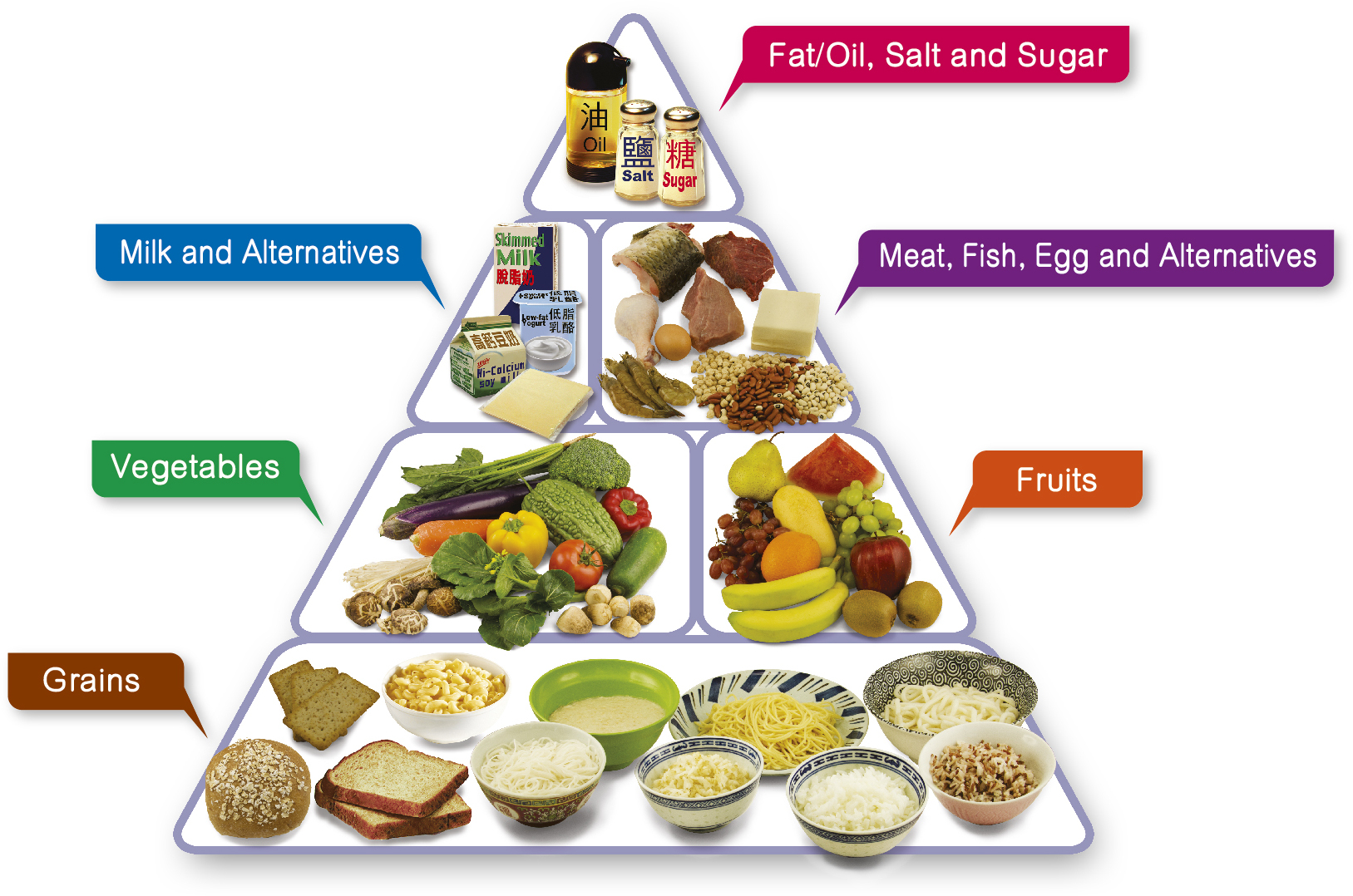
A balanced diet provides the essential nutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, fiber, and water—needed for optimal bodily function, growth, and disease prevention. It generally consists of 50-60% carbohydrates (whole grains), 10-15% protein, 20-30% healthy fats, and high intake of fruits and vegetables. A simple, effective method is the "plate method": half vegetables/fruits, one-quarter protein, and one-quarter whole grains.
A healthy diet is essential for good health and nutrition. It protects you against many chronic noncommunicable diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes and cancer. Eating a variety of foods and consuming less salt, sugars and saturated and industrially-produced trans-fats, are essential for healthy diet.
What is a balanced diet?
This means eating a wide variety of foods in the right proportions, and consuming the right amount of food and drink to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight.
Summary
A balanced diet is essential for a healthy body, but given all the different opinions and trends around food, figuring out what constitutes a healthy diet can be confusing. One source says to cut carbs, another says to eat more fat, but a balanced diet isn't just about following strict rules or cutting out foods you enjoy; it's about including a variety of foods in the right amounts to give your body the nutrients it needs to function well. It supports everything from your energy levels and digestion to immunity and overall health. This blog will demystify what constitutes a balanced diet, explore its numerous benefits beyond just physical health, and provide practical sample meal plans that you can easily adapt to your personal preferences and lifestyle.
What is a Balanced Diet?
A balanced diet isn’t defined by one specific food or meal — it’s about the overall pattern of your eating habits over time. It means getting the right proportion of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) along with essential micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) through a varied and consistent diet.
To put it into perspective:
* Around 50–60% of your daily energy should ideally come from carbohydrates (preferably whole grains and fibre-rich sources).
* 10–15% should come from protein (from both animal and plant sources).
* 20–30% from fats (focusing on unsaturated fats and limiting trans fats and excess saturated fats).
But numbers aside, a practical way to visualise a balanced meal is the “plate method”: half your plate should contain vegetables and fruits, one-quarter should have whole grains, and the remaining quarter should include a protein source. Adding a small serving of healthy fat — such as nuts, seeds, or a dash of oil — rounds it out.
Water, too, is an often-overlooked part of a balanced diet. Staying hydrated supports digestion, metabolism, and even appetite regulation.
A balanced diet isn’t about rigid rules — it’s flexible, adaptable, and can look different for each person depending on their age, activity level, health status, and cultural food preferences.
What are the Components of a Balanced Diet?
A balanced diet is made up of several key components, each serving a vital function to keep your body healthy and operating at its best. Here's a more detailed look at the main nutrients and their roles:
1. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body's primary source of energy. They fuel your muscles, brain, and organs, and are particularly important during physical activity. Carbohydrates are found in both simple and complex forms:
Simple carbohydrates: These are sugars found in fruits, dairy, and processed foods (like sweets and sugary drinks). While they provide quick energy, it’s best to limit refined sugars.
Complex carbohydrates: These come from whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables (like sweet potatoes). They are broken down more slowly, providing sustained energy and supporting digestive health due to their fibre content.
2. Proteins
Proteins are essential for growth, muscle repair, and immune function. They help in the production of enzymes, hormones, and other vital body chemicals. Proteins are made up of amino acids, some of which must be obtained from food. High-quality protein sources include:
Animal-based: Chicken, fish, eggs, and dairy.
Plant-based: Lentils, beans, chickpeas, tofu, quinoa, and seeds. Proteins also help keep you full longer, making them a great part of weight management.
3. Fats
Fats are crucial for maintaining healthy cell membranes, producing hormones, and absorbing fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). While fats are often viewed negatively, healthy fats are essential for overall health:
Unsaturated fats: Found in avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish (such as salmon and mackerel), these fats support heart health and help reduce inflammation.
Saturated fats: Present in animal products (like butter and cheese) and some plant oils (like coconut oil), these should be consumed in moderation.
Trans fats: These artificial fats are found in processed and fried foods and should be avoided as they contribute to poor heart health.
4. Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are micronutrients that regulate processes in the body, from immunity and energy production to bone health and wound healing. They don't provide energy but are essential for a variety of functions:
Vitamins: Different vitamins play various roles in maintaining health. For example, Vitamin C (found in citrus fruits) helps boost immunity, while Vitamin A (found in carrots and leafy greens) supports vision and skin health.
Minerals: Key minerals like calcium (for bones and teeth), iron (for oxygen transport in blood), and magnesium (for muscle function) are found in foods such as dairy, leafy greens, meats, and legumes.
5. Fibre
Fibre is an essential part of a healthy diet, particularly for digestive health. It helps regulate bowel movements, prevents constipation, and can reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Fibre is found in:
Soluble fibre: Found in oats, apples, beans, and peas, this type helps lower cholesterol and regulate blood sugar levels.
Insoluble fibre: Found in whole grains, vegetables, and nuts, this type helps with bowel regularity and digestive health
6. Water
Water is often overlooked but is a critical component of a balanced diet. It makes up about 60% of your body and is involved in nearly every bodily function, including temperature regulation, digestion, and nutrient transport. Staying well-hydrated is essential for maintaining energy, supporting brain function, and keeping your skin healthy. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day, or more if you're physically active.
Why Is a Balanced Diet Important?
A balanced diet is crucial for maintaining optimal health and supporting the body’s daily functions. It provides essential nutrients that help the body perform key tasks, from boosting energy levels to supporting immune function. Without the proper mix of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals, the body cannot function efficiently, leading to fatigue, illness, and long-term health issues. By prioritising a balanced diet, you can reduce the risk of chronic diseases, improve mental and physical well-being, and ensure the body has everything it needs to thrive.
Details
Generally, a healthy diet consists of many fresh fruits and vegetables and limits processed foods. But ask your doctor or a dietitian for advice on making more specific dietary changes to improve your health.
What is a balanced diet?
A balanced diet gives your body the nutrients it needs to function correctly. To get the nutrition you need, most of your daily calories should come from:
* fresh fruits
* fresh vegetables
* whole grains
* legumes
* nuts
* lean proteins
About calories
The number of calories in a food refers to the amount of energy stored in that food. Your body uses calories from food for walking, thinking, breathing, and other important functions.
The average person needs about 2,000 calories every day to maintain their weight, but the amount will depend on their age, sex, and physical activity level.
Males tend to need more calories than females, and people who exercise need more calories than people who don’t.
The source of your daily calories are also important. Foods that provide mainly calories and very little nutrition are known as “empty calories.”
Examples of foods that provide empty calories include:
* cakes, cookies, and donuts
* processed meats
* energy drinks and sodas
* fruit drinks with added sugar
* ice cream
* chips and fries
* pizza
* sodas
However, it’s not only the type of food but the ingredients that make it nutritious.
A homemade pizza with a wholemeal base and plenty of fresh veggies on top may be a healthy choice. In contrast, premade pizzas and other highly processed foods often contain empty calories.
To maintain good health, limit your consumption of empty calories and instead try to get your calories from foods that are rich in other nutrients.
Get some tips for curbing cravings of less nutritious foods.
Calories are a measure of energy that foods supply. The number of calories you need will depend on your sex, age, and activity level.
Why a balanced diet is important
A balanced diet supplies the nutrients your body needs to work effectively. Without balanced nutrition, your body is more prone to disease, infection, fatigue, and low performance.
Children who don’t get enough healthy foods may face growth and developmental problems, poor academic performance, and frequent infections.
They can also develop unhealthy eating habits that may persist into adulthood.
Without exercise, they’ll also have a higher risk of obesity and various diseases that make up metabolic syndrome, such as type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure.
According to the Center for Science in the Public Interest, 4 of the top 10 leading causes of death in the United States are directly linked to diet.
These are:
* heart disease
* cancer
* stroke
* type 2 diabetes
Your body needs nutrients to stay healthy, and food supplies essential nutrients that stop us from getting sick.
What to eat for a balanced diet
A healthy, balanced diet will usually include the following nutrients:
* vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants
* carbohydrates, including starches and fiber
* protein
* healthy fats
A balanced diet will include a variety of foods from the following groups:
* fruits
* vegetables
* grains
* dairy
* protein foods
Examples of protein foods include meat, eggs, fish, beans, nuts, and legumes.
People who follow a vegan diet will focus entirely on plant-based foods. They won’t eat meat, fish, or dairy, but their diet will include other items that provide similar nutrients.
Tofu and beans, for example, are plant-based sources of protein. Some people are intolerant of dairy but can still build a balanced diet by choosing a variety of nutrient-rich replacements.
Foods to avoid
Foods to avoid or limit on a healthy diet include:
* highly processed foods
* refined grains
* added sugar and salt
* red and processed meat
* alcohol
* trans fats
What’s healthy for one person may not be suitable for another.
Whole wheat flour can be a healthy ingredient for many people but isn’t suitable for those with a gluten intolerance, for example.
Fruits
Fruits are nutritious, they make a tasty snack or dessert, and they can satisfy a sweet tooth.
Local fruits that are in season are fresher and provide more nutrients than imported fruits.
Fruits are high in sugar, but this sugar is natural. Unlike candies and many sweet desserts, fruits also provide fiber and other nutrients. This means they’re less likely to cause a sugar spike and they’ll boost the body’s supply of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
If you have diabetes, your doctor or dietitian can advise you on which fruits to choose, how much to eat, and when.
Vegetables
Vegetables are a key source of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Eat a variety of vegetables with different colors for a full range of nutrients.
Dark, leafy greens are an excellent source of many nutrients. They include:
* spinach
* kale
* green beans
* broccoli
* collard greens
* Swiss chard
Local, seasonal vegetables are often reasonable in price and easy to prepare. Use them in the following ways:
* as a side dish
* roasted in a tray with a splash of olive oil
* as the base in soups, stews, and pasta dishes
* as a salad
* in purées
* in juices and smoothies
Grains
Refined white flour is featured in many breads and baked goods, but it has limited nutritional value. This is because much of the goodness is in the hull of the grain, or outer shell, and the center, or “wheat germ,” which manufacturers remove during processing.
Whole grain products include the entire grain, including the hull and germ. They provide additional vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Many people also find that whole grains add flavor and texture to a dish.
Try switching from white breads, pastas, and rice to whole grain options.
Proteins
Meats and beans are primary sources of protein, which is essential for wound healing and muscle maintenance and development, among other functions.
Additional Information
A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthful diet provides the body with essential nutrition: water, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy.
A healthy diet may contain fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and may include little to no ultra-processed foods or sweetened beverages. The requirements for a healthy diet can be met from a variety of plant-based and animal-based foods, although additional sources of vitamin B12 are needed for those following a vegan diet. Various nutrition guides are published by medical and governmental institutions to educate individuals on what they should be eating to be healthy. Not only advertising may drive preferences towards unhealthy foods. To reverse this trend, consumers should be informed, motivated and empowered to choose healthy diets. Nutrition facts labels are also mandatory in some countries to allow consumers to choose between foods based on the components relevant to health.
It was estimated that 40% of the world population in 2023 could not afford a healthy diet. This is often a political issue. The Food and Agriculture Organization and the World Health Organization have formulatedfour core principles of what constitutes healthy diets. According to these two organizations, health diets are:
* Adequate, as they meet, without exceeding, our body's energy and essential nutrient requirements in support of all the many body functions.
* Diverse, as they include various nutritious foods within and across food groups to help secure the sufficient nutrients needed by our bodies.
* Balanced, as they include energy from the three primary sources (protein, fats, and carbohydrates) in a balanced way and foster healthy weight, growth and activity, and to prevent disease.
* Moderate, as they include only small quantities (or none) of foods that may have a negative impact on health, such as highly salty and sugary foods.
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
Pages: 1