Math Is Fun Forum
You are not logged in.
- Topics: Active | Unanswered
Pages: 1
#1 2023-10-09 21:43:18
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,057
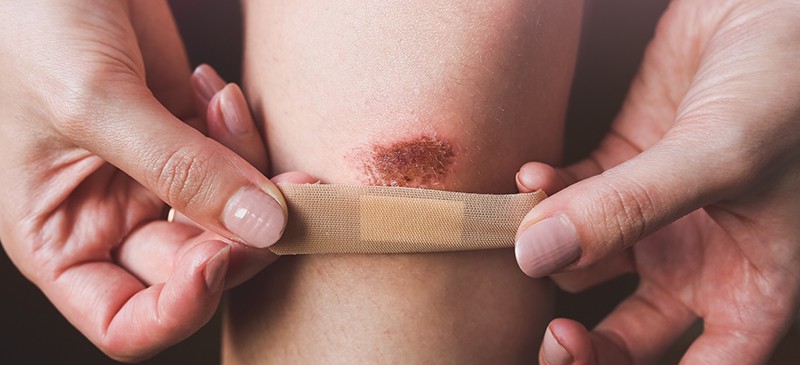
Abrasion (medical)
Abrasion (medical)
Gist
An abrasion is a superficial rub or wearing off of the skin, usually caused by a scrape or a brush burn. Abrasions are usually minor injuries that can be treated at home. The skin may bleed or drain small amounts at the time of the injury or at times over the next few days if rubbed or scratched.
Summary
An abrasion is a partial thickness wound caused by damage to the skin and can be superficial involving only the epidermis to deep, involving the deep dermis. Abrasions usually involve minimal bleeding. Mild abrasions, also known as grazes or scrapes, do not scar or bleed because the dermis is left intact, but deep abrasions that disrupt the normal dermal structures may lead to the formation of scar tissue. A more traumatic abrasion that removes all layers of skin is called an avulsion.
Abrasion injuries most commonly occur when exposed skin comes into moving contact with a rough surface, causing a grinding or rubbing away of the upper layers of the epidermis.
By degree
Abrasions on elbow and lower arm. The elbow wound will produce a permanent scar.
* A first-degree abrasion involves only epidermal injury.
* A second-degree abrasion involves the epidermis as well as the dermis and may bleed slightly.
* A third-degree abrasion involves damage to the subcutaneous layer and the skin and is often called an avulsion.
Treatment
The abrasion should be cleaned and any debris removed. A topical antibiotic (such as neomycin or bacitracin) should be applied to prevent infection and to keep the wound moist. Dressing the wound is beneficial because it helps keep the wound from drying out, providing a moist environment conducive for healing. If the abrasion is painful, a topical analgesic (such as lidocaine or benzocaine) can be applied, but for large abrasions, a systemic analgesic may be necessary. Avoid exposing abraded skin to the sun as permanent hyperpigmentation can develop.
Details
What is an abrasion?
An abrasion is a superficial rub or wearing off of the skin, usually caused by a scrape or a brush burn. Abrasions are usually minor injuries that can be treated at home. The skin may bleed or drain small amounts at the time of the injury or at times over the next few days if rubbed or scratched.
First aid for abrasions
* Calm your child and let them know you can help.
* Wash your hands well.
* Wash the abraded area well with soap and water, but don't scrub the wound. Remove any dirt particles from the area and let the water from the faucet run over it for several minutes. A dirty abrasion that isn't well cleaned can cause scarring or infection
* Apply an antiseptic lotion, cream, or petroleum jelly.
* Cover the area with an adhesive bandage or gauze pad if the area is on the hands or feet, or if it is likely to drain onto clothing. Change the dressing often.
* Check the area each day and keep it clean and dry.
* Don't blow on the abrasion. This can cause germs from your mouth to grow.
When should I call my child's healthcare provider?
Specific treatment for skin wounds will be determined by your child's healthcare provider. In general, call your child's provider for abrasions that:
* Are located close to the eye or on the face.
* Are embedded with debris, such as dirt, stones, or gravel.
* Show signs of infection, such as fever, increased warmth, redness, swelling, or drainage.
* Cover a large area of the body, such as the chest, back, or an entire arm or leg.
* Bleed significantly after applying pressure for 5 minutes.
Additional Information
Abrasion is damage to the epidermis of the skin. Abrasions are caused primarily by friction against a rough surface, which removes the superficial skin layers. Although most abrasions are simply scrapes and are easily treated, large, very painful, or infected abrasions may require medical attention and may result in scarring. Common sites of abrasion injury include the knees, the elbows, and the palms of the hands.
The first goal of abrasion treatment is to stop the bleeding, which can be accomplished by applying pressure to the injury with a clean cloth or other absorbent material. Next, the wound is cleaned, usually with warm water or a sterile saline solution, and foreign materials are removed. Depending on the depth of debris within the epidermis, more or less pressure may be needed while irrigating the wound. In some instances, the removal of foreign material from an injury may require treatment by a physician. Once clean, the abrasion may be dressed with petroleum jelly or a topical antibiotic ointment. Pain associated with an abrasion can be alleviated with a topical anesthetic.
Abrasions are typically painful and bleed right away, but as with all skin injuries, they can be put on a spectrum of severity. Often, an abrasion is minor or superficial, yet it’s still a wound that needs to be treated properly to prevent infection and encourage optimal healing.
How do you heal an abrasion fast? There are a lot of natural ways to encourage healing and ward off harmful bacteria including through your diet, essential oils and some household items you probably already have on hand!
What Is an Abrasion?
To simply define abrasion: it’s a superficial rub or wearing off of the skin, which is usually caused by a scrape or the friction of skin rubbing against a surface. Abrasions may involve the epidermis (the top layer of skin) or some/all of the dermis (the layer of skin below the epidermis).
Most of the time abrasions are minor skin injuries that can be treated at home. You should follow basic first aid instructions, including keeping the area covered with a clean bandage. This will help to keep the abrasion from any further rubbing that can cause additional bleeding or drainage in addition to what occurred after the skin was initially abraded.
There are abrasions called raspberries/strawberries/road rash which are typically bright red and painful but generally only involve the outer most layer of skin (the epidermis). A more traumatic abrasion that removes all layers of skin is called an avulsion, which always warrants emergency medical care.
How long do abrasion wounds take to heal? Minor abrasions only take a short time to heal, while more severe abrasions can take weeks or even months to completely heal.
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
Pages: 1