Math Is Fun Forum
You are not logged in.
- Topics: Active | Unanswered
Pages: 1
#1 2025-02-09 18:37:34
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 52,751
Acetic Acid
Acetic Acid
Gist
Acetic acid is also known as ethanoic acid, ethylic acid, vinegar acid, and methane carboxylic acid. Acetic acid is a byproduct of fermentation, and gives vinegar its characteristic odor.
In the chemical industry, acetic acid is used in the production of cleaning products and, in the pharmaceutical industry, in supplements and some medicines, as it is capable of stabilising blood pressure and reducing blood sugar levels. It is also a common ingredient in ointments.
It is also used in some skin care products to adjust and maintain their pH. Acetic acid has antimicrobial properties – but not of the same potency or effectiveness as FDA-approved antimicrobial agents such as benzoyl peroxide.
Summary
Acetic acid is also known as ethanoic acid, ethylic acid, vinegar acid, and methane carboxylic acid. Acetic acid is a byproduct of fermentation, and gives vinegar its characteristic odor. Vinegar is about 4-6% acetic acid in water. More concentrated solutions can be found in laboratory use, and pure acetic acid containing only traces of water is known as glacial acetic acid. Dilute solutions like vinegar can contact skin with no harm, but more concentrated solutions will burn the skin. Glacial acetic acid can cause skin burns and permanent eye damage, and will corrode metal.
What is acetic acid used for?
Acetic acid is used in the manufacture of acetic anhydride, cellulose acetate, vinyl acetate monomer, acetic esters, chloracetic acid, plastics, dyes, insecticides, photographic chemicals, and rubber. Other commercial uses include the manufacture of vitamins, antibiotics, hormones, and organic chemicals, and as a food additive (acidulant). It is also used in various textile printing processes.
What are natural sources of acetic acid?
Acetates (salts of acetic acid) are common constituents of animal and plant tissues and are formed during the metabolism of food substances. Acetate is readily metabolized by most tissues and may give rise to the production of ketones as intermediates. Acetate is used by the body as a building block to make phospholipids, neutral lipids, steroids, sterols, and saturated and unsaturated fatty acids in a variety of human and animal tissue preparations.
What are the health effects of acetic acid exposure?
The low concentrations most people encounter in vinegar and other foods are harmless. At higher concentrations that could be encountered in a laboratory or factory, acetic acid is a strong eye, skin, and mucous membrane irritant. Prolonged skin contact with concentrated acetic acid may result in tissue destruction. Inhalation exposure to high concentrations of acetic acid vapors causes irritation of eyes, nose, and throat. People with high occupational exposure can develop conjunctivitis, bronchitis and pharyngitis, and erosion of exposed teeth (incisors and canines).
Details
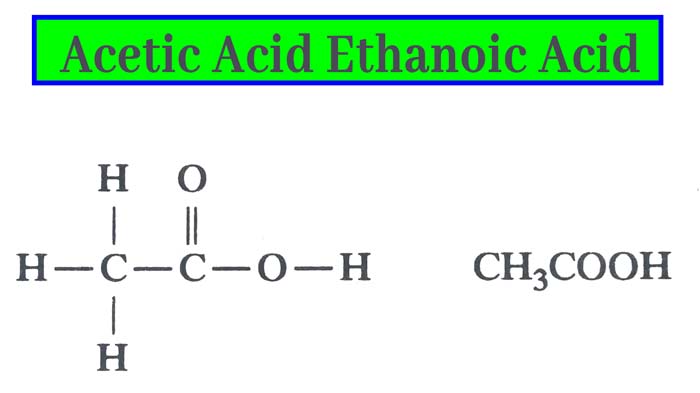
Acetic acid, systematically named ethanoic acid, is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH (also written as CH3CO2H, C2H4O2, or HC2H3O2). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. It has been used, as a component of vinegar, throughout history from at least the third century BC.
Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important chemical reagent and industrial chemical across various fields, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is fundamental to all forms of life. When bound to coenzyme A, it is central to the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats.
The global demand for acetic acid as of 2023 is about 17.88 million metric tonnes per year (t/a). Most of the world's acetic acid is produced via the carbonylation of methanol. Its production and subsequent industrial use poses health hazards to workers, including incidental skin damage and chronic respiratory injuries from inhalation.
Nomenclature
The trivial name "acetic acid" is the most commonly used and preferred IUPAC name. The systematic name "ethanoic acid", a valid IUPAC name, is constructed according to the substitutive nomenclature. The name "acetic acid" derives from the Latin word for vinegar, "acetum", which is related to the word "acid" itself.
"Glacial acetic acid" is a name for water-free (anhydrous) acetic acid. Similar to the German name "Eisessig" ("ice vinegar"), the name comes from the solid ice-like crystals that form with agitation, slightly below room temperature at 16.6 °C (61.9 °F). Acetic acid can never be truly water-free in an atmosphere that contains water, so the presence of 0.1% water in glacial acetic acid lowers its melting point by 0.2 °C.
A common symbol for acetic acid is AcOH (or HOAc), where Ac is the pseudoelement symbol representing the acetyl group CH3−C(=O)−; the conjugate base, acetate (CH3COO−), is thus represented as AcO−. Acetate is the ion resulting from loss of H+ from acetic acid. The name "acetate" can also refer to a salt containing this anion, or an ester of acetic acid. (The symbol Ac for the acetyl functional group is not to be confused with the symbol Ac for the element actinium; context prevents confusion among organic chemists). To better reflect its structure, acetic acid is often written as CH3−C(O)OH, CH3−C(=O)−OH, CH3COOH, and CH3CO2H. In the context of acid–base reactions, the abbreviation HAc is sometimes used, where Ac in this case is a symbol for acetate (rather than acetyl).
The carboxymethyl functional group derived from removing one hydrogen from the methyl group of acetic acid has the chemical formula −CH2−C(=O)−OH.
Additional Information
Acetic acid (CH3COOH) is the most important of the carboxylic acids. A dilute (approximately 5 percent by volume) solution of acetic acid produced by fermentation and oxidation of natural carbohydrates is called vinegar; a salt, ester, or acylal of acetic acid is called acetate. Industrially, acetic acid is used in the preparation of metal acetates, used in some printing processes; vinyl acetate, employed in the production of plastics; cellulose acetate, used in making photographic films and textiles; and volatile organic esters (such as ethyl and butyl acetates), widely used as solvents for resins, paints, and lacquers. Biologically, acetic acid is an important metabolic intermediate, and it occurs naturally in body fluids and in plant juices.
Acetic acid has been prepared on an industrial scale by air oxidation of acetaldehyde, by oxidation of ethanol (ethyl alcohol), and by oxidation of butane and butene. Today acetic acid is manufactured by a process developed by the chemical company Monsanto in the 1960s; it involves a rhodium-iodine catalyzed carbonylation of methanol (methyl alcohol).
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
Pages: 1