Math Is Fun Forum
You are not logged in.
- Topics: Active | Unanswered
#2376 2024-12-13 16:49:25
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2276) Gastroenteritis
Gist
Gastroenteritis means inflammation in your stomach and intestine. Inflammation makes these organs feel swollen and sore. It causes symptoms of illness, like nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea. Gastroenteritis often happens when you get an infection in your gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Summary
Gastroenteritis is an acute infectious syndrome of the stomach lining and the intestine. It is characterized by diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps. Other symptoms can include nausea, fever, and chills. The severity of gastroenteritis varies from a sudden but transient attack of diarrhea to severe dehydration.
Numerous viruses, bacteria, and parasites can cause gastroenteritis. Microorganisms cause gastroenteritis by secreting toxins that stimulate excessive water and electrolyte loss, thereby causing watery diarrhea, or by directly invading the walls of the gut, triggering inflammation that upsets the balance between the absorption of nutrients and the secretion of wastes.
Viral gastroenteritis, or viral diarrhea, is perhaps the most common type of diarrhea worldwide; rotaviruses, caliciviruses, Norwalk viruses, and adenoviruses are the most common causes. Other forms of gastroenteritis include food poisoning, cholera, and traveler’s diarrhea, which develops within a few days after traveling to a country or region that has unsanitary water or food. Traveler’s diarrhea is caused by exposure to enterotoxin-producing strains of the common intestinal bacterium Escherichia coli.
Details
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea, is an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of energy, and dehydration may also occur. This typically lasts less than two weeks. Although it is not related to influenza, in the U.S. and U.K., it is sometimes called the "stomach flu".
Gastroenteritis is usually caused by viruses; however, gut bacteria, parasites, and fungi can also cause gastroenteritis. In children, rotavirus is the most common cause of severe disease. In adults, norovirus and Campylobacter are common causes. Eating improperly prepared food, drinking contaminated water or close contact with a person who is infected can spread the disease. Treatment is generally the same with or without a definitive diagnosis, so testing to confirm is usually not needed.
For young children in impoverished countries, prevention includes hand washing with soap, drinking clean water, breastfeeding babies instead of using formula, and proper disposal of human waste. The rotavirus vaccine is recommended as a prevention for children. Treatment involves getting enough fluids. For mild or moderate cases, this can typically be achieved by drinking oral rehydration solution (a combination of water, salts and sugar). In those who are breastfed, continued breastfeeding is recommended. For more severe cases, intravenous fluids may be needed. Fluids may also be given by a nasogastric tube. Zinc supplementation is recommended in children. Antibiotics are generally not needed. However, antibiotics are recommended for young children with a fever and bloody diarrhea.
In 2015, there were two billion cases of gastroenteritis, resulting in 1.3 million deaths globally. Children and those in the developing world are affected the most. In 2011, there were about 1.7 billion cases, resulting in about 700,000 deaths of children under the age of five. In the developing world, children less than two years of age frequently get six or more infections a year. It is less common in adults, partly due to the development of immunity.
Signs and symptoms
Gastroenteritis usually involves both diarrhea and vomiting. Sometimes, only one or the other is present. This may be accompanied by abdominal cramps. Signs and symptoms usually begin 12–72 hours after contracting the infectious agent. If due to a virus, the condition usually resolves within one week. Some viral infections also involve fever, fatigue, headache and muscle pain. If the stool is bloody, the cause is less likely to be viral and more likely to be bacterial. Some bacterial infections cause severe abdominal pain and may persist for several weeks.
Children infected with rotavirus usually make a full recovery within three to eight days. However, in poor countries treatment for severe infections is often out of reach and persistent diarrhea is common. Dehydration is a common complication of diarrhea. Severe dehydration in children may be recognized if the skin color and position returns slowly when pressed. This is called "prolonged capillary refill" and "poor skin turgor". Abnormal breathing is another sign of severe dehydration. Repeat infections are typically seen in areas with poor sanitation, and malnutrition. Stunted growth and long-term cognitive delays can result.
Reactive arthritis occurs in 1% of people following infections with Campylobacter species. Guillain–Barré syndrome occurs in 0.1%. Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) may occur due to infection with Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli or Shigella species. HUS causes low platelet counts, poor kidney function, and low red blood cell count (due to their breakdown). Children are more predisposed to getting HUS than adults. Some viral infections may produce benign infantile seizures.
Additional Information
Gastroenteritis is when your stomach and intestines are irritated and inflamed. This can cause belly pain, cramping, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The cause is typically inflammation triggered by your immune system's response to a viral or bacterial infection. However, infections caused by fungi or parasites or irritation from chemicals can also lead to gastroenteritis.
You may have heard the term "stomach flu." When people say this, they usually mean gastroenteritis caused by a virus. However, it's not actually related to the flu, or influenza, which is a different virus that affects your upper respiratory system (nose, throat, and lungs).
Gastroenteritis Symptoms
Gastroenteritis symptoms often start with little warning. You'll usually get nausea, cramps, diarrhea, and vomiting. Expect to make several trips to the toilet in rapid succession. Other symptoms tend to develop a little later on and include:
* Belly pain
* Loss of appetite
* Chills
* Fatigue
* Body aches
* Fever
Because of diarrhea and vomiting, you also can become dehydrated. Watch for signs of dehydration, such as dry skin, a dry mouth, feeling lightheaded, and being really thirsty. Call your doctor if you have any of these symptoms.
How long does gastroenteritis last?
It depends on what caused it. But generally, acute gastroenteritis lasts about 14 days. Persistent gastroenteritis lasts between 14 and 30 days, and chronic gastroenteritis lasts over 30 days.
Stomach Flu and Children
Children and infants can get dehydrated quickly. If they do, they need to go to the doctor as soon as possible. Some signs of dehydration in kids include:
* Sunken soft spot on your baby's head
* Sunken eyes
* Dry mouth
* No tears come out when they cry
* Not peeing or peeing very little
* Low alertness and energy (lethargy)
* Irritability
When caused by an infection — most often a virus — gastroenteritis is contagious. Young kids are more likely to have severe symptoms. Keep children with gastroenteritis out of day care or school until all their symptoms are gone.
Two vaccines are available by mouth to help protect children from infection with one of the most common causes of viral gastroenteritis: rotavirus. The two vaccines are called RotaTeq and Rotarix. Kids can get them starting at 2 months of age. Ask your doctor if your child should get a vaccine.
Check with your doctor before giving your child any medicine. Doctors don't usually recommend giving kids younger than 5 years over-the-counter drugs to control vomiting. They also don't recommend giving kids younger than 12 drugs to control diarrhea (some doctors won't recommend them for people under 18).

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2377 2024-12-14 16:14:17
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
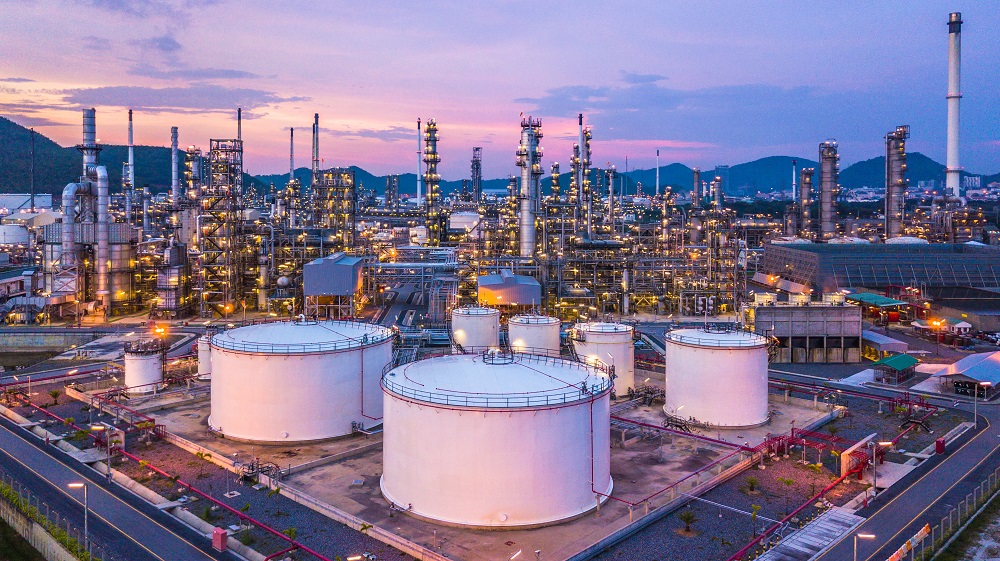
2277) Refinery/Oil Refinery - I
Gist
A refinery is a facility where raw materials are converted into some valuable substance by having impurities removed.
A refinery is a facility where raw materials are converted into some valuable substance by having impurities removed. At an oil refinery, crude oil is treated and made into gasoline and other petroleum products.
Whenever a material needs to have unwanted parts removed in order to be made into a useable product, it must be refined — clarified or processed. This is done at a plant called a refinery. A sugar refinery, for example, converts sugar cane or beets into familiar white, refined crystals of sugar. Refinery comes from refine, which is rooted in the now-obsolete verb fine, "make fine."
Summary
What do refineries do?
Petroleum refineries convert (refine) crude oil into petroleum products for use as fuels for transportation, heating, paving roads, and generating electricity and as feedstocks for making chemicals. Refining breaks crude oil down into its various components, which are then selectively reconfigured into new products.
A refinery is a production facility composed of a group of chemical engineering unit processes and unit operations refining certain materials or converting raw material into products of value.
Types of refineries
Different types of refineries are as follows:
* Petroleum oil refinery, which converts crude oil into high-octane motor spirit (gasoline/petrol), diesel oil, liquefied petroleum gases (LPG), kerosene, heating fuel oils, hexane, lubricating oils, bitumen, and petroleum coke
* Edible oil refinery which converts cooking oil into a product that is uniform in taste, smell and appearance, and stability
* Natural gas processing plant, which purifies and converts raw natural gas into residential, commercial and industrial fuel gas, and also recovers natural gas liquids (NGL) such as ethane, propane, butanes and pentanes
* Sugar refinery, which converts sugar cane and sugar beets into crystallized sugar and sugar syrups
* Salt refinery, which cleans common salt (NaCl), produced by the solar evaporation of sea water, followed by washing and re-crystallization
* Metal refineries refining metals such as alumina, copper, gold, lead, nickel, silver, uranium, zinc, magnesium and cobalt
* Iron refining, a stage of refining pig iron (typically grey cast iron to white cast iron), before fining, which converts pig iron into bar iron or steel.
Details
The refining process begins with crude oil.
Crude oil is unrefined liquid petroleum. Crude oil is composed of thousands of different chemical compounds called hydrocarbons, all with different boiling points. Science — combined with an infrastructure of pipelines, refineries, and transportation systems - enables crude oil to be transformed into useful and affordable products.
Refining turns crude oil into usable products.
Petroleum refining separates crude oil into components used for a variety of purposes. The crude petroleum is heated and the hot gases are passed into the bottom of a distillation column. As the gases move up the height of the column, the gases cool below their boiling point and condense into a liquid. The liquids are then drawn off the distilling column at specific heights to obtain fuels like gasoline, jet fuel and diesel fuel.
The liquids are processed further to make more gasoline or other finished products.
Some of the liquids undergo additional processing after the distillation process to create other products. These processes include: cracking, which is breaking down large molecules of heavy oils; reforming, which is changing molecular structures of low-quality gasoline molecules; and isomerization, which is rearranging the atoms in a molecule so that the product has the same chemical formula but has a different structure. These processes ensure that every drop of crude oil in a barrel is converted into a usable product.
What Is an Oil Refinery?
An oil refinery is an industrial plant that transforms, or refines crude oil into various usable petroleum products such as diesel, gasoline, and heating oils like kerosene. Oil refineries essentially serve as the second stage in the crude oil production process following the actual extraction of crude oil up-stream, and refinery services are considered to be a down-stream segment of the oil and gas industry.
The first step in the refining process is distillation, where crude oil is heated at extreme temperatures to separate the different hydrocarbons.
Key Takeaways
* An oil refinery is a facility that takes crude oil and distills it into various useful petroleum products such as gasoline, kerosene, or jet fuel.
* Refining is classified as a downstream operation of the oil and gas industry, although many integrated oil companies will operate both extraction and refining services.
* Refineries and oil traders look to the crack spread, the relative difference in production cost and market price of various petroleum products in the derivatives market to hedge their exposure to crude oil prices.
Understanding Oil Refineries
Oil refineries serve an important role in the production of transportation and other fuels. The crude oil components, once separated, can be sold to different industries for a broad range of purposes. Lubricants can be sold to industrial plants immediately after distillation, but other products require more refining before reaching the final user. Major refineries have the capacity to process hundreds of thousand barrels of crude oil daily.
In the industry, the refining process is commonly called the "downstream" sector, while raw crude oil production is known as the "upstream" sector. The term downstream is associated with the concept that oil is sent down the product value chain to an oil refinery to be processed into fuel. The downstream stage also includes the actual sale of petroleum products to other businesses, governments, or private individuals.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), U.S. refineries produce—from a 42-gallon barrel of crude oil—19 to 20 gallons of motor gasoline, 11 to 12 gallons of distillate fuel (most of which is sold as diesel), and four gallons of jet fuel.
More than a dozen other petroleum products are also produced in refineries. Petroleum refineries produce liquids the petrochemical industry uses to make a variety of chemicals and plastics.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2378 2024-12-15 16:19:08
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
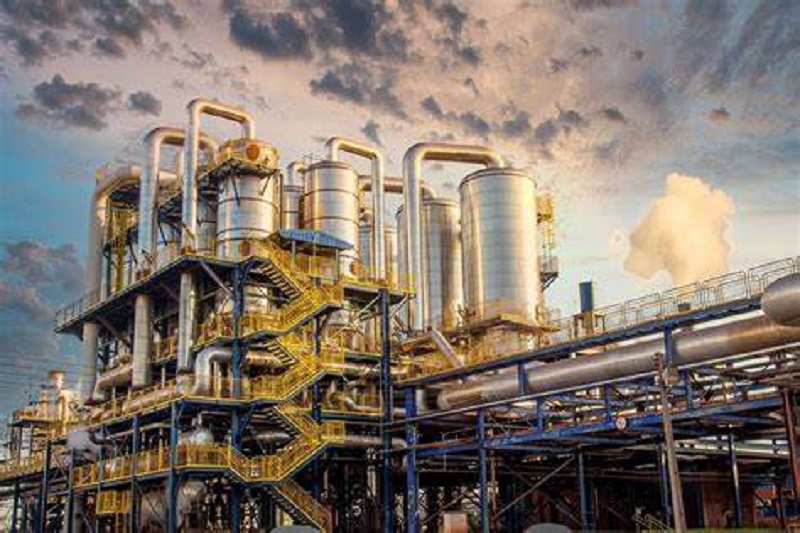
2278) Refinery/Oil Refinery - II
Gist
What is oil refinery?
Petroleum refineries convert (refine) crude oil into petroleum products for use as fuels for transportation, heating, paving roads, and generating electricity and as feedstocks for making chemicals.
Summary
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, liquefied petroleum gas and petroleum naphtha. Petrochemical feedstock like ethylene and propylene can also be produced directly by cracking crude oil without the need of using refined products of crude oil such as naphtha. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products. In 2020, the total capacity of global refineries for crude oil was about 101.2 million barrels per day.
Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units, such as distillation columns. In many ways, oil refineries use many different technologies and can be thought of as types of chemical plants. Since December 2008, the world's largest oil refinery has been the Jamnagar Refinery owned by Reliance Industries, located in Gujarat, India, with a processing capacity of 1.24 million barrels (197,000 m^3) per day.
Oil refineries are an essential part of the petroleum industry's downstream sector.
Details:
"Cracking" Crude Oil
An oil refinery runs 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, and requires a large number of employees. Refineries come offline or stop working for a few weeks each year to undergo seasonal maintenance and other repair work. A refinery can occupy as much land as several hundred football fields. Famous oil refining companies include the Koch Pipeline Company, and many others.
Crack or crack spread is a trading strategy used in energy futures to establish a refining margin. Crack is one primary indicator of oil refining companies' earnings. Crack allows refining companies to hedge against the risks associated with crude oil and those associated with petroleum products. By simultaneously purchasing crude oil futures and selling petroleum product futures, a trader is attempting to establish an artificial position in the refinement of oil created through a spread.
Important : The Nelson Complexity Index (NCI) is a measure of the sophistication of an oil refinery, where more complex refineries are able to produce lighter, more heavily refined and valuable products from a barrel of oil.
The proportions of petroleum products a refinery produces from crude oil can also affect crack spreads. Some of these products include asphalt, aviation fuel, diesel, gasoline, and kerosene. In some cases, the proportion produced varies based on demand from the local market.
The mix of products also depends on the kind of crude oil processed. Heavier crude oils are more difficult to refine into lighter products like gasoline. Refineries that use simpler refining processes may be restricted in their ability to produce products from heavy crude oil.
Refinery Services
Oil refining is a purely downstream function, although many of the companies doing it have midstream and even upstream production. This integrated approach to oil production allows companies like Exxon (XOM), Shell (RDS.A), and Chevron (CVX) to take oil from exploration all the way to sale. The refining side of the business is actually hurt by high prices, because demand for many petroleum products, including gas, is price sensitive. However, when oil prices drop, selling value-added products becomes more profitable. Refining pure plays include Marathon Petroleum Corporation (MPC), CVR Energy Inc. (CVI), and Valero Energy Corp (VLO).
One area service companies and refiners agree on is creating more pipeline capacity and transport. Refiners want more pipeline to keep down the cost of transporting oil by truck or rail. Service companies want more pipeline because they make money in the design and laying stages, and get a steady income from maintenance and testing.
Oil Refinery Safety
Oil refineries can be dangerous places to work at times. For example, in 2005 there was an accident at BP's Texas City oil refinery. According to the U.S. Chemical Safety Board, a series of explosions occurred during the restarting of a hydrocarbon isomerization unit. Fifteen workers were killed and 180 others were injured. The explosions occurred when a distillation tower flooded with hydrocarbons and was over-pressurized, causing a geyser-like release from the vent stack.
How Many Oil Refineries Are There in the United States?
As of Jan. 1, 2021, there were 129 operable petroleum refineries in the United States.
U.S. Energy Information Agency. "When was the last refinery built in the United States?"
The last refinery to enter operation was in 2019 in Texas.
How Much Crude Oil Does It Take to Make a Gallon of Gasoline?
One barrel of oil (42 gallons) produces 19 to 20 gallons of gasoline and 11 to 12 gallons of diesel fuel.
What Is the Crack Spread?
In commodities trading, the "crack spread" is the differences in price between a barrel of unrefined crude oil and the refined products (such as gasoline) that are derived from it. Traders look to changes in the crack spread as a market signal for price movements in oil and refined products.
Trade on the Go. Anywhere, Anytime
One of the world's largest crypto-asset exchanges is ready for you. Enjoy competitive fees and dedicated customer support while trading securely. You'll also have access to Binance tools that make it easier than ever to view your trade history, manage auto-investments, view price charts, and make conversions with zero fees. Make an account for free and join millions of traders and investors on the global crypto market.
Additional Information:
How crude oil is refined into petroleum products
Petroleum refineries convert (refine) crude oil into petroleum products for use as fuels for transportation, heating, paving roads, and generating electricity and as feedstocks for making chemicals.
Refining breaks crude oil down into its various components, which are then selectively reconfigured into new products. Petroleum refineries are complex and expensive industrial facilities. All refineries have three basic steps:
* Separation
* Conversion
* Treatment
Separation
Modern separation involves piping crude oil through hot furnaces. The resulting liquids and vapors are discharged into distillation units. All refineries have atmospheric distillation units, but more complex refineries may have vacuum distillation units.
Inside the distillation units, the liquids and vapors separate into petroleum components, called fractions, according to their boiling points. Heavy fractions are on the bottom and light fractions are on the top.
The lightest fractions, including gasoline and liquefied refinery gases, vaporize and rise to the top of the distillation tower, where they condense back to liquids.
Medium weight liquids, including kerosene and distillates, stay in the middle of the distillation tower.
Heavier liquids, called gas oils, separate lower down in the distillation tower, and the heaviest fractions with the highest boiling points settle at the bottom of the tower.
Conversion
After distillation, heavy, lower-value distillation fractions can be processed further into lighter, higher-value products such as gasoline. At this point in the process, fractions from the distillation units are transformed into streams (intermediate components) that eventually become finished products.
The most widely used conversion method is called cracking because it uses heat, pressure, catalysts, and sometimes hydrogen to crack heavy hydrocarbon molecules into lighter ones. A cracking unit consists of one or more tall, thick-walled, rocket-shaped reactors and a network of furnaces, heat exchangers, and other vessels. Complex refineries may have one or more types of crackers, including fluid catalytic cracking units and hydrocracking/hydrocracker units.
Cracking is not the only form of crude oil conversion. Other refinery processes rearrange molecules rather than splitting molecules to add value.
Alkylation, for example, makes gasoline components by combining some of the gaseous byproducts of cracking. The process, which essentially is cracking in reverse, takes place in a series of large, horizontal vessels and tall, skinny towers.
Reforming uses heat, moderate pressure, and catalysts to turn naphtha, a light, relatively low-value fraction, into high-octane gasoline components.
Treatment
The finishing touches occur during the final treatment. To make gasoline, refinery technicians carefully combine a variety of streams from the processing units. Octane level, vapor pressure ratings, and other special considerations determine the gasoline blend.
Storage
Both incoming crude oil and the outgoing final products are stored temporarily in large tanks on a tank farm near the refinery. Pipelines, trains, and trucks carry the final products from the storage tanks to locations across the country.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2379 2024-12-16 16:30:38
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2279) Training
Gist
Training is the process of learning the skills you need to do a particular job or activity.
Summary
Training is the action of informing or instructing your employees on a certain task in order to help them improve their performance or knowledge. If people are to perform their job to the highest possible standard, they must be effectively and efficiently trained.
Effective training will mean the activities have achieved the specific outcomes required. In addition, your workers need to gain or maintain the skills and knowledge they need to perform their work, direct others to perform work and to supervise work. Lack of training can be attributed to one of the reasons of real quality problems.
Effective training should be cost efficient, while also ensuring that time and money is a good investment.
Details
Training is teaching, or developing in oneself or others, any skills and knowledge or fitness that relate to specific useful competencies. Training has specific goals of improving one's capability, capacity, productivity and performance. It forms the core of apprenticeships and provides the backbone of content at institutes of technology (also known as technical colleges or polytechnics). In addition to the basic training required for a trade, occupation or profession, training may continue beyond initial competence to maintain, upgrade and update skills throughout working life. People within some professions and occupations may refer to this sort of training as professional development. Training also refers to the development of physical fitness related to a specific competence, such as sport, martial arts, military applications and some other occupations.
Types:
Physical training
Physical training concentrates on mechanistic goals: training programs in this area develop specific motor skills, agility, strength or physical fitness, often with an intention of peaking at a particular time.
In military use, training means gaining the physical ability to perform and survive in combat, and learn the many skills needed in a time of war. These include how to use a variety of weapons, outdoor survival skills, and how to survive being captured by the enemy, among many others.
For psychological or physiological reasons, people who believe it may be beneficial to them can choose to practice relaxation training, or autogenic training, in an attempt to increase their ability to relax or deal with stress. While some studies have indicated relaxation training is useful for some medical conditions, autogenic training has limited results or has been the result of few studies.
Occupational skills training
Some occupations are inherently hazardous, and require a minimum level of competence before the practitioners can perform the work at an acceptable level of safety to themselves or others in the vicinity. Occupational diving, rescue, firefighting and operation of certain types of machinery and vehicles may require assessment and certification of a minimum acceptable competence before the person is allowed to practice as a licensed instructor.
On-job training
Some commentators use a similar term for workplace learning to improve performance: "training and development". There are also additional services available online for those who wish to receive training above and beyond what is offered by their employers. Some examples of these services include career counseling, skill assessment, and supportive services. One can generally categorize such training as on-the-job or off-the-job.
The on-the-job training method takes place in a normal working situation, using the actual tools, equipment, documents or materials that trainees will use when fully trained. On-the-job training has a general reputation as most effective for vocational work. It involves employees training at the place of work while they are doing the actual job. Usually, a professional trainer (or sometimes an experienced and skilled employee) serves as the instructor using hands-on practical experience which may be supported by formal classroom presentations. Sometimes training can occur by using web-based technology or video conferencing tools. On-the-job training is applicable on all departments within an organization.
Simulation based training is another method which uses technology to assist in trainee development. This is particularly common in the training of skills requiring a very high degree of practice, and in those which include a significant responsibility for life and property. An advantage is that simulation training allows the trainer to find, study, and remedy skill deficiencies in their trainees in a controlled, virtual environment. This also allows the trainees an opportunity to experience and study events that would otherwise be rare on the job, e.g., in-flight emergencies, system failure, etc., wherein the trainer can run 'scenarios' and study how the trainee reacts, thus assisting in improving his/her skills if the event was to occur in the real world. Examples of skills that commonly include simulator training during stages of development include piloting aircraft, spacecraft, locomotives, and ships, operating air traffic control airspace/sectors, power plant operations training, advanced military/defense system training, and advanced emergency response training like fire training or first-aid training.
Off-the-job training method takes place away from normal work situations — implying that the employee does not count as a directly productive worker while such training takes place. Off-the-job training method also involves employee training at a site away from the actual work environment. It often utilizes lectures, seminars, case studies, role playing, and simulation, having the advantage of allowing people to get away from work and concentrate more thoroughly on the training itself. This type of training has proven more effective in inculcating concepts and ideas. Many personnel selection companies offer a service which would help to improve employee competencies and change the attitude towards the job. The internal personnel training topics can vary from effective problem-solving skills to leadership training.
A more recent development in job training is the On-the-Job Training Plan or OJT Plan. According to the United States Department of the Interior, a proper OJT plan should include: An overview of the subjects to be covered, the number of hours the training is expected to take, an estimated completion date, and a method by which the training will be evaluated.
Religion and spirituality
In religious and spiritual use, the word "training" may refer to the purification of the mind, heart, understanding and actions to obtain a variety of spiritual goals such as (for example) closeness to God or freedom from suffering. Note for example the institutionalised spiritual training of Threefold Training in Buddhism, meditation in Hinduism or discipleship in Christianity. These aspects of training can be short-term or can last a lifetime, depending on the context of the training and which religious group it is a part of.
Artificial-intelligence feedback
Learning processes developed for artificial intelligence are typically also known as training. Evolutionary algorithms, including genetic programming and other methods of machine learning, use a system of feedback based on "fitness functions" to allow computer programs to determine how well an entity performs a task. The methods construct a series of programs, known as a “population” of programs, and then automatically test them for "fitness", observing how well they perform the intended task. The system automatically generates new programs based on members of the population that perform the best. These new members replace programs that perform the worst. The procedure repeats until the achievement of optimum performance. In robotics, such a system can continue to run in real-time after initial training, allowing robots to adapt to new situations and to changes in themselves, for example, due to wear or damage. Researchers have also developed robots that can appear to mimic simple human behavior as a starting point for training.
Additional Information
Employee training and development includes any activity that helps employees acquire new, or improve existing, knowledge or skills. Training is a formal process by which talent development professionals help individuals improve performance at work. Development is the acquisition of knowledge, skill, or attitude that prepares people for new directions or responsibilities. Training is one specific and common form of employee development; other forms include coaching, mentoring, informal learning, self-directed learning, or experiential learning.
What Are the Benefits of Employee Training and Development?
Employee training and development can help employees become better at their jobs and overcome performance gaps that are based on lack of knowledge or skills. This can help organizations and teams be more productive and obtain improved business outcomes, leading to a competitive advantage over other companies.
Training can help organizations be more innovative and agile in responding to change and can help with necessary upskilling and reskilling to help organizations ensure that their labor force meets their current needs. Employee training and development also can help with succession planning by helping to identify high-performing employees and then assisting those employees with the development of the knowledge and skills they need to advance into more senior roles. Employee training and development can be an effective tool for recruiting and retention, since many employees cite a lack of development opportunities at their current job as a primary reason for leaving. Employees who have access to training and development opportunities are more likely to stay at their organizations for a longer period of time and be more engaged while there; in fact, LinkedIn’s 2018 Workplace Learning Report found that 93 percent of employees would stay at a company longer if it invested in their careers. Their 2021 Workplace Leaning Report additionally found that companies with high internal mobility retain employees for twice as long. Finally, some forms of employee training, such as compliance training or safety training, can help organizations avoid lawsuits, workplace injuries, or other adverse outcomes.
What Types of Employee Training and Development Exist?
There are many types of employee training and development. In high performing organizations, training and development initiatives are based on organizational needs, the target audience for the initiative, and the type of knowledge or skill that learners are expected to obtain. Some of the most common types of employee training and development include:
* Technical training is training based on a technical product or task. Technical training if often specifically tailored to a particular job task at a single organization. Skills training is training to help employees develop or practice skills that are necessary for their jobs.
* Soft skills training is a subset of skills training that focuses specifically on soft skills, as opposed to technical or “hard” skills. Soft skills include emotional intelligence, adaptability, creativity, influence, communication, and teamwork. Some trainers refer to soft skills as “power skills” or “professional life skills” to emphasize their importance.
* Compliance training is training on actions that are mandated by a law, agency, or policy outside the organization’s purview. Compliance training is often industry-specific but may include topics such as cybersecurity and sexual harassment.
* Safety training is training that focuses on improving organizational health and safety and reducing workplace injury. It can encompass employee safety, workplace safety, customer safety, and digital and information safety. Safety training can include both training that is required by law and training that organizations offer without legally being required to do so.
* Management development focuses on providing managers with the knowledge and skills that they need to be effective managers and developers of talent. Topics may include accountability, collaboration, communication, engagement, and listening and assessing.
* Leadership development is any activity that increases an individual’s leadership ability or an organization’s leadership capability, including activities such as learning events, mentoring, coaching, self-study, job rotation, and special assignments to develop the knowledge and skills required to lead.
* Executive development provides senior leaders and executives with the knowledge and skills that they need to improve in their roles. In contrast to leadership development, which focuses on helping non-executive employees develop the skills they need to obtain a leadership position, executive development is targeted at people already at a leadership level within their organization.
* Customer service training focuses on providing employees with the knowledge and skills to provide exceptional customer service. Customer service training should include content on essential employee behaviors, service strategies, and service systems.
* Customer education training is when employees—often at technology or SaaS companies—teach customers how to use a company’s products and services. Customer education training differs from traditional employee learning and development because the intended audience is customers, not employees.
* Workforce training focuses on upskilling workers to help them obtain career success. Workforce training programs are often offered by federal, state, or local governments, or by nonprofit organizations. Workforce training may include job-specific content but also may include content on organizational culture, leadership skills, and professionalism. Workforce training is often accessed by people who are new to the workforce or who are trying to enter a new job type or industry.
* Corporate training focuses on helping workers already employed by an organization obtain new knowledge and skills. That company or organization offers training to their internal employees to help them become better at their current jobs, advance in their careers, or close organizational skill gaps.
* Onboarding sometimes known as new employee orientation, is the process through which organizations equip new employees with the knowledge and skills they need to succeed at their jobs.
* Sales enablement is the strategic and cross functional effort to increase the productivity of market-facing teams by providing ongoing and relevant resources throughout the buyer journey to drive business impact. It encompasses sales training, coaching, content creation, process improvement, talent development, and compensation, among other areas.
What Are Examples of Effective Employee Training Methods?
There are many types of employee training and development methods, including:
* Instructor-led training, which can be either in-person or virtual.
* In-person training refers to training in which the instructor is physically in the same room as the learners. This also may be referred to as face-to-face training or classroom training.
* Virtual Instructor-Led Training (VILT) refers to instructor-led training that occurs virtually when the instructor and learners are physically dispersed. VILT takes place through a virtual platform such as Zoom or Webex. VILT also may be referred to as synchronous e-learning, live-online training, synchronous online training, or virtual classroom training
* E-learning is a structured course or learning experience delivered electronically. E-learning can be either asynchronous or synchronous. Asynchronous e-learning is self-paced and may include pre-recorded lecture content and video, visuals and/or text, knowledge quizzes, simulations, games, and other interactive elements.
* Microlearning enhances learning and performance through short pieces of content. Microlearning assets can usually be accessed on-demand when the learner needs them. Common forms of microlearning include how-to videos, self-paced e-learning, games, blogs, job aids, podcasts, infographics, and other visuals.
* Simulation is a broad genre of experiences, including games for entertainment and immersive learning simulations for formal learning programs. Simulations use simulation elements to model and present situations; portraying actions and demonstrating how the actions affect relevant systems, and how those systems produce feedback and results.
* On-the-job training is a delivery system that dispenses training to employees as they need it. As opposed to sending an employee away from work to a training session, on-the-job training allows employees to learn while in the flow of work.
* Coaching is a discipline that helps to enhance individual, team, and organizational performance. Coaching is an interactive process that involves listening, asking powerful questions, strengthening conversations, and creating action plans, with the goal of helping individuals develop towards their preferred future state.
* Mentoring is a reciprocal and collaborative at-will relationship that most often occurs between a senior and junior employee for the purpose of the mentee’s growth, learning, and career development. Mentors often act as role models for their mentee and provide guidance to help them reach their goals.
* Blended learning refers to a training program that includes more than one of the training types referenced above. Traditionally blended learning most often includes a mix of in-person training and e-learning. However, it can refer to any combination of formal and informal learning events, such as classroom instruction, online resources, and on-the-job coaching.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2380 2024-12-17 16:23:44
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2280) Waterbed
Gist
Waterbeds reduce back problems, help asthma sufferers and have many benefits that are good for your health. Many conditions - including that of perfect health - will derive benefit from a waterbed, as members of the medical profession have long acknowledged.
Summary
This is an unique mattress that is specifically meant to prevent bed-ridden patients from developing bed sores. The water bed also dons an elegant look and ensures maximum comfort. Water beds are proven to help you sleep better, reduce back problems effectively, help asthma sufferers, and have many other benefits that are good for your health. The principles of flotation have been documented to be especially helpful with the following conditions: premature infants and newborns, orthopedic problems, paralysis, severe burns, trauma, auto accidents, plastic surgery, general surgery, cardiac rehabilitation, cystic fibrosis, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, and wheelchair patients. Water beds have become an essential therapeutic fixture in benefiting many patients with different medical problems.
Waterbed can bring relief from pain and provide a cool and soothing sensation. Product features Medical Water Bed (Water mattress). This bed is used by the patients who are to lie on the bed for a long time. The patient with broken legs, waist, coma, cerebral attack, heart patient, arthritis patient who cannot move etc. use. As constantly lying in the same position results in pressure and abrasion in particular places of the body for a long time gives rise to the possibilities of developing sores in those parts of the body. By using this bed the possibility of developing bed sores is eliminated. Waterbed can bring relief from pain and provide a cool and soothing sensation. It is a single textured rubberized fabric having 3 compartments. It is completely leak proof, comfortable, hygienic and durable.
Details
A waterbed, water mattress, or flotation mattress is a bed or mattress filled with water. Waterbeds intended for medical therapies appear in various reports through the 19th century. The modern version, invented in San Francisco and patented in 1971, became a popular consumer item in the United States through the 1980s with up to 20% of the market in 1986 and 22% in 1987. By 2013, they accounted for less than 5% of new bed sales.
Construction
Waterbeds primarily consist of two types, hard-sided beds and soft-sided beds.
A hard-sided waterbed consists of a water-containing mattress inside a rectangular frame of wood resting on a plywood deck that sits on a platform.
A soft-sided waterbed consists of a water-containing mattress inside of a rectangular frame of sturdy foam, zippered inside a fabric casing, which sits on a platform. It looks like a conventional bed and is designed to fit existing bedroom furniture. The platform usually looks like a conventional foundation or box spring, and sits atop a reinforced metal frame.
Early waterbed mattresses, and many inexpensive modern mattresses, have a single water chamber. When the water mass in these "free flow" mattresses is disturbed, significant wave motion can be felt, and they need time to stabilize after a disturbance. Later models employed wave-reducing methods, including fiber batting. Some models only partially reduce wave motion, while more expensive models almost eliminate wave motion.
Water beds are normally heated. If no heater is used, the water will equalize with the room air temperature (around 70 °F). In models with no heater, there are at least several inches of insulation above the water chamber. This partially eliminates the body-contouring benefit of a waterbed, and the ability to control the bed temperature. For these reasons, most waterbeds have temperature control systems. Temperature is controlled via a thermostat and set to personal preference, most commonly around average skin temperature, 30 °C (86 °F). A typical heating pad consumes 150–400 watts of power. Depending on insulation, bedding, temperature, use, and other factors, electricity usage may vary significantly.
Waterbeds are usually constructed from soft polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or similar material. They can be repaired with practically any vinyl repair kit.
Types of waterbed mattresses
* Free flow mattress: Also known as a full wave mattress. It contains only water but no baffles or inserts.
* Semi-waveless mattress: Contains a few fiber inserts and/or baffles to control the water motion and increase support.
* Waveless mattress: Contains many layers of fiber inserts and/or baffles to control the water motion and increase support. Frequently, the better mattresses contain additional layers in the center third of the mattress called special lumbar support.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2381 2024-12-18 16:16:09
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
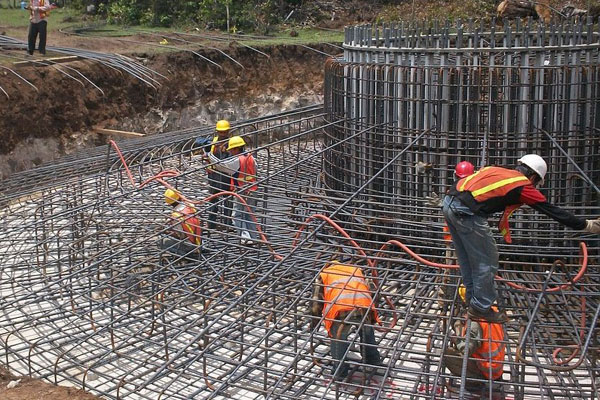
2281) Foundation (Engineering)
Gist
The base on which something stands. The act of founding or establishing or the state of being founded or established. An endowment or legacy for the perpetual support of an institution such as a school or hospital. Entitled to benefit from the funds of a foundation.
Summary
Foundation is a Part of a structural system that supports and anchors the superstructure of a building and transmits its loads directly to the earth. To prevent damage from repeated freeze-thaw cycles, the bottom of the foundation must be below the frost line. The foundations of low-rise residential buildings are nearly all supported on spread footings, wide bases (usually of concrete) that support walls or piers and distribute the load over a greater area. A concrete grade beam supported by isolated footings, piers, or piles may be placed at ground level, especially in a building without a basement, to support the exterior wall. Spread footings are also used—in greatly enlarged form—for high-rise buildings. Other systems for supporting heavy loads include piles, concrete caisson columns, and building directly on exposed rock. In yielding soil, a floating foundation—consisting of rigid, boxlike structures set at such a depth that the weight of the soil removed to place it equals the weight of the construction supported—may be used.
Details
In engineering, a foundation is the element of a structure which connects it to the ground or more rarely, water (as with floating structures), transferring loads from the structure to the ground. Foundations are generally considered either shallow or deep. Foundation engineering is the application of soil mechanics and rock mechanics (geotechnical engineering) in the design of foundation elements of structures.
Purpose
Foundations provide the structure's stability from the ground:
* To distribute the weight of the structure over a large area in order to avoid overloading the underlying soil (possibly causing unequal settlement).
* To anchor the structure against natural forces including earthquakes, floods, droughts, frost heaves, tornadoes and wind.
* To provide a level surface for construction.
* To anchor the structure deeply into the ground, increasing its stability and preventing overloading.
* To prevent lateral movements of the supported structure (in some cases).
Requirements of a good foundation
The design and the construction of a well-performing foundation must possess some basic requirements:
* The design and the construction of the foundation is done such that it can sustain as well as transmit the dead and the imposed loads to the soil. This transfer has to be carried out without resulting in any form of settlement that can cause stability issues for the structure.
* Differential settlements can be avoided by having a rigid base for the foundation. These issues are more pronounced in areas where the superimposed loads are not uniform in nature.
* Based on the soil and area it is recommended to have a deeper foundation so that it can guard any form of damage or distress. These are mainly caused due to the problem of shrinkage and swelling because of temperature changes.
* The location of the foundation chosen must be an area that is not affected or influenced by future works or factors.
Historic types:
Earthfast or post in ground construction
Buildings and structures have a long history of being built with wood in contact with the ground. Post in ground construction may technically have no foundation. Timber pilings were used on soft or wet ground even below stone or masonry walls. In marine construction and bridge building a crisscross of timbers or steel beams in concrete is called grillage.
Padstones
Perhaps the simplest foundation is the padstone, a single stone which both spreads the weight on the ground and raises the timber off the ground. Staddle stones are a specific type of padstone.
Stone foundations
Dry stone and stones laid in mortar to build foundations are common in many parts of the world. Dry laid stone foundations may have been painted with mortar after construction. Sometimes the top, visible course of stone is hewn, quarried stones. Besides using mortar, stones can also be put in a gabion. One disadvantage is that if using regular steel rebars, the gabion would last much less long than when using mortar (due to rusting). Using weathering steel rebars could reduce this disadvantage somewhat.
Rubble-trench foundations
Rubble trench foundations are a shallow trench filled with rubble or stones. These foundations extend below the frost line and may have a drain pipe which helps groundwater drain away. They are suitable for soils with a capacity of more than 10 tonnes/m^2 (2,000 pounds per square foot).
Modern types:
Shallow foundations
Often called footings, are usually embedded about a meter or so into soil. One common type is the spread footing which consists of strips or pads of concrete (or other materials) which extend below the frost line and transfer the weight from walls and columns to the soil or bedrock.
Another common type of shallow foundation is the slab-on-grade foundation where the weight of the structure is transferred to the soil through a concrete slab placed at the surface. Slab-on-grade foundations can be reinforced mat slabs, which range from 25 cm to several meters thick, depending on the size of the building, or post-tensioned slabs, which are typically at least 20 cm for houses, and thicker for heavier structures.
Another way to install ready-to-build foundations that is more environmentally friendly is to use screw piles. Screw pile installations have also extended to residential applications, with many homeowners choosing a screw pile foundation over other options. Some common applications for helical pile foundations include wooden decks, fences, garden houses, pergolas, and carports.
Deep foundations
Used to transfer the load of a structure down through the upper weak layer of topsoil to the stronger layer of subsoil below. There are different types of deep footings including impact driven piles, drilled shafts, caissons, screw piles, geo-piers and earth-stabilized columns. The naming conventions for different types of footings vary between different engineers. Historically, piles were wood, later steel, reinforced concrete, and pre-tensioned concrete.
Monopile foundation
A type of deep foundation which uses a single, generally large-diameter, structural element embedded into the earth to support all the loads (weight, wind, etc.) of a large above-surface structure.
Many monopile foundations have been used in recent years for economically constructing fixed-bottom offshore wind farms in shallow-water subsea locations. For example, a single wind farm off the coast of England went online in 2008 with over 100 turbines, each mounted on a 4.74-meter-diameter monopile footing in ocean depths up to 16 meters of water.
Floating\barge
A floating foundation is one that sits on a body of water, rather than dry land. This type of foundation is used for some bridges and floating buildings.
Design:
Foundations are designed to have an adequate load capacity depending on the type of subsoil/rock supporting the foundation by a geotechnical engineer, and the footing itself may be designed structurally by a structural engineer. The primary design concerns are settlement and bearing capacity. When considering settlement, total settlement and differential settlement is normally considered. Differential settlement is when one part of a foundation settles more than another part. This can cause problems to the structure which the foundation is supporting. Expansive clay soils can also cause problems.
Additional Information
In engineering, a foundation is the element of a structure which connects it to the ground, and transfers loads from the structure to the ground. Foundations are generally considered either shallow or deep. Foundation engineering is the application of soil mechanics and rock mechanics in the design of foundation elements of structures.
Requirements of a good foundation
The design and the construction of a well-performing foundation must possess some basic requirements that must not be ignored. They are:
* The design and the construction of the foundation is done such that it can sustain as well as transmit the dead and the imposed loads to the soil.
* This transfer has to be carried out without resulting in any form of settlement that can result in any form of stability issues for the structure.
* Differential settlements can be avoided by having a rigid base for the foundation. These issues are more pronounced in areas where the superimposed loads are not uniform in nature.
* Based on the soil and area it is recommended to have a deeper foundation so that it can guard any form of damage or distress. These are mainly caused due to the problem of shrinkage and swelling because of temperature changes.
* The location of the foundation chosen must be an area that is not affected or influenced by future works or factors.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2382 2024-12-19 17:08:55
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2282) Sweetness
Gist
Sweetness is the quality of being sweet.
Summary
Sweetness is an important and easily identifiable characteristic of glucose- and fructose-containing sweeteners. The sensation of sweetness has been extensively studied. Shallenberger defines sweetness as a primary taste. He furthermore asserts that no two substances can have the same taste. Thus, when compared to sucrose, no other sweetener will have the unique properties of sweetness onset, duration and intensity of sucrose. It is possible to compare the relative sweetness values of various sweeteners, but it must be kept in mind that these are relative values. There will be variations in onset, which is a function of the chirality of the sweetener, variations in duration, which is a function of the molecular weight profile and is impacted by the viscosity, and changes in intensity, which is affected by the solids level and the particular isomers present. Such variables are demonstrated by the performance of fructose in solution. The fructose molecule may exist in any of several forms. The exact concentration of any of these isomers depends on the temperature of the solution. At cold temperatures the sweetest form, β-D-fructopyranose, predominates, but at hot temperatures, fructofuranose forms predominate and the perceived sweetness lessens.
Details
Sweetness is a basic taste most commonly perceived when eating foods rich in sugars. Sweet tastes are generally regarded as pleasurable. In addition to sugars like sucrose, many other chemical compounds are sweet, including aldehydes, ketones, and sugar alcohols. Some are sweet at very low concentrations, allowing their use as non-caloric sugar substitutes. Such non-sugar sweeteners include saccharin, aspartame, sucralose and stevia. Other compounds, such as miraculin, may alter perception of sweetness itself.
The perceived intensity of sugars and high-potency sweeteners, such as aspartame and neohesperidin dihydrochalcone, are heritable, with gene effect accounting for approximately 30% of the variation.
The chemosensory basis for detecting sweetness, which varies between both individuals and species, has only begun to be understood since the late 20th century. One theoretical model of sweetness is the multipoint attachment theory, which involves multiple binding sites between a sweetness receptor and a sweet substance.
Studies indicate that responsiveness to sugars and sweetness has very ancient evolutionary beginnings, being manifest as chemotaxis even in motile bacteria such as E. coli. Newborn human infants also demonstrate preferences for high sugar concentrations and prefer solutions that are sweeter than lactose, the sugar found in breast milk. Sweetness appears to have the highest taste recognition threshold, being detectable at around 1 part in 200 of sucrose in solution. By comparison, bitterness appears to have the lowest detection threshold, at about 1 part in 2 million for quinine in solution. In the natural settings that human primate ancestors evolved in, sweetness intensity should indicate energy density, while bitterness tends to indicate toxicity. The high sweetness detection threshold and low bitterness detection threshold would have predisposed our primate ancestors to seek out sweet-tasting (and energy-dense) foods and avoid bitter-tasting foods. Even amongst leaf-eating primates, there is a tendency to prefer immature leaves, which tend to be higher in protein and lower in fibre and poisons than mature leaves. The "sweet tooth" thus has an ancient heritage, and while food processing has changed consumption patterns, human physiology remains largely unchanged. Biologically, a variant in fibroblast growth factor 21 increases craving for sweet foods.
Examples of sweet substances
A great diversity of chemical compounds, such as aldehydes and ketones, are sweet. Among common biological substances, all of the simple carbohydrates are sweet to at least some degree. Sucrose (table sugar) is the prototypical example of a sweet substance. Sucrose in solution has a sweetness perception rating of 1, and other substances are rated relative to this. For example, another sugar, fructose, is somewhat sweeter, being rated at 1.7 times the sweetness of sucrose. Some of the amino acids are mildly sweet: alanine, glycine, and serine are the sweetest. Some other amino acids are perceived as both sweet and bitter.
The sweetness of 5% solution of glycine in water compares to a solution of 5.6% glucose or 2.6% fructose.
A number of plant species produce glycosides that are sweet at concentrations much lower than common sugars. The most well-known example is glycyrrhizin, the sweet component of licorice root, which is about 30 times sweeter than sucrose. Another commercially important example is stevioside, from the South American shrub Stevia rebaudiana. It is roughly 250 times sweeter than sucrose. Another class of potent natural sweeteners are the sweet proteins such as thaumatin, found in the West African katemfe fruit. Hen egg lysozyme, an antibiotic protein found in chicken eggs, is also sweet.
Some variation in values is not uncommon between various studies. Such variations may arise from a range of methodological variables, from sampling to analysis and interpretation. Indeed, the taste index of 1, assigned to reference substances such as sucrose (for sweetness), hydrochloric acid (for sourness), quinine (for bitterness), and sodium chloride (for saltiness), is itself arbitrary for practical purposes. Some values, such as those for maltose and glucose, vary little. Others, such as aspartame and sodium saccharin, have much larger variation.
Even some inorganic compounds are sweet, including beryllium chloride and lead(II) acetate. The latter may have contributed to lead poisoning among the ancient Roman aristocracy: the Roman delicacy sapa was prepared by boiling soured wine (containing acetic acid) in lead pots.
Hundreds of synthetic organic compounds are known to be sweet, but only a few of these are legally permitted as food additives. For example, chloroform, nitrobenzene, and ethylene glycol are sweet, but also toxic. Saccharin, cyclamate, aspartame, acesulfame potassium, sucralose, alitame, and neotame are commonly used.
Sweetness modifiers
A few substances alter the way sweet taste is perceived. One class of these inhibits the perception of sweet tastes, whether from sugars or from highly potent sweeteners. Commercially, the most important of these is lactisole, a compound produced by Domino Sugar. It is used in some jellies and other fruit preserves to bring out their fruit flavors by suppressing their otherwise strong sweetness.
Two natural products have been documented to have similar sweetness-inhibiting properties: gymnemic acid, extracted from the leaves of the Indian vine Gymnema sylvestre and ziziphin, from the leaves of the Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujuba). Gymnemic acid has been widely promoted within herbal medicine as a treatment for sugar cravings and diabetes.
On the other hand, two plant proteins, miraculin and curculin, cause sour foods to taste sweet. Once the tongue has been exposed to either of these proteins, sourness is perceived as sweetness for up to an hour afterwards. While curculin has some innate sweet taste of its own, miraculin is by itself quite tasteless.
The sweetness receptor
Despite the wide variety of chemical substances known to be sweet, and knowledge that the ability to perceive sweet taste must reside in taste buds on the tongue, the biomolecular mechanism of sweet taste was sufficiently elusive that as recently as the 1990s, there was some doubt whether any single "sweetness receptor" actually exists.
The breakthrough for the present understanding of sweetness occurred in 2001, when experiments with laboratory mice showed that mice possessing different versions of the gene T1R3 prefer sweet foods to different extents. Subsequent research has shown that the T1R3 protein forms a complex with a related protein, called T1R2, to form a G-protein coupled receptor that is the sweetness receptor in mammals.
Human studies have shown that sweet taste receptors are not only found in the tongue, but also in the lining of the gastrointestinal tract as well as the nasal epithelium, pancreatic islet cells, sperm and testes. It is proposed that the presence of sweet taste receptors in the GI tract controls the feeling of hunger and satiety.
Another research has shown that the threshold of sweet taste perception is in direct correlation with the time of day. This is believed to be the consequence of oscillating leptin levels in blood that may impact the overall sweetness of food. Scientists hypothesize that this is an evolutionary relict of diurnal animals like humans.
Sweetness perception may differ between species significantly. For example, even amongst the primates sweetness is quite variable. New World monkeys do not find aspartame sweet, while Old World monkeys and apes (including most humans) all do. Felids like domestic cats cannot perceive sweetness at all. The ability to taste sweetness often atrophies genetically in species of carnivores who do not eat sweet foods like fruits, including bottlenose dolphins, sea lions, spotted hyenas and fossas.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2383 2024-12-20 00:10:43
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2283) Iron ore
Gist
Mining iron ore is a high-volume, low-margin business, as the value of iron is significantly lower than base metals. It is highly capital intensive, and requires significant investment in infrastructure such as rail in order to transport the ore from the mine to a freight ship.
Summary
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the form of magnetite (Fe3O4, 72.4% Fe), hematite (Fe2O3, 69.9% Fe), goethite (FeO(OH), 62.9% Fe), limonite (FeO(OH)·n(H2O), 55% Fe), or siderite (FeCO3, 48.2% Fe).
Ores containing very high quantities of hematite or magnetite, typically greater than about 60% iron, are known as natural ore or direct shipping ore, and can be fed directly into iron-making blast furnaces. Iron ore is the raw material used to make pig iron, which is one of the main raw materials to make steel—98% of the mined iron ore is used to make steel. In 2011 the Financial Times quoted Christopher LaFemina, mining analyst at Barclays Capital, saying that iron ore is "more integral to the global economy than any other commodity, except perhaps oil".
Metallic iron is virtually unknown on the Earth's surface except as iron-nickel alloys from meteorites and very rare forms of deep mantle xenoliths. Although iron is the fourth-most abundant element in the Earth's crust, composing about 5%, the vast majority is bound in silicate or, more rarely, carbonate minerals, and smelting pure iron from these minerals would require a prohibitive amount of energy. Therefore, all sources of iron used by human industry exploit comparatively rarer iron oxide minerals, primarily hematite.
Prehistoric societies used laterite as a source of iron ore. Prior to the industrial revolution, most iron was obtained from widely-available goethite or bog ore, for example, during the American Revolution and the Napoleonic Wars. Historically, much of the iron ore utilized by industrialized societies has been mined from predominantly hematite deposits with grades of around 70% Fe. These deposits are commonly referred to as "direct shipping ores" or "natural ores". Increasing iron ore demand, coupled with the depletion of high-grade hematite ores in the United States, led after World War II to the development of lower-grade iron ore sources, principally the use of magnetite and taconite.
Iron ore mining methods vary by the type of ore being mined. There are four main types of iron ore deposits worked currently, depending on the mineralogy and geology of the ore deposits. These are magnetite, titanomagnetite, massive hematite, and pisolitic ironstone deposits.
The origin of iron can be ultimately traced to its formation through nuclear fusion in stars, and most of the iron is thought to have originated in dying stars that are large enough to explode as supernovae. The Earth's core is thought to consist mainly of iron, but this is inaccessible from the surface. Some iron meteorites are thought to have originated from asteroids 1,000 km (620 mi) in diameter or larger.
Details
Iron ores occur in igneous, metamorphic (transformed), or sedimentary rocks in a variety of geologic environments. Most are sedimentary, but many have been changed by weathering, and so their precise origin is difficult to determine. The most widely distributed iron-bearing minerals are oxides, and iron ores consist mainly of hematite (Fe2O3), which is red; magnetite (Fe3O4), which is black; limonite or bog-iron ore (2Fe2O3·3H2O), which is brown; and siderite (FeCO3), which is pale brown. Hematite and magnetite are by far the most common types of ore.
Pure magnetite contains 72.4 percent iron, hematite 69.9 percent, limonite 59.8 percent, and siderite 48.2 percent, but, since these minerals never occur alone, the metal content of real ores is lower. Deposits with less than 30 percent iron are commercially unattractive, and, although some ores contain as much as 66 percent iron, there are many in the 50–60 percent range. An ore’s quality is also influenced by its other constituents, which are collectively known as gangue. Silica (SiO2) and phosphorus-bearing compounds (usually reported as P2O5) are especially important because they affect the composition of the metal and pose extra problems in steelmaking.
China, Brazil, Australia, Russia, and Ukraine are the five biggest producers of iron ore, but significant amounts are also mined in India, the United States, Canada, and Kazakhstan. Together, these nine countries produce 80 percent of the world’s iron ore. Brazil, Australia, Canada, and India export the most, although Sweden, Liberia, Venezuela, Mauritania, and South Africa also sell large amounts. Japan, the European Union, and the United States are the major importers.
Mining and concentrating
Most iron ores are extracted by surface mining. Some underground mines do exist, but, wherever possible, surface mining is preferred because it is cheaper.
Lumps and fines:
Crushing
As-mined iron ore contains lumps of varying size, the biggest being more than 1 metre (40 inches) across and the smallest about 1 millimetre (0.04 inch). The blast furnace, however, requires lumps between 7 and 25 millimetres, so the ore must be crushed to reduce the maximum particle size. Crushed ore is divided into various fractions by passing it over sieves through which undersized material falls. In this way, lump or rubble ore (7 to 25 millimetres in size) is separated from the fines (less than 7 millimetres). If the lump ore is of the appropriate quality, it can be charged to the blast furnace without any further processing. Fines, however, must first be agglomerated, which means reforming them into lumps of suitable size by a process called sintering.
Sintering
Iron ore sintering consists of heating a layer of fines until partial melting occurs and individual ore particles fuse together. For this purpose, a traveling-grate machine is used, and the burning of fine coke (known as coke breeze) within the ore generates the necessary heat. Before being delivered to the sinter machine, the ore mixture is moistened to cause fine particles to stick to larger ones, and then the appropriate amount of coke is added. Initially, coke on the upper surface of the bed is ignited when the mixture passes under burners in an ignition hood, but thereafter its combustion is maintained by air drawn through the bed of materials by a suction fan, so that by the time the sinter reaches the end of the machine it has completely fused. The grate on which the sinter mix rests consists of a series of cast-iron bars with narrow spaces between them to allow the air through. After cooling, the sinter is broken up and screened to yield blast-furnace feed and an undersize fraction that is recycled. Modern sinter plants are capable of producing up to 25,000 tons per day. Sintering machines are usually measured by hearth area; the biggest machines are 5 metres (16 feet) wide by 120 metres long, and the effective hearth area is 600 square metres (6,500 square feet).
Concentrates:
Upgrading
Crushing and screening are straightforward mechanical operations that do not alter an ore’s composition, but some ores need to be upgraded before smelting. Concentration refers to the methods of producing ore fractions richer in iron and lower in silica than the original material. Most processes rely on density differences to separate light minerals from heavier ones, so the ore is crushed and ground to release the ore minerals from the gangue. Magnetic techniques also are used.
The upgraded ore, or concentrate, is in the form of a very fine powder that is physically unsuitable for blast furnace use. It has a much smaller particle size than ore fines and cannot be agglomerated by sintering. Instead, concentrates must be agglomerated by pelletizing, a process that originated in Sweden and Germany about 1912–13 but was adapted in the 1940s to deal with low-grade taconite ores found in the Mesabi Range of Minnesota, U.S.
Pelletizing
First, moistened concentrates are fed to a rotating drum or an inclined disc, the tumbling action of which produces soft, spherical agglomerates. These “green” balls are then dried and hardened by firing in air to a temperature in the range of 1,250° to 1,340° C (2,300° to 2,440° F). Finally, they are slowly cooled. Finished pellets are round and have diameters of 10 to 15 millimetres, making them almost the ideal shape for the blast furnace.
The earliest kind of firing equipment was the shaft furnace. This was followed by the grate-kiln and the traveling grate, which together account for more than 90 percent of world pellet output. In shaft furnaces the charge moves down by gravity and is heated by a counterflow of hot combustion gases, but the grate-kiln system combines a horizontal traveling grate with a rotating kiln and a cooler so that drying, firing, and cooling are performed separately. In the traveling-grate process, pellets are charged at one end and dried, preheated, fired, and cooled as they are carried through successive sections of the equipment before exiting at the other end. Traveling grates and grate-kilns have similar capacities, and up to five million tons of pellets can be made in one unit annually.
Iron making
The primary objective of iron making is to release iron from chemical combination with oxygen, and, since the blast furnace is much the most efficient process, it receives the most attention here. Alternative methods known as direct reduction are used in over a score of countries, but less than 5 percent of iron is made this way. A third group of iron-making techniques classed as smelting-reduction is still in its infancy.
The blast furnace
Basically, the blast furnace is a countercurrent heat and oxygen exchanger in which rising combustion gas loses most of its heat on the way up, leaving the furnace at a temperature of about 200° C (390° F), while descending iron oxides are wholly converted to metallic iron. Process control and productivity improvements all follow from a consideration of these fundamental features. For example, the most important advance of the 20th century has been a switch from the use of randomly sized ore to evenly sized sinter and pellet charges. The main benefit is that the charge descends regularly, without sticking, because the narrowing of the range of particle sizes makes the gas flow more evenly, enhancing contact with the descending solids. (Even so, it is impossible to eliminate size variations completely; at the very least, some breakdown occurs between the sinter plant or coke ovens and the furnace.)
Structure
The furnace itself is a tall, vertical shaft that consists of a steel shell with a refractory lining of firebrick and graphite. Five sections can be identified. At the bottom is a parallel-sided hearth where liquid metal and slag collect, and this is surmounted by an inverted truncated cone known as the bosh. Air is blown into the furnace through tuyeres, water-cooled nozzles made of copper and mounted at the top of the hearth close to its junction with the bosh. A short vertical section called the bosh parallel, or the barrel, connects the bosh to the truncated upright cone that is the stack. Finally, the fifth and topmost section, through which the charge enters the furnace, is the throat. The lining in the bosh and hearth, where the highest temperatures occur, is usually made of carbon bricks, which are manufactured by pressing and baking a mixture of coke, anthracite, and pitch. Carbon is more resistant to the corrosive action of molten iron and slag than are the aluminosilicate firebricks used for the remainder of the lining. Firebrick quality is measured by the alumina (Al203) content, so that bricks containing 63 percent alumina are used in the bosh parallel, while 45 percent alumina is adequate for the stack.
Until recently, all blast furnaces used the double-bell system to introduce the charge into the stack. This equipment consists of two cones, called bells, each of which can be closed to provide a gas-tight seal. In operation, material is first deposited on the upper, smaller bell, which is then lowered a short distance to allow the charge to fall onto the larger bell. Next, the small bell is closed, and the large bell is lowered to allow the charge to drop into the furnace. In this way, gas is prevented from escaping into the atmosphere. Because it is difficult to distribute the burden evenly over the furnace cross section with this system, and because the abrasive action of the charge causes the bells to wear so that gas leakage eventually occurs, more and more furnaces are equipped with a bell-less top, in which the rate of material flow from each hopper is controlled by an adjustable gate and delivery to the stack is through a rotating chute whose angle of inclination can be altered. This arrangement gives good control of burden distribution, since successive portions of the charge can be placed in the furnace as rings of differing diameter. The charging pattern that gives the best furnace performance can then be found easily.
The general principles upon which blast-furnace design is based are as follows. Cold charge (mainly ore and coke), entering at the top of the stack, increases in temperature as it descends, so that it expands. For this reason the stack diameter must increase to let the charge move down freely, and typically the stack wall is displaced outward at an angle of 6° to 7° to the vertical. Eventually, melting of iron and slag takes place, and the voids between the solids are filled with liquid so that there is an apparent decrease in volume. This requires a smaller diameter, and the bosh wall therefore slopes inward and makes an angle to the vertical in the range of 6° to 9°. Over the years, the internal lines of the furnace that give it its characteristic shape have undergone a series of evolutionary changes, but the major alteration has been an increase in girth so that the ratio of height to bosh parallel has been progressively reduced as furnaces have become bigger.
For many years, the accepted method of building a furnace was to use the steel shell to give the structure rigidity and to support the stack with steel columns at regular intervals around the furnace. With very large furnaces, however, the mass is too great, so that a different construction must be used in which four large columns are joined to a box girder surrounding the furnace at a level near the top of the stack. The steel shell still takes most of the mass of the stack, but the furnace top is supported independently.
Operation
Solid charge is raised to the top of the furnace either in hydraulically operated skips or by the use of conveyor belts. Air blown into the furnace through the tuyeres is preheated to a temperature between 900° and 1,350° C (1,650° and 2,450° F) in hot-blast stoves, and in some cases it is enriched with up to 25 percent oxygen. The main product, molten pig iron (also called hot metal or blast-furnace iron), is tapped from the bottom of the furnace at regular intervals. Productivity is measured by dividing the output by the internal working volume of the furnace; 2 to 2.5 tons per cubic metre (125 to 150 pounds per cubic foot) can be obtained every 24 hours from furnaces with working volumes of 4,000 cubic metres (140,000 cubic feet).
Two by-products, slag and gas, are also formed. Slag leaves the furnace by the same taphole as the iron (upon which it floats), and its composition generally lies in the range of 30–40 percent silica (SiO2), 5–15 percent alumina (Al2O3), 35–45 percent lime (CaO), and 5–15 percent magnesia (MgO). The gas exiting at the top of the furnace is composed mainly of carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogen (N2); a typical composition would be 23 percent CO, 22 percent CO2, 3 percent water, and 49 percent N2. Its net combustion energy is roughly one-tenth that of methane. After the dust has been removed, this gas, together with some coke-oven gas, is burned in hot-blast stoves to heat the air blown in through the tuyeres. Hot-blast stoves are in effect temporary heat-storage devices consisting of a combustion chamber and a checkerwork of firebricks that absorb heat during the combustion period. When the stove is hot enough, combustion is stopped and cold air is blown through in the reverse direction, so that the checkerwork surrenders its heat to the air, which then travels to the furnace and enters via the tuyeres. Each furnace has three or four stoves to ensure a continuous supply of hot blast.
Chemistry
The internal workings of a blast furnace used to be something of a mystery, but iron-making chemistry is now well established. Coke burns in oxygen present in the air blast in a combustion reaction taking place near the bottom of the furnace immediately in front of the tuyeres:
Chemical equation.
The heat generated by the reaction is carried upward by the rising gases and transferred to the descending charge. The CO in the gas then reacts with iron oxide in the stack, producing metallic iron and CO2:
Not all the oxygen originally present in the ore is removed like this; some remaining oxide reacts directly with carbon at the higher temperatures encountered in the bosh:
Chemical equation.
Softening and melting of the ore takes place here, droplets of metal and slag forming and trickling down through a layer of coke to collect on the hearth.
The conditions that cause the chemical reduction of iron oxides to occur also affect other oxides. All the phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) and some of the silica and manganous oxide (MnO) are reduced, while phosphorus, silicon, and manganese all dissolve in the hot metal together with some carbon from the coke.
Direct reduction (DR)
This is any process in which iron is extracted from ore at a temperature below the melting points of the materials involved. Gangue remains in the spongelike product, known as direct-reduced iron, or DRI, and must be removed in a subsequent steelmaking process. Only high-grade ores and pellets made from superconcentrates (66 percent iron) are therefore really suitable for DR iron making.
Direct reduction is used mostly in special circumstances, often linked to cheap supplies of natural gas. Several processes are based on the use of a slightly inclined rotating kiln to which ore, coal, and recycled material are charged at the upper end, with heat supplied by an oil or gas burner. Results are modest, however, compared to gas-based processes, many of which are conducted in shaft furnaces. In the most successful of these, known as the Midrex (after its developer, a division of the Midland-Ross Corporation), a gas reformer converts methane (CH4) to a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen (H2) and feeds these gases to the top half of a small shaft furnace. There descending pellets are chemically reduced at a temperature of 850° C (1,550° F). The metallized charge is cooled in the bottom half of the shaft before being discharged.
Smelting reduction
The scarcity of coking coals for blast-furnace use and the high cost of coke ovens are two reasons for the emergence of this other alternative iron-making process. Smelting reduction employs two units: in the first, iron ore is heated and reduced by gases exiting from the second unit, which is a smelter-gasifier supplied with coal and oxygen. The partially reduced ore is then smelted in the second unit, and liquid iron is produced. Smelting-reduction technology enables a wide range of coals to be used for iron making.
The metal:
Hot metal (blast-furnace iron)
Most blast furnaces are linked to a basic oxygen steel plant, for which the hot metal typically contains 4 to 4.5 percent carbon, 0.6 to 0.8 percent silicon, 0.03 percent sulfur, 0.7 to 0.8 percent manganese, and 0.15 percent phosphorus. Tapping temperatures are in the range 1,400° to 1,500° C (2,550° to 2,700° F); to save energy, the hot metal is transferred directly to the steel plant with a temperature loss of about 100° C (200° F).
The major determinants of the composition of basic iron are the hearth temperature and the choice of iron ores. For instance, carbon content is fixed both by the temperature and by the amounts of other elements present in the iron. Sulfur and silicon are both temperature-dependent and generally vary in opposite directions, a high temperature producing low sulfur and high silicon levels. Furnace size also influences silicon, so that large furnaces yield low-silicon iron. Phosphorus, on the other hand, is determined entirely by the amount present in the original charge. Like silica, manganous oxide is partially reduced by carbon, and its final concentration depends on the hearth temperature and slag composition.
Cast iron
Iron production is relatively unsophisticated. It mostly involves remelting charges consisting of pig iron, steel scrap, foundry scrap, and ferroalloys to give the appropriate composition. The cupola, which resembles a small blast furnace, is the most common melting unit. Cold pig iron and scrap are charged from the top onto a bed of hot coke through which air is blown. Alternatively, a metallic charge is melted in a coreless induction furnace or in a small electric-arc furnace.
There are two basic types of cast iron—namely, white and gray.
White iron
White cast irons are usually made by limiting the silicon content to a maximum of 1.3 percent, so that no graphite is present and all of the carbon exists as cementite (Fe3C). The name white refers to the bright appearance of the fracture surfaces when a piece of the iron is broken in two. White irons are too hard to be machined and must be ground to shape. Brittleness limits their range of applications, but they are sometimes used when wear resistance is required, as in brake linings.
The main use for white irons is as the starting material for malleable cast irons, in which the cementite formed during casting is decomposed by heat treatment. Such irons contain about 0.6 to 1.3 percent silicon, which is enough to promote cementite decomposition during the heat treatment but not enough to produce graphite flakes during casting. Whiteheart malleable iron is made by using an oxidizing atmosphere to remove carbon from the surface of white iron castings heated to a temperature of 900° C (1,650° F). Blackheart malleable iron, on the other hand, is made by annealing white iron in a neutral atmosphere, again at a temperature of 900° C. In this process, cementite is decomposed to form rosette-shaped graphite nodules, which are less embrittling than flakes. Blackheart iron is an important material that is widely used in agricultural and engineering machinery. Even better mechanical properties can be obtained by the addition of small amounts of magnesium or cerium to molten iron, since these elements have the effect of transforming the graphite into spherical nodules. These SG (spheroidal graphite) irons, which are also called ductile irons, are strong and malleable; they are also easy to cast and are sometimes preferred to steel castings and forgings.
Gray iron
Gray cast irons generally contain more than 2 percent silicon, and carbon exists as flakes of graphite embedded in a combination of ferrite and pearlite. The name arises because graphite imparts a dull gray appearance to fracture surfaces. Phosphorus is present in most cast irons, lowering the freezing point and lengthening the solidification period so that gray irons can be cast into intricate shapes. Unfortunately, graphite formation is enhanced by slow solidification, and the crack-inducing effect of graphite flakes reduces the metal’s strength and malleability. Gray cast irons are therefore unsuitable when shock resistance is required, but they are ideal for such purposes as engine cylinder blocks, domestic stoves, and manhole covers. They are easy to machine because the graphite causes the metal to break off in small chips, and they also have a high damping capacity (i.e., they are able to absorb vibration). As a result, gray cast irons are used as frames for rotating machinery such as lathes.
High-alloy iron
The properties of both white and gray cast irons can be enhanced by the inclusion of alloying elements such as nickel (Ni), chromium (Cr), and molybdenum (Mo). For example, Ni-Hard, a white iron containing 4 to 5 percent nickel and up to 1.5 percent chromium, is used to make metalworking rolls. Irons in the Ni-Resist range, which contain 14 to 25 percent nickel, are nonmagnetic and have good heat and corrosion resistance.
Casting methods
Iron castings can be made in many ways, but sand-casting is the most common. First, a pattern of the required shape (slightly enlarged to allow for shrinkage) is made in wood, metal, or plastic. It is then placed in a two-piece molding box and firmly packed in sand that is held together by a bonding agent. After the sand has hardened, the molding box is split open to allow the pattern to be removed and used again, and then the box is reassembled and molten metal poured into the cavity to create the casting.
A greensand casting is made in a sand mold bonded with clay, the name referring not to the colour of the sand but to the fact that the mold is uncured. Dry-sand molds are similar, except that the sand is baked before receiving any metal. Alternatively, hardening can be effected by mixing sodium silicate into the sand to create chemical bonds that make baking unnecessary. For heavy castings, molds made of coarse loam sand backed up with brick and faced with highly refractory material are used.
Sand-casting produces rough surfaces, and a much better finish can be achieved by shell molding. This process involves bringing a mixture of sand and a thermosetting resin into contact with a heated metal pattern to form an envelope or shell of hardened sand. Two half-shells are then assembled to make a mold. Wax patterns also can be used to make one-piece shell molds, the wax being removed by melting before the resin is cured in an oven.
For some high-precision applications, iron is cast into permanent molds made of either cast iron or graphite. It is important, however, to ensure that the molds are warmed before use and that their internal surfaces are given a coating to release the casting after solidification.
Most castings are static in that they rely on gravity to cause the liquid metal to fill the mold. Centrifugal casting, however, uses a rotating mold to produce hollow cylindrical castings, such as cast-iron drainpipes.
Wrought iron
Although it is no longer manufactured, the wrought iron that survives contains less than 0.035 percent carbon. It therefore consists essentially of ferrite, but its strength and malleability are reduced by entrained puddling slag, which is elongated into stringers by rolling. As a result, breaking a bar of wrought iron reveals a fibrous fracture not unlike that of wood. The other elements present are silicon (0.075 to 0.15 percent), sulfur (0.01 to 0.2 percent), phosphorus (0.1 to 0.25 percent), and manganese (0.05 to 0.1 percent). This relative purity is the reason why wrought iron has a reputation for good corrosion resistance.
Iron powder
Iron powders produced by crushing and grinding or by atomizing a stream of molten metal are made into small components by pressing or rolling them into compacts, which are then sintered. The density of the compacts depends on the pressure used, but porous compacts suitable for self-lubricating bearings or filters can be given accurate dimensions by using this technique.
Chemical compounds
Apart from being a source of iron, hematite is used for its reddish colour in cosmetics and as a pigment in paints and roof tiles. Also, when cobalt and nickel oxides are added to hematite, a group of ceramic materials closely related to magnetite, known as ferrites, are formed. These are ferromagnetic (i.e., highly magnetic) and are widely used in computers and in electronic transmission and receiving equipment.
Iron is a constituent of human blood, and various iron compounds have medical uses. Ferric ammonium citrate is an appetite stimulator, and ferrous gluconate, ferrous sulfate, and ferric pyrophosphate are among compounds used to treat anemia. Ferric salts act as coagulants and are applied to wounds to promote healing.
Iron compounds are also widely used in agriculture. For example, ferrous sulfate is applied as a spray to acid-loving plants, and other compounds are used as fungicides.
Additional Information
The iron ore deposits are found in sedimentary rocks. They are formed by the chemical reaction of iron and oxygen mixed in the marine and fresh water. The important iron oxides in these deposits are hematite and magnetite. These are ores from where iron is extracted.
Iron ore formation
The iron ore formation started over 1.8 billion years ago when abundant iron was dissolved in the ocean water which then needed oxygen to make hematite and magnetite. The oxygen was provided when the first organism capable of photosynthesis began releasing oxygen into the waters. This oxygen combined with dissolved iron to form hematite and magnetite. These then deposited on the ocean floor abundantly which are now known as banded iron formation.
Sources of iron ore
Metallic iron is basically obscure on the surface of the Earth aside from as iron-nickel composites from shooting stars and exceptionally uncommon types of profound mantle xenoliths. Albeit iron is the fourth most plentiful component in the Earth's covering, containing around 5%, by far most is bound in silicate or all the more seldom carbonate minerals. The thermodynamic obstructions to isolating unadulterated iron from these minerals are imposing and vitality serious, in this way all wellsprings of iron utilised by human industry misuse relatively rarer iron oxide minerals, fundamentally hematite.
Before the modern upheaval, most iron was acquired from broadly accessible goethite or lowland mineral, for instance amid the American Revolution and the Napoleonic Wars. Ancient social orders utilised laterite as a wellspring of iron mineral. Truly, a great part of the iron mineral used by industrialised social orders has been mined from transcendently hematite stores with grades of around 70% Fe. These stores are usually alluded to as "immediate delivery minerals" or "characteristic metals". Expanding iron metal request, combined with the consumption of high-review hematite minerals in the United States, after World War II prompted to improvement of lower-review press metal sources, basically the usage of magnetite and taconite.
Press metal mining strategies change by the kind of mineral being mined. There are four fundamental sorts of iron-metal stores worked right now, contingent upon the mineralogy and topography of the metal stores. These are magnetite, titanomagnetite, monstrous hematite and pisolitic ironstone stores.
Banded iron formations
Banded iron formations (BIFs) are sedimentary rocks containing over 15% iron made dominatingly out of daintily had relations with iron minerals and silica (as quartz). Banded iron formations happen only in Precambrian shakes, and are regularly feebly to strongly transformed. Banded iron formations may contain press in carbonates (siderite or ankerite) or silicates (minnesotaite, greenalite, or grunerite), however in those mined as iron metals, oxides (magnetite or hematite) are the chief iron mineral. Banded iron formations are known as taconite inside North America.
The mining includes moving enormous measures of metal and waste. The waste comes in two structures, non-metal bedrock in the mine (overburden or inter-burden privately known as mullock), and undesirable minerals which are a characteristic part of the metal shake itself (gangue). The mullock is mined and heaped in waste dumps, and the gangue is isolated amid the beneficiation procedure and is expelled as tailings. Taconite tailings are for the most part the mineral quartz, which is artificially latent. This material is put away in vast, directed water settling lakes.
Magnetite ores
The key monetary parameters for magnetite mineral being financial are the crystallinity of the magnetite, the review of the iron inside the joined iron arrangement have shake, and the contaminant components which exist inside the magnetite think. The size and strip proportion of most magnetite assets is immaterial as a united iron development can be many meters thick, augment several kilometres along strike, and can undoubtedly come to more than three billion or more huge amounts of contained metal.
The normal review of iron at which a magnetite-bearing united iron arrangement gets to be distinctly financial is around 25% iron, which can for the most part yield a 33% to 40% recuperation of magnetite by weight, to create a move evaluating in abundance of 64% iron by weight. The average magnetite press metal focus has under 0.1% phosphorus, 3–7% silica and under 3% aluminium.
Presently magnetite press mineral is mined in Minnesota and Michigan in the U.S., Eastern Canada and Northern Sweden. Magnetite bearing united iron development is presently mined broadly in Brazil, which sends out huge amounts to Asia, and there is an early and huge magnetite press mineral industry in Australia.
Magmatic magnetite ore deposits
Occasionally granite and ultrapotassic igneous rocks segregate magnetite crystals and form masses of magnetite suitable for economic concentration. A few iron ore deposits, notably in Chile, are formed from volcanic flows containing significant accumulations of magnetite phenocrysts. Chilean magnetite iron ore deposits within the Atacama Desert have also formed alluvial accumulations of magnetite in streams leading from these volcanic formations.
Some magnetite skarn and hydrothermal deposits have been worked in the past as high-grade iron ore deposits requiring little beneficiation. There are several granite-associated deposits of this nature in Malaysia and Indonesia.
Other sources of magnetite iron ore include metamorphic accumulations of massive magnetite ore such as at Savage River, Tasmania, formed by shearing of ophiolite ultramafics.
Another, minor, source of iron ores are magmatic accumulations in layered intrusions which contain a typically titanium-bearing magnetite often with vanadium. These ores form a niche market, with specialty smelters used to recover the iron, titanium and vanadium. These ores are beneficiated essentially similar to banded iron formation ores, but usually are more easily upgraded via crushing and screening. The typical titanomagnetite concentrate grades 57% Fe, 12% Ti and 0.5% V2O5.
Beneficiation of iron ore
Lower-grade sources of iron ore generally require beneficiation, using techniques like crushing, milling, gravity or heavy media separation, screening, and silica froth flotation to improve the concentration of the ore and remove impurities. The results, high quality fine ore powders, are known as fines.
Magnetite
Magnetite is attractive, and subsequently effortlessly isolated from the gangue minerals and equipped for creating a high-review think with low levels of polluting influences.
The grain size of the magnetite and its level of mixing together with the silica groundmass decide the pound size to which the stone must be comminuted to empower effective attractive partition to give a high immaculateness magnetite focus. This decides the vitality inputs required to run a processing operation.
Mining of united iron developments includes coarse smashing and screening, trailed by unpleasant pounding and fine granulating to comminute the mineral to the point where the solidified magnetite and quartz are sufficiently fine that the quartz is deserted when the resultant powder is passed under an attractive separator.
By and large most magnetite grouped iron arrangement stores must be ground to in the vicinity of 32 and 45 micrometers keeping in mind the end goal to deliver a low-silica magnetite think. Magnetite focus evaluations are by and large in overabundance of 70% iron by weight and generally are low phosphorus, low aluminum, low titanium and low silica and request a top notch cost.
Hematite
Because of the high thickness of hematite in respect to related silicate gangue, hematite beneficiation as a rule includes a blend of beneficiation strategies.
One strategy depends on passing the finely smashed metal over a slurry containing magnetite or other specialist, for example, ferrosilicon which expands its thickness. At the point when the thickness of the slurry is appropriately adjusted, the hematite will sink and the silicate mineral parts will coast and can be evacuated.
Uses
The primary use of iron ore is in the production of iron. Most of the iron produced is then used to make steel. Steel is used to make automobiles, locomotives, ships, beams used in buildings, furniture, paper clips, tools, reinforcing rods for concrete, bicycles, and thousands of other items. It is the most-used metal by both tonnage and purpose.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2384 2024-12-21 16:37:31
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2284) Darien Gap
Gist
The Darién Gap is a roadless, 60-mile stretch of rainforest straddling the Colombia-Panama border, was named for being the only break in the Pan-American Highway, a 19,000-mile-long network of roads that otherwise runs uninterrupted from Alaska to the southern tip of Argentina.
Summary
Darién Gap, is an approximately 60-mile (100-km) break in the Pan-American Highway, which otherwise runs continuously from Alaska to the southern tip of Argentina. The gap is located in the thickly vegetated marshland and jungle of the Darién region, which spans the easternmost part of Panama and northwestern Colombia. The Darién Gap is infamously difficult to traverse, but, as the only overland route connecting North and South America, it has become a crucial path for migrants traveling northward to the United States and Canada in the 21st century.
History
The region of Darién, situated largely on the isthmus of Panama, lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean and at the crossroads of two continents. This seemingly ideal location drew a number of European settlers during the colonial period. Indeed, one of the first European settlements on the American mainland was the Spanish city of Santa María la Antigua del Darién, founded in 1510 on the western side of the Gulf of Urabá. A few years later some colonists left the Darién settlement to found Panama City; eventually, Santa María was abandoned. Another short-lived attempt at colonization was made in the 17th century, when a Scottish trading company founded a settlement about halfway between Portobelo, Panama, and Cartagena, Colombia. The area’s hot humid weather and geography typified by tropical rainforests, mangrove swamps, and low mountain ranges perhaps hampered other settlements, and in subsequent centuries Darién remained sparsely populated. A few Indigenous peoples, including the Chocó (specifically the Embera and Wounaan, or Waunana) and the Kuna (Cuna), have traditionally lived in villages scattered throughout the forest. Estimates of their combined local populations range widely, from 1,200 to some 25,000.
Gap in the Pan-American Highway
Discussions of constructing a single route to connect North America and South America began in the 1920s, and by 1937, 14 countries, including the United States, had signed the Convention on the Pan-American Highway, whereby they agreed to achieve speedy construction of their respective sections of the highway. By the 1970s most of the highway had been constructed except for the crucial region of Darién. By this time environmentalists and Indigenous peoples had raised concerns about the destruction the highway would cause to the area’s sensitive rainforests and marshlands as well as to the Indigenous peoples’ ways of living. The last of the highway project was ultimately suspended for a number of reasons, including the prevention of the spread of foot-and-mouth disease. The highly contagious viral disease that affects most cloven-footed domesticated mammals, including cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs, was then infecting large numbers of livestock in South America. The suspension was lifted in 1992, but opposition to the construction of the highway remained among environmentalists and Indigenous peoples. There were also concerns about facilitating drug trafficking and illegal immigration if the road were continued.
21st-century migration
By the 21st century, notwithstanding the lack of infrastructure in the Darién Gap, drug traffickers and armed guerrilla groups had entrenched themselves in the region, benefiting from the area’s remoteness and ineffective security. In addition, the numbers of migrants crossing the Darién Gap began to increase in the mid-2010s and accelerated in the 2020s. In the early 2010s Panamanian officials recorded an average of 2,400 crossings per year. That figure rose between 2015 and 2021 to approximately 30,000 per year and intensified in 2021 to more than 130,000. In 2023 more than 500,000 individuals made the crossing. Despite the area’s geographic dangers and the threat from criminals, most migrants were crossing the Gap as part of a northward journey to North America. The largest groups were fleeing violence, economic collapse, and political instability in Venezuela, Ecuador, and Haiti. Changes to immigration policies in Central America had driven many of these refugees, who had been unable to obtain legal entry, to take the more hazardous journey across the Darién Gap. This was seen in the data as an exponential rise in Venezuelans making the crossing in 2022, the same year Mexico began to impose new visa requirements for those arriving from Venezuela.
Details
The Darién Gap is a geographic region that connects the American continents, stretching across southern Panama's Darién Province and the northern portion of Colombia's Chocó Department. Consisting of a large watershed, dense rainforest, and mountains, it is known for its remoteness, difficult terrain, and extreme environment, with a reputation as one of the most inhospitable regions in the world. Nevertheless, as the only land bridge between North and South America, the Darién Gap has historically served as a major route for both humans and wildlife.
The geography of the Darién Gap is highly diverse. The Colombian side is dominated primarily by the river delta of the Atrato River, which creates a flat marshland at least 80 km (50 mi) wide. The Tanela River, which flows toward Atrato, was Hispanicized to Darién by 16th Century European conquistadors. The Serranía del Baudó mountain range extends along Colombia's Pacific coast and into Panama. The Panamanian side, in stark contrast, is a mountainous rainforest, with terrain reaching from 60 m (197 ft) in the valley floors to 1,845 m (6,053 ft) at the tallest peak, Cerro Tacarcuna, in the Serranía del Darién.
The Darién Gap is inhabited mostly by the indigenous Embera-Wounaan and Guna peoples; in 1995, it had a reported population of 8,000 among five tribes. The only sizable settlement in the region is La Palma, the capital of Darién Province, with roughly 4,200 residents; other population centers include Yaviza and El Real, both on the Panamanian side.
Owing to its isolation and harsh geography, the Darién Gap is largely undeveloped, with most economic activity consisting of small-scale farming, cattle ranching, and lumber. Criminal enterprises such as human and drug trafficking are widespread. There is no road, not even a primitive one, across the Darién: Colombia and Panama are the only countries in the Americas that share a land border but lack even a rudimentary link. The "Gap" interrupts the Pan-American Highway, which breaks at Yaviza, Panama and resumes at Turbo, Colombia roughly 106 km (66 mi) away. Infrastructure development has long been constrained by logistical challenges, financial costs, and environmental concerns; attempts failed in the 1970s and 1990s. As of 2024, there is no active plan to build a road through the Gap, although there is discussion of reestablishing a ferry service and building a rail link.
Consequently, travel within and across Darién Gap is often conducted with small boats or traditional watercraft such as pirogues. Otherwise, hiking is the only remaining option, and it is strenuous and dangerous. Aside from natural threats such as deadly wildlife, tropical diseases, and frequent heavy rains and flash floods, law enforcement and medical support are nonexistent, resulting in rampant violent crime, and causing otherwise minor injuries to ultimately become fatal.
Despite its perilous conditions, since the 2010s, the Darién Gap has become one of the heaviest migration routes in the world, with hundreds of thousands of migrants, primarily Haitians and Venezuelans, traversing north to the Mexico–United States border. In 2022, there were 250,000 crossings, compared to only 24,000 in 2019. In 2023, more than 520,000 passed through the gap, more than doubling the previous year's number of crossings.
Pan-American Highway
The Pan-American Highway is a system of roads measuring about 30,000 km (19,000 mi) in length that runs north–south through the entirety of North, Central and South America, with the sole exception of a 106 km (66 mi) stretch of marshland and mountains between Panama and Colombia known as the Darién Gap. On the South American side, the Highway terminates at Turbo, Colombia, near 8°6′N 76°40′W. On the Panamanian side, the road terminus, for many years in Chepo, Panama Province, is since 2010 in the town of Yaviza at 8°9′N 77°41′W.
Many people, including local indigenous populations, groups and governments are opposed to completing the Darién portion of the highway. Reasons for opposition include protecting the rainforest, containing the spread of tropical diseases, protecting the livelihood of indigenous peoples in the area, preventing drug trafficking and its associated violence, and preventing foot-and-mouth disease from entering North America. The extension of the highway as far as Yaviza resulted in severe deforestation alongside the highway route within a decade.
Efforts were made for decades to fill this sole gap in the Pan-American Highway. Planning began in 1971 with the help of American funding, but was halted in 1974 after concerns were raised by environmentalists. US support was further blocked by the US Department of Agriculture in 1978, from its desire to stop the spread of foot-and-mouth disease. Another effort to build the road began in 1992, but, by 1994 a United Nations agency reported that the road, and the subsequent development, would cause extensive environmental damage. Cited reasons include evidence that the Darién Gap has prevented the spread of diseased cattle into Central and North America, which have not seen foot-and-mouth disease since 1954, and, since at least the 1970s, this has been a substantial factor in preventing a road link through the Darién Gap. The Embera-Wounaan and Guna are among five tribes, comprising 8,000 people, who have expressed concern that the road would bring about the potential erosion of their cultures by destroying their food sources.
An alternative to the Darién Gap highway would be a river ferry service between Turbo or Necoclí, Colombia and one of several sites along Panama's Caribbean coast. Ferry services such as Crucero Express and Ferry Xpress operated to link the gap, but closed because the service was not profitable. As of 2023, nothing has come of this idea.
Another idea is to use a combination of bridges and tunnels to avoid the environmentally sensitive regions.
Migrants traveling northward
Venezuelan migrants being processed in Ecuador in preparation to make the long journey north to New York City, including crossing the Darién Gap
While the Darién Gap has been considered to be essentially impassable, in the 21st century thousands of migrants, primarily Haitian during the 2010s and Venezuelan during the 2020s, crossed the Darién Gap to reach the United States. By 2021, the number was more than 130,000, increasing to 520,000 in 2023, but dropping to 300,000 in 2024, for the now more organized 2½ day trek, which used to take a week. Of the 334,000 migrants who crossed over the first eight months of 2023, 60% were Venezuelan, motivating the Biden administration to provide foreign assistance to help Panama deport migrants.
The hike, which involves crossing rivers which flood frequently, is unpleasant, demanding, and dangerous, with math and robbery common, and there are numerous fatalities. In 2024 there were 55 known deaths, probably more, and 180 unaccompanied minors were abandoned and looked after by child care institutions, some because their relatives died or got lost, others travelling unaccompanied..
By 2013, the coastal route on the east side of the Darién Isthmus became relatively safe, by taking a motorboat across the Gulf of Uraba from Turbo to Capurganá and then hopping the coast to Sapzurro and hiking from there to La Miel, Panama. All inland routes through the Darién remain highly dangerous. In June 2017, CBS journalist Adam Yamaguchi filmed smugglers leading refugees on a nine-day journey from Colombia to Panama through the Darién.
People from Africa, South Asia, the Middle East, the Caribbean, and China have been known to cross the Darién Gap as a method of migrating to the United States. This route may entail flying to Ecuador to take advantage of its liberal visa policy, and attempting to cross the gap on foot. Journalist Jason Motlagh was interviewed by Sacha Pfeiffer on NPR's nationally syndicated radio show On Point in 2016 concerning his work following migrants through the Darién Gap.[ Journalists Nadja Drost and Bruno Federico were interviewed by Nick Schifrin about their work following migrants through the Darién Gap in mid-2019, and the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic a year later, as part of a series on migration to the United States for PBS NewsHour.
In 2023, people fleeing China travelled to Ecuador, then to Necoclí in Colombia, with the intention of crossing the Darién Gap on foot. The number of Chinese people crossing the Darién Gap increased with each passing month in 2023.
In August 2024, journalist Caitlin Dickinson reported on immigration through the Darién Gap for The Atlantic.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2385 2024-12-21 22:06:57
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2285) Fashion Design
Gist
Fashion design is the art of applying design, aesthetics, clothing construction and natural beauty to clothing and its accessories. It is influenced by culture and different trends and has varied over time and place.
Summary
Fashion design is the art and practice of creating clothing and accessories. It involves the application of design, aesthetics, and natural beauty to garments and their embellishments. Fashion designers work in a variety of ways, including designing ready-to-wear clothing, haute couture collections, and custom pieces for individual clients. The process of fashion design entails several stages, such as concept creation, sketching, fabric selection, pattern making, garment construction, and final presentation. Fashion design not only focuses on the physical creation of garments but also encompasses the cultural and social influences that shape trends and styles.
Importance of Fashion Design in Society
Fashion design holds a significant place in society due to its influence on culture, identity, and economy. It serves as a form of self-expression, allowing individuals to communicate their personality, mood, and social status through their clothing choices. Fashion reflects societal changes, capturing the spirit of the times and often driving social movements.
Economically, the fashion industry is a major global player, generating employment and contributing to economic growth. It includes a wide range of professions, from designers and models to marketers and retailers, impacting various sectors.
Moreover, fashion design plays a role in innovation and sustainability. Designers are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly materials and ethical production methods, to address environmental and ethical concerns. Fashion also fosters creativity and artistic expression, pushing the boundaries of what is possible and continually evolving to meet the needs and desires of society.
Details
Fashion design is the art of applying design, aesthetics, clothing construction and natural beauty to clothing and its accessories. It is influenced by culture and different trends and has varied over time and place. "A fashion designer creates clothing, including dresses, suits, pants, and skirts, and accessories like shoes and handbags, for consumers. He or she can specialize in clothing, accessory, or jewelry design, or may work in more than one of these areas."
Fashion designers
Fashion designers work in a variety of ways when designing their pieces and accessories such as rings, bracelets, necklaces and earrings. Due to the time required to put a garment out on the market, designers must anticipate changes to consumer desires. Fashion designers are responsible for creating looks for individual garments, involving shape, color, fabric, trimming, and more.
Fashion designers attempt to design clothes that are functional as well as aesthetically pleasing. They consider who is likely to wear a garment and the situations in which it will be worn, and they work with a wide range of materials, colors, patterns, and styles. Though most clothing worn for everyday wear falls within a narrow range of conventional styles, unusual garments are usually sought for special occasions such as evening wear or party dresses.
Some clothes are made specifically for an individual, as in the case of haute couture or bespoke tailoring. Today, most clothing is designed for the mass market, especially casual and everyday wear, which are commonly known as ready to wear or fast fashion.
Structure
There are different lines of work for designers in the fashion industry. Fashion designers who work full-time for a fashion house, as 'in-house designers', own the designs and may either work alone or as a part of a design team. Freelance designers who work for themselves sell their designs to fashion houses, directly to shops, or to clothing manufacturers. There are quite a few fashion designers who choose to set up their labels, which offers them full control over their designs. Others are self-employed and design for individual clients. Other high-end fashion designers cater to specialty stores or high-end fashion department stores. These designers create original garments, as well as those that follow established fashion trends. Most fashion designers, however, work for apparel manufacturers, creating designs of men's, women's, and children's fashions for the mass market. Large designer brands that have a 'name' as their brand such as Abercrombie & Fitch, Justice, or Juicy are likely to be designed by a team of individual designers under the direction of a design director.
Designing a garment
Garment design includes components of "color, texture, space, lines, pattern, silhouette, shape, proportion, balance, emphasis, rhythm, and harmony". All of these elements come together to design a garment by creating visual interest for consumers.
Fashion designers work in various ways, some start with a vision in their head and later move into drawing it on paper or on a computer, while others go directly into draping fabric onto a dress form, also known as a mannequin. The design process is unique to the designer and it is rather intriguing to see the various steps that go into the process. Designing a garment starts with patternmaking. The process begins with creating a sloper or base pattern. The sloper will fit the size of the model a designer is working with or a base can be made by utilizing standard size charting.
Three major manipulations within patternmaking include dart manipulation, contouring, and added fullness. Dart manipulation allows for a dart to be moved on a garment in various places but does not change the overall fit of the garment. Contouring allows for areas of a garment to fit closer to areas of the torso such as the bust or shoulders. Added fullness increases the length or width of a pattern to change the frame as well as fit of the garment. The fullness can be added on one side, unequal, or equally to the pattern.
A designer may choose to work with certain apps that can help connect all their ideas together and expand their thoughts to create a cohesive design. When a designer is completely satisfied with the fit of the toile (or muslin), they will consult a professional pattern maker who will then create the finished, working version of the pattern out of paper or using a computer program. Finally, a sample garment is made up and tested on a model to make sure it is an operational outfit. Fashion design is expressive, the designers create art that may be functional or non-functional.
Technology within fashion
Technology is "the study and knowledge of the practical, especially industrial, use of scientific discoveries". Technology within fashion has broadened the industry and allowed for faster production processes.
Over the years, there has been an increase in the use of technology within Fashion Design as it offers new platforms for creativity. Technology is constantly changing and there have been innovations within the industry. 3D printing allows a larger area of personalized products and widening originality. Iris van Herpen, a Dutch designer, has showcased the incorporation of 3D printing as her Crystallization used 3D printing for the first time on a runway. The innovation has re-shaped the fashion industry and creates a new area of creativity.
Apps and software have increasingly changed how designers can use technology to create. Adobe Creative Cloud, specifically Photoshop and Illustrator, is a new means of communication for designers and allows ideas to flow. Designers are provided with a space to also create more professional and industry standard specifications such as technical flats and tech packs.
Software such as Browzwear, Clo3D, and Optitex aid designers in the product development stage. Virtual reality has allowed a new way to prototype clothing to originally see designers. This eliminates the need for a live model and fittings, which shortens the production process. 3D modeling within software allows for initial sampling and development stages for partnerships with suppliers before the garments are produced. Mock-ups of designs in the 3D modeling allows for problems to be solved before a final sample is made and sent to a manufacturer.
Technology can also be used and aid within the material of a garment. Material innovation creates a new way for fibers to be re-imagined or for new materials to be constructed. This overall aids in functional and aesthetic purposes for the designer. The material technology has been used with brands such as Werewool and Bananatex. These brands innovate the way designers can construct their garments and provide new materials to be used.
Types of fashion
Garments produced by clothing manufacturers fall into three main categories, although these may be split up into additional, different types.
Haute couture
Until the 1950s, fashion clothing was predominately designed and manufactured on a made-to-measure or haute couture basis (French for high-sewing), with each garment being created for a specific client. A couture garment is made to order for an individual customer, and is usually made from high-quality, expensive fabric, sewn with extreme attention to detail and finish, often using time-consuming, hand-executed techniques. Look and fit take priority over the cost of materials and the time it takes to make. Due to the high cost of each garment, haute couture makes little direct profit for the fashion houses, but is important for prestige and publicity.
Ready-to-wear
Ready-to-wear, or prêt-à-porter, clothes are a cross between haute couture and mass market. They are not made for individual customers, but great care is taken in the choice and cut of the fabric. Clothes are made in small quantities to guarantee exclusivity, so they are rather expensive. Ready-to-wear collections are usually presented by fashion houses each season during a period known as Fashion Week. This takes place on a citywide basis and occurs twice a year. The main seasons of Fashion Week include; spring/summer, fall/winter, resort, swim, and bridal.
Half-way garments are an alternative to ready-to-wear, "off-the-peg", or prêt-à-porter fashion. Half-way garments are intentionally unfinished pieces of clothing that encourage co-design between the "primary designer" of the garment, and what would usually be considered, the passive "consumer". This differs from ready-to-wear fashion, as the consumer is able to participate in the process of making and co-designing their clothing. During the Make{able} workshop, Hirscher and Niinimaki found that personal involvement in the garment-making process created a meaningful "narrative" for the user, which established a person-product attachment and increased the sentimental value of the final product.
Otto von Busch also explores half-way garments and fashion co-design in his thesis, "Fashion-able, Hacktivism and engaged Fashion Design".
Mass market
Currently, the fashion industry relies more on mass-market sales. The mass market caters for a wide range of customers, producing ready-to-wear garments using trends set by the famous names in fashion. They often wait around a season to make sure a style is going to catch on before producing their versions of the original look. To save money and time, they use cheaper fabrics and simpler production techniques which can easily be done by machines. The end product can, therefore, be sold much more cheaply.
There is a type of design called "kutch" originated from the German word kitschig, meaning "trashy" or "not aesthetically pleasing". Kitsch can also refer to "wearing or displaying something that is therefore no longer in fashion".
Income
The median annual wages for salaried fashion designers was $79,290 in May 2023, approximately $38.12 per hour. The middle 50 percent earned an average of 76,700. The lowest 10 percent earned $37,090 and the highest 10 percent earned $160,850. The highest number of employment lies within Apparel, Piece Goods, and Notions Merchant Wholesalers with a percentage of 5.4. The average is 7,820 based on employment. The lowest employment is within Apparel Knitting Mills at .46% of the industry employed, which averages to 30 workers within the specific specialty. In 2016, 23,800 people were counted as fashion designers in the United States.
Geographically, the largest employment state of Fashion designers is New York with an employment of 7,930. New York is considered a hub for fashion designers due to a large percentage of luxury designers and brands.
Fashion industry
Fashion today is a global industry, and most major countries have a fashion industry. Seven countries have established an international reputation in fashion: the United States, France, Italy, United Kingdom, Japan, Germany and Belgium. The "big four" fashion capitals of the fashion industry are New York City, Paris, Milan, and London.
Fashion design terms
* A fashion designer conceives garment combinations of line, proportion, color, and texture. While sewing and pattern-making skills are beneficial, they are not a pre-requisite of successful fashion design. Most fashion designers are formally trained or apprenticed.
* A technical designer works with the design team and the factories overseas to ensure correct garment construction, appropriate fabric choices and a good fit. The technical designer fits the garment samples on a fit model, and decides which fit and construction changes to make before mass-producing the garment.
* A pattern maker (also referred as pattern master or pattern cutter) drafts the shapes and sizes of a garment's pieces. This may be done manually with paper and measuring tools or by using a CAD computer software program. Another method is to drape fabric directly onto a dress form. The resulting pattern pieces can be constructed to produce the intended design of the garment and required size. Formal training is usually required for working as a pattern marker.
* A tailor makes custom designed garments made to the client's measure; especially suits (coat and trousers, jacket and skirt, et cetera). Tailors usually undergo an apprenticeship or other formal training.
* A textile designer designs fabric weaves and prints for clothes and furnishings. Most textile designers are formally trained as apprentices and in school.
* A stylist co-ordinates the clothes, jewelry, and accessories used in fashion photography and catwalk presentations. A stylist may also work with an individual client to design a coordinated wardrobe of garments. Many stylists are trained in fashion design, the history of fashion, and historical costume, and have a high level of expertise in the current fashion market and future market trends. However, some simply have a strong aesthetic sense for pulling great looks together.
* A fashion buyer selects and buys the mix of clothing available in retail shops, department stores, and chain stores. Most fashion buyers are trained in business and/or fashion studies.
* A seamstress sews ready-to-wear or mass-produced clothing by hand or with a sewing machine, either in a garment shop or as a sewing machine operator in a factory. She (or he) may not have the skills to make (design and cut) the garments, or to fit them on a model.
* A dressmaker specializes in custom-made women's clothes: day, math, and evening dresses, business clothes and suits, trousseaus, sports clothes, and lingerie.
* A fashion forecaster predicts what colours, styles and shapes will be popular ("on-trend") before the garments are on sale in stores.
* A model wears and displays clothes at fashion shows and in photographs.
* A fit model aids the fashion designer by wearing and commenting on the fit of clothes during their design and pre-manufacture. Fit models need to be a particular size for this purpose.
* A fashion journalist writes fashion articles describing the garments presented or fashion trends, for magazines or newspapers.
* A fashion photographer produces photographs about garments and other fashion items along with models and stylists for magazines or advertising agencies.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2386 2024-12-22 00:02:32
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2286) Computer Science
Gist
Computer Science is the study of computers and computational systems. Unlike electrical and computer engineers, computer scientists deal mostly with software and software systems; this includes their theory, design, development, and application.
Summary
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of hardware and software).
Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of repositories of data. Human–computer interaction investigates the interfaces through which humans and computers interact, and software engineering focuses on the design and principles behind developing software. Areas such as operating systems, networks and embedded systems investigate the principles and design behind complex systems. Computer architecture describes the construction of computer components and computer-operated equipment. Artificial intelligence and machine learning aim to synthesize goal-orientated processes such as problem-solving, decision-making, environmental adaptation, planning and learning found in humans and animals. Within artificial intelligence, computer vision aims to understand and process image and video data, while natural language processing aims to understand and process textual and linguistic data.
The fundamental concern of computer science is determining what can and cannot be automated. The Turing Award is generally recognized as the highest distinction in computer science.
Details
Computer science is the study of computers and computing, including their theoretical and algorithmic foundations, hardware and software, and their uses for processing information. The discipline of computer science includes the study of algorithms and data structures, computer and network design, modeling data and information processes, and artificial intelligence. Computer science draws some of its foundations from mathematics and engineering and therefore incorporates techniques from areas such as queueing theory, probability and statistics, and electronic circuit design. Computer science also makes heavy use of hypothesis testing and experimentation during the conceptualization, design, measurement, and refinement of new algorithms, information structures, and computer architectures.
Computer science is considered as part of a family of five separate yet interrelated disciplines: computer engineering, computer science, information systems, information technology, and software engineering. This family has come to be known collectively as the discipline of computing. These five disciplines are interrelated in the sense that computing is their object of study, but they are separate since each has its own research perspective and curricular focus. (Since 1991 the Association for Computing Machinery [ACM], the IEEE Computer Society [IEEE-CS], and the Association for Information Systems [AIS] have collaborated to develop and update the taxonomy of these five interrelated disciplines and the guidelines that educational institutions worldwide use for their undergraduate, graduate, and research programs.)
The major subfields of computer science include the traditional study of computer architecture, programming languages, and software development. However, they also include computational science (the use of algorithmic techniques for modeling scientific data), graphics and visualization, human-computer interaction, databases and information systems, networks, and the social and professional issues that are unique to the practice of computer science. As may be evident, some of these subfields overlap in their activities with other modern fields, such as bioinformatics and computational chemistry. These overlaps are the consequence of a tendency among computer scientists to recognize and act upon their field’s many interdisciplinary connections.
Development of computer science
Computer science emerged as an independent discipline in the early 1960s, although the electronic digital computer that is the object of its study was invented some two decades earlier. The roots of computer science lie primarily in the related fields of mathematics, electrical engineering, physics, and management information systems.
Mathematics is the source of two key concepts in the development of the computer—the idea that all information can be represented as sequences of zeros and ones and the abstract notion of a “stored program.” In the binary number system, numbers are represented by a sequence of the binary digits 0 and 1 in the same way that numbers in the familiar decimal system are represented using the digits 0 through 9. The relative ease with which two states (e.g., high and low voltage) can be realized in electrical and electronic devices led naturally to the binary digit, or bit, becoming the basic unit of data storage and transmission in a computer system.
Electrical engineering provides the basics of circuit design—namely, the idea that electrical impulses input to a circuit can be combined using Boolean algebra to produce arbitrary outputs. (The Boolean algebra developed in the 19th century supplied a formalism for designing a circuit with binary input values of zeros and ones [false or true, respectively, in the terminology of logic] to yield any desired combination of zeros and ones as output.) The invention of the transistor and the miniaturization of circuits, along with the invention of electronic, magnetic, and optical media for the storage and transmission of information, resulted from advances in electrical engineering and physics.
Management information systems, originally called data processing systems, provided early ideas from which various computer science concepts such as sorting, searching, databases, information retrieval, and graphical user interfaces evolved. Large corporations housed computers that stored information that was central to the activities of running a business—payroll, accounting, inventory management, production control, shipping, and receiving.
Theoretical work on computability, which began in the 1930s, provided the needed extension of these advances to the design of whole machines; a milestone was the 1936 specification of the Turing machine (a theoretical computational model that carries out instructions represented as a series of zeros and ones) by the British mathematician Alan Turing and his proof of the model’s computational power. Another breakthrough was the concept of the stored-program computer, usually credited to Hungarian American mathematician John von Neumann. These are the origins of the computer science field that later became known as architecture and organization.
In the 1950s, most computer users worked either in scientific research labs or in large corporations. The former group used computers to help them make complex mathematical calculations (e.g., missile trajectories), while the latter group used computers to manage large amounts of corporate data (e.g., payrolls and inventories). Both groups quickly learned that writing programs in the machine language of zeros and ones was not practical or reliable. This discovery led to the development of assembly language in the early 1950s, which allows programmers to use symbols for instructions (e.g., ADD for addition) and variables (e.g., X). Another program, known as an assembler, translated these symbolic programs into an equivalent binary program whose steps the computer could carry out, or “execute.”
Other system software elements known as linking loaders were developed to combine pieces of assembled code and load them into the computer’s memory, where they could be executed. The concept of linking separate pieces of code was important, since it allowed “libraries” of programs for carrying out common tasks to be reused. This was a first step in the development of the computer science field called software engineering.
Later in the 1950s, assembly language was found to be so cumbersome that the development of high-level languages (closer to natural languages) began to support easier, faster programming. FORTRAN emerged as the main high-level language for scientific programming, while COBOL became the main language for business programming. These languages carried with them the need for different software, called compilers, that translate high-level language programs into machine code. As programming languages became more powerful and abstract, building compilers that create high-quality machine code and that are efficient in terms of execution speed and storage consumption became a challenging computer science problem. The design and implementation of high-level languages is at the heart of the computer science field called programming languages.
Increasing use of computers in the early 1960s provided the impetus for the development of the first operating systems, which consisted of system-resident software that automatically handled input and output and the execution of programs called “jobs.” The demand for better computational techniques led to a resurgence of interest in numerical methods and their analysis, an activity that expanded so widely that it became known as computational science.
The 1970s and ’80s saw the emergence of powerful computer graphics devices, both for scientific modeling and other visual activities. (Computerized graphical devices were introduced in the early 1950s with the display of crude images on paper plots and cathode-ray tube [CRT] screens.) Expensive hardware and the limited availability of software kept the field from growing until the early 1980s, when the computer memory required for bitmap graphics (in which an image is made up of small rectangular pixels) became more affordable. Bitmap technology, together with high-resolution display screens and the development of graphics standards that make software less machine-dependent, has led to the explosive growth of the field. Support for all these activities evolved into the field of computer science known as graphics and visual computing.
Closely related to this field is the design and analysis of systems that interact directly with users who are carrying out various computational tasks. These systems came into wide use during the 1980s and ’90s, when line-edited interactions with users were replaced by graphical user interfaces (GUIs). GUI design, which was pioneered by Xerox and was later picked up by Apple (Macintosh) and finally by Microsoft (Windows), is important because it constitutes what people see and do when they interact with a computing device. The design of appropriate user interfaces for all types of users has evolved into the computer science field known as human-computer interaction (HCI).
The field of computer architecture and organization has also evolved dramatically since the first stored-program computers were developed in the 1950s. So called time-sharing systems emerged in the 1960s to allow several users to run programs at the same time from different terminals that were hard-wired to the computer. The 1970s saw the development of the first wide-area computer networks (WANs) and protocols for transferring information at high speeds between computers separated by large distances. As these activities evolved, they coalesced into the computer science field called networking and communications. A major accomplishment of this field was the development of the Internet.
The idea that instructions, as well as data, could be stored in a computer’s memory was critical to fundamental discoveries about the theoretical behaviour of algorithms. That is, questions such as, “What can/cannot be computed?” have been formally addressed using these abstract ideas. These discoveries were the origin of the computer science field known as algorithms and complexity. A key part of this field is the study and application of data structures that are appropriate to different applications. Data structures, along with the development of optimal algorithms for inserting, deleting, and locating data in such structures, are a major concern of computer scientists because they are so heavily used in computer software, most notably in compilers, operating systems, file systems, and search engines.
In the 1960s the invention of magnetic disk storage provided rapid access to data located at an arbitrary place on the disk. This invention led not only to more cleverly designed file systems but also to the development of database and information retrieval systems, which later became essential for storing, retrieving, and transmitting large amounts and wide varieties of data across the Internet. This field of computer science is known as information management.
Another long-term goal of computer science research is the creation of computing machines and robotic devices that can carry out tasks that are typically thought of as requiring human intelligence. Such tasks include moving, seeing, hearing, speaking, understanding natural language, thinking, and even exhibiting human emotions. The computer science field of intelligent systems, originally known as artificial intelligence (AI), actually predates the first electronic computers in the 1940s, although the term artificial intelligence was not coined until 1956.
Three developments in computing in the early part of the 21st century—mobile computing, client-server computing, and computer hacking—contributed to the emergence of three new fields in computer science: platform-based development, parallel and distributed computing, and security and information assurance. Platform-based development is the study of the special needs of mobile devices, their operating systems, and their applications. Parallel and distributed computing concerns the development of architectures and programming languages that support the development of algorithms whose components can run simultaneously and asynchronously (rather than sequentially), in order to make better use of time and space. Security and information assurance deals with the design of computing systems and software that protects the integrity and security of data, as well as the privacy of individuals who are characterized by that data.
Finally, a particular concern of computer science throughout its history is the unique societal impact that accompanies computer science research and technological advancements. With the emergence of the Internet in the 1980s, for example, software developers needed to address important issues related to information security, personal privacy, and system reliability. In addition, the question of whether computer software constitutes intellectual property and the related question “Who owns it?” gave rise to a whole new legal area of licensing and licensing standards that applied to software and related artifacts. These concerns and others form the basis of social and professional issues of computer science, and they appear in almost all the other fields identified above.
So, to summarize, the discipline of computer science has evolved into the following 15 distinct fields:
* Algorithms and complexity
* Architecture and organization
* Computational science
* Graphics and visual computing
* Human-computer interaction
* Information management
* Intelligent systems
* Networking and communication
* Operating systems
* Parallel and distributed computing
* Platform-based development
* Programming languages
* Security and information assurance
* Software engineering
* Social and professional issues
Computer science continues to have strong mathematical and engineering roots. Computer science bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degree programs are routinely offered by postsecondary academic institutions, and these programs require students to complete appropriate mathematics and engineering courses, depending on their area of focus. For example, all undergraduate computer science majors must study discrete mathematics (logic, combinatorics, and elementary graph theory). Many programs also require students to complete courses in calculus, statistics, numerical analysis, physics, and principles of engineering early in their studies.
Algorithms and complexity
An algorithm is a specific procedure for solving a well-defined computational problem. The development and analysis of algorithms is fundamental to all aspects of computer science: artificial intelligence, databases, graphics, networking, operating systems, security, and so on. Algorithm development is more than just programming. It requires an understanding of the alternatives available for solving a computational problem, including the hardware, networking, programming language, and performance constraints that accompany any particular solution. It also requires understanding what it means for an algorithm to be “correct” in the sense that it fully and efficiently solves the problem at hand.
An accompanying notion is the design of a particular data structure that enables an algorithm to run efficiently. The importance of data structures stems from the fact that the main memory of a computer (where the data is stored) is linear, consisting of a sequence of memory cells that are serially numbered 0, 1, 2,…. Thus, the simplest data structure is a linear array, in which adjacent elements are numbered with consecutive integer “indexes” and an element’s value is accessed by its unique index. An array can be used, for example, to store a list of names, and efficient methods are needed to efficiently search for and retrieve a particular name from the array. For example, sorting the list into alphabetical order permits a so-called binary search technique to be used, in which the remainder of the list to be searched at each step is cut in half. This search technique is similar to searching a telephone book for a particular name. Knowing that the book is in alphabetical order allows one to turn quickly to a page that is close to the page containing the desired name. Many algorithms have been developed for sorting and searching lists of data efficiently.
Although data items are stored consecutively in memory, they may be linked together by pointers (essentially, memory addresses stored with an item to indicate where the next item or items in the structure are found) so that the data can be organized in ways similar to those in which they will be accessed. The simplest such structure is called the linked list, in which noncontiguously stored items may be accessed in a pre-specified order by following the pointers from one item in the list to the next. The list may be circular, with the last item pointing to the first, or each element may have pointers in both directions to form a doubly linked list. Algorithms have been developed for efficiently manipulating such lists by searching for, inserting, and removing items.
Pointers also provide the ability to implement more complex data structures. A graph, for example, is a set of nodes (items) and links (known as edges) that connect pairs of items. Such a graph might represent a set of cities and the highways joining them, the layout of circuit elements and connecting wires on a memory chip, or the configuration of persons interacting via a social network. Typical graph algorithms include graph traversal strategies, such as how to follow the links from node to node (perhaps searching for a node with a particular property) in a way that each node is visited only once. A related problem is the determination of the shortest path between two given nodes on an arbitrary graph. (See graph theory.) A problem of practical interest in network algorithms, for instance, is to determine how many “broken” links can be tolerated before communications begin to fail. Similarly, in very-large-scale integration (VLSI) chip design it is important to know whether the graph representing a circuit is planar, that is, whether it can be drawn in two dimensions without any links crossing (wires touching).
The (computational) complexity of an algorithm is a measure of the amount of computing resources (time and space) that a particular algorithm consumes when it runs. Computer scientists use mathematical measures of complexity that allow them to predict, before writing the code, how fast an algorithm will run and how much memory it will require. Such predictions are important guides for programmers implementing and selecting algorithms for real-world applications.
Computational complexity is a continuum, in that some algorithms require linear time (that is, the time required increases directly with the number of items or nodes in the list, graph, or network being processed), whereas others require quadratic or even exponential time to complete (that is, the time required increases with the number of items squared or with the exponential of that number). At the far end of this continuum lie the murky seas of intractable problems—those whose solutions cannot be efficiently implemented. For these problems, computer scientists seek to find heuristic algorithms that can almost solve the problem and run in a reasonable amount of time.
Further away still are those algorithmic problems that can be stated but are not solvable; that is, one can prove that no program can be written to solve the problem. A classic example of an unsolvable algorithmic problem is the halting problem, which states that no program can be written that can predict whether or not any other program halts after a finite number of steps. The unsolvability of the halting problem has immediate practical bearing on software development. For instance, it would be frivolous to try to develop a software tool that predicts whether another program being developed has an infinite loop in it (although having such a tool would be immensely beneficial).
Architecture and organization
Computer architecture deals with the design of computers, data storage devices, and networking components that store and run programs, transmit data, and drive interactions between computers, across networks, and with users. Computer architects use parallelism and various strategies for memory organization to design computing systems with very high performance. Computer architecture requires strong communication between computer scientists and computer engineers, since they both focus fundamentally on hardware design.
At its most fundamental level, a computer consists of a control unit, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU), a memory unit, and input/output (I/O) controllers. The ALU performs simple addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and logic operations, such as OR and AND. The memory stores the program’s instructions and data. The control unit fetches data and instructions from memory and uses operations of the ALU to carry out those instructions using that data. (The control unit and ALU together are referred to as the central processing unit [CPU].) When an input or output instruction is encountered, the control unit transfers the data between the memory and the designated I/O controller. The operational speed of the CPU primarily determines the speed of the computer as a whole. All of these components—the control unit, the ALU, the memory, and the I/O controllers—are realized with transistor circuits.
Computers also have another level of memory called a cache, a small, extremely fast (compared with the main memory, or random access memory [RAM]) unit that can be used to store information that is urgently or frequently needed. Current research includes cache design and algorithms that can predict what data is likely to be needed next and preload it into the cache for improved performance.
I/O controllers connect the computer to specific input devices (such as keyboards and touch screen displays) for feeding information to the memory, and output devices (such as printers and displays) for transmitting information from the memory to users. Additional I/O controllers connect the computer to a network via ports that provide the conduit through which data flows when the computer is connected to the Internet.
Linked to the I/O controllers are secondary storage devices, such as a disk drive, that are slower and have a larger capacity than main or cache memory. Disk drives are used for maintaining permanent data. They can be either permanently or temporarily attached to the computer in the form of a compact disc (CD), a digital video disc (DVD), or a memory stick (also called a flash drive).
The operation of a computer, once a program and some data have been loaded into RAM, takes place as follows. The first instruction is transferred from RAM into the control unit and interpreted by the hardware circuitry. For instance, suppose that the instruction is a string of bits that is the code for LOAD 10. This instruction loads the contents of memory location 10 into the ALU. The next instruction, say ADD 15, is fetched. The control unit then loads the contents of memory location 15 into the ALU and adds it to the number already there. Finally, the instruction STORE 20 would store that sum into location 20. At this level, the operation of a computer is not much different from that of a pocket calculator.
In general, programs are not just lengthy sequences of LOAD, STORE, and arithmetic operations. Most importantly, computer languages include conditional instructions—essentially, rules that say, “If memory location n satisfies condition a, do instruction number x next, otherwise do instruction y.” This allows the course of a program to be determined by the results of previous operations—a critically important ability.
Finally, programs typically contain sequences of instructions that are repeated a number of times until a predetermined condition becomes true. Such a sequence is called a loop. For example, a loop would be needed to compute the sum of the first n integers, where n is a value stored in a separate memory location. Computer architectures that can execute sequences of instructions, conditional instructions, and loops are called “Turing complete,” which means that they can carry out the execution of any algorithm that can be defined. Turing completeness is a fundamental and essential characteristic of any computer organization.
Logic design is the area of computer science that deals with the design of electronic circuits using the fundamental principles and properties of logic (see Boolean algebra) to carry out the operations of the control unit, the ALU, the I/O controllers, and other hardware. Each logical function (AND, OR, and NOT) is realized by a particular type of device called a gate. For example, the addition circuit of the ALU has inputs corresponding to all the bits of the two numbers to be added and outputs corresponding to the bits of the sum. The arrangement of wires and gates that link inputs to outputs is determined by the mathematical definition of addition. The design of the control unit provides the circuits that interpret instructions. Due to the need for efficiency, logic design must also optimize the circuitry to function with maximum speed and has a minimum number of gates and circuits.
An important area related to architecture is the design of microprocessors, which are complete CPUs—control unit, ALU, and memory—on a single integrated circuit chip. Additional memory and I/O control circuitry are linked to this chip to form a complete computer. These thumbnail-sized devices contain millions of transistors that implement the processing and memory units of modern computers.
VLSI microprocessor design occurs in a number of stages, which include creating the initial functional or behavioral specification, encoding this specification into a hardware description language, and breaking down the design into modules and generating sizes and shapes for the eventual chip components. It also involves chip planning, which includes building a “floor plan” to indicate where on the chip each component should be placed and connected to other components. Computer scientists are also involved in creating the computer-aided design (CAD) tools that support engineers in the various stages of chip design and in developing the necessary theoretical results, such as how to efficiently design a floor plan with near-minimal area that satisfies the given constraints.
Advances in integrated circuit technology have been incredible. For example, in 1971 the first microprocessor chip (Intel Corporation’s 4004) had only 2,300 transistors, in 1993 Intel’s Pentium chip had more than 3 million transistors, and by 2000 the number of transistors on such a chip was about 50 million. The Power7 chip introduced in 2010 by IBM contained approximately 1 billion transistors. The phenomenon of the number of transistors in an integrated circuit doubling about every two years is widely known as Moore’s law.
Fault tolerance is the ability of a computer to continue operation when one or more of its components fails. To ensure fault tolerance, key components are often replicated so that the backup component can take over if needed. Such applications as aircraft control and manufacturing process control run on systems with backup processors ready to take over if the main processor fails, and the backup systems often run in parallel so the transition is smooth. If the systems are critical in that their failure would be potentially disastrous (as in aircraft control), incompatible outcomes collected from replicated processes running in parallel on separate machines are resolved by a voting mechanism. Computer scientists are involved in the analysis of such replicated systems, providing theoretical approaches to estimating the reliability achieved by a given configuration and processor parameters, such as average time between failures and average time required to repair the processor. Fault tolerance is also a desirable feature in distributed systems and networks. For example, an advantage of a distributed database is that data replicated on different network hosts can provide a natural backup mechanism when one host fails.
Computational science
Computational science applies computer simulation, scientific visualization, mathematical modeling, algorithms, data structures, networking, database design, symbolic computation, and high-performance computing to help advance the goals of various disciplines. These disciplines include biology, chemistry, fluid dynamics, archaeology, finance, sociology, and forensics. Computational science has evolved rapidly, especially because of the dramatic growth in the volume of data transmitted from scientific instruments. This phenomenon has been called the “big data” problem.
The mathematical methods needed for computational science require the transformation of equations and functions from the continuous to the discrete. For example, the computer integration of a function over an interval is accomplished not by applying integral calculus but rather by approximating the area under the function graph as a sum of the areas obtained from evaluating the function at discrete points. Similarly, the solution of a differential equation is obtained as a sequence of discrete points determined by approximating the true solution curve by a sequence of tangential line segments. When discretized in this way, many problems can be recast as an equation involving a matrix (a rectangular array of numbers) solvable using linear algebra. Numerical analysis is the study of such computational methods. Several factors must be considered when applying numerical methods: (1) the conditions under which the method yields a solution, (2) the accuracy of the solution, (3) whether the solution process is stable (i.e., does not exhibit error growth), and (4) the computational complexity (in the sense described above) of obtaining a solution of the desired accuracy.
The requirements of big-data scientific problems, including the solution of ever larger systems of equations, engage the use of large and powerful arrays of processors (called multiprocessors or supercomputers) that allow many calculations to proceed in parallel by assigning them to separate processing elements. These activities have sparked much interest in parallel computer architecture and algorithms that can be carried out efficiently on such machines.
Graphics and visual computing
Graphics and visual computing is the field that deals with the display and control of images on a computer screen. This field encompasses the efficient implementation of four interrelated computational tasks: rendering, modeling, animation, and visualization. Graphics techniques incorporate principles of linear algebra, numerical integration, computational geometry, special-purpose hardware, file formats, and graphical user interfaces (GUIs) to accomplish these complex tasks.
Applications of graphics include CAD, fine arts, medical imaging, scientific data visualization, and video games. CAD systems allow the computer to be used for designing objects ranging from automobile parts to bridges to computer chips by providing an interactive drawing tool and an engineering interface to simulation and analysis tools. Fine arts applications allow artists to use the computer screen as a medium to create images, cinematographic special effects, animated cartoons, and television commercials. Medical imaging applications involve the visualization of data obtained from technologies such as X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRIs) to assist doctors in diagnosing medical conditions. Scientific visualization uses massive amounts of data to define simulations of scientific phenomena, such as ocean modeling, to produce pictures that provide more insight into the phenomena than would tables of numbers. Graphics also provide realistic visualizations for video gaming, flight simulation, and other representations of reality or fantasy. The term virtual reality has been coined to refer to any interaction with a computer-simulated virtual world.
A challenge for computer graphics is the development of efficient algorithms that manipulate the myriad of lines, triangles, and polygons that make up a computer image. In order for realistic on-screen images to be presented, each object must be rendered as a set of planar units. Edges must be smoothed and textured so that their underlying construction from polygons is not obvious to the naked eye. In many applications, still pictures are inadequate, and rapid display of real-time images is required. Both extremely efficient algorithms and state-of-the-art hardware are needed to accomplish real-time animation.
Human-computer interaction
Human-computer interaction (HCI) is concerned with designing effective interaction between users and computers and the construction of interfaces that support this interaction. HCI occurs at an interface that includes both software and hardware. User interface design impacts the life cycle of software, so it should occur early in the design process. Because user interfaces must accommodate a variety of user styles and capabilities, HCI research draws on several disciplines including psychology, sociology, anthropology, and engineering. In the 1960s, user interfaces consisted of computer consoles that allowed an operator directly to type commands that could be executed immediately or at some future time. With the advent of more user-friendly personal computers in the 1980s, user interfaces became more sophisticated, so that the user could “point and click” to send a command to the operating system.
Thus, the field of HCI emerged to model, develop, and measure the effectiveness of various types of interfaces between a computer application and the person accessing its services. GUIs enable users to communicate with the computer by such simple means as pointing to an icon with a mouse or touching it with a stylus or forefinger. This technology also supports windowing environments on a computer screen, which allow users to work with different applications simultaneously, one in each window.
Information management
Information management (IM) is primarily concerned with the capture, digitization, representation, organization, transformation, and presentation of information. Because a computer’s main memory provides only temporary storage, computers are equipped with auxiliary disk storage devices that permanently store data. These devices are characterized by having much higher capacity than main memory but slower read/write (access) speed. Data stored on a disk must be read into main memory before it can be processed. A major goal of IM systems, therefore, is to develop efficient algorithms to store and retrieve specific data for processing.
IM systems comprise databases and algorithms for the efficient storage, retrieval, updating, and deleting of specific items in the database. The underlying structure of a database is a set of files residing permanently on a disk storage device. Each file can be further broken down into a series of records, which contains individual data items, or fields. Each field gives the value of some property (or attribute) of the entity represented by a record. For example, a personnel file may contain a series of records, one for each individual in the organization, and each record would contain fields that contain that person’s name, address, phone number, e-mail address, and so forth.
Many file systems are sequential, meaning that successive records are processed in the order in which they are stored, starting from the beginning and proceeding to the end. This file structure was particularly popular in the early days of computing, when files were stored on reels of magnetic tape and these reels could be processed only in a sequential manner. Sequential files are generally stored in some sorted order (e.g., alphabetic) for printing of reports (e.g., a telephone directory) and for efficient processing of batches of transactions. Banking transactions (deposits and withdrawals), for instance, might be sorted in the same order as the accounts file, so that as each transaction is read the system need only scan ahead to find the accounts record to which it applies.
With modern storage systems, it is possible to access any data record in a random fashion. To facilitate efficient random access, the data records in a file are stored with indexes called keys. An index of a file is much like an index of a book; it contains a key for each record in the file along with the location where the record is stored. Since indexes might be long, they are usually structured in some hierarchical fashion so that they can be navigated efficiently. The top level of an index, for example, might contain locations of (point to) indexes to items beginning with the letters A, B, etc. The A index itself may contain not locations of data items but pointers to indexes of items beginning with the letters Ab, Ac, and so on. Locating the index for the desired record by traversing a treelike structure is quite efficient.
Many applications require access to many independent files containing related and even overlapping data. Their information management activities frequently require data from several files to be linked, and hence the need for a database model emerges. Historically, three different types of database models have been developed to support the linkage of records of different types: (1) the hierarchical model, in which record types are linked in a treelike structure (e.g., employee records might be grouped under records describing the departments in which employees work), (2) the network model, in which arbitrary linkages of record types may be created (e.g., employee records might be linked on one hand to employees’ departments and on the other hand to their supervisors—that is, other employees), and (3) the relational model, in which all data are represented in simple tabular form.
In the relational model, each individual entry is described by the set of its attribute values (called a relation), stored in one row of the table. This linkage of n attribute values to provide a meaningful description of a real-world entity or a relationship among such entities forms a mathematical n-tuple. The relational model also supports queries (requests for information) that involve several tables by providing automatic linkage across tables by means of a “join” operation that combines records with identical values of common attributes. Payroll data, for example, can be stored in one table and personnel benefits data in another; complete information on an employee could be obtained by joining the two tables using the employee’s unique identification number as a common attribute.
To support database processing, a software artifact known as a database management system (DBMS) is required to manage the data and provide the user with commands to retrieve information from the database. For example, a widely used DBMS that supports the relational model is MySQL.
Another development in database technology is to incorporate the object concept. In object-oriented databases, all data are objects. Objects may be linked together by an “is-part-of” relationship to represent larger, composite objects. Data describing a truck, for instance, may be stored as a composite of a particular engine, chassis, drive train, and so forth. Classes of objects may form a hierarchy in which individual objects may inherit properties from objects farther up in the hierarchy. For example, objects of the class “motorized vehicle” all have an engine; members of the subclasses “truck” or “airplane” will then also have an engine.
NoSQL, or non-relational databases, have also emerged. These databases are different from the classic relational databases because they do not require fixed tables. Many of them are document-oriented databases, in which voice, music, images, and video clips are stored along with traditional textual information. An important subset of NoSQL are the XML databases, which are widely used in the development of Android smartphone and tablet applications.
Data integrity refers to designing a DBMS that ensures the correctness and stability of its data across all applications that access the system. When a database is designed, integrity checking is enabled by specifying the data type of each column in the table. For example, if an identification number is specified to be nine digits, the DBMS will reject an update attempting to assign a value with more or fewer digits or one including an alphabetic character. Another type of integrity, known as referential integrity, requires that each entity referenced by some other entity must itself exist in the database. For example, if an airline reservation is requested for a particular flight number, then the flight referenced by that number must actually exist.
Access to a database by multiple simultaneous users requires that the DBMS include a concurrency control mechanism (called locking) to maintain integrity whenever two different users attempt to access the same data at the same time. For example, two travel agents may try to book the last seat on a plane at more or less the same time. Without concurrency control, both may think they have succeeded, though only one booking is actually entered into the database.
A key concept in studying concurrency control and the maintenance of data integrity is the transaction, defined as an indivisible operation that transforms the database from one state into another. To illustrate, consider an electronic transfer of funds of $5 from bank account A to account B. The operation that deducts $5 from account A leaves the database without integrity since the total over all accounts is $5 short. Similarly, the operation that adds $5 to account B in itself makes the total $5 too much. Combining these two operations into a single transaction, however, maintains data integrity. The key here is to ensure that only complete transactions are applied to the data and that multiple concurrent transactions are executed using locking so that serializing them would produce the same result. A transaction-oriented control mechanism for database access becomes difficult in the case of a long transaction, for example, when several engineers are working, perhaps over the course of several days, on a product design that may not exhibit data integrity until the project is complete.
As mentioned previously, a database may be distributed in that its data can be spread among different host computers on a network. If the distributed data contains duplicates, the concurrency control problem is more complex. Distributed databases must have a distributed DBMS to provide overall control of queries and updates in a manner that does not require that the user know the location of the data. A closely related concept is interoperability, meaning the ability of the user of one member of a group of disparate systems (all having the same functionality) to work with any of the systems of the group with equal ease and via the same interface.
Additional Information:
What is Computer Science?
Computing is part of everything we do. Computing drives innovation in engineering, business, entertainment, education, and the sciences—and it provides solutions to complex, challenging problems of all kinds.
Computer science is the study of computers and computational systems. It is a broad field which includes everything from the algorithms that make up software to how software interacts with hardware to how well software is developed and designed. Computer scientists use various mathematical algorithms, coding procedures, and their expert programming skills to study computer processes and develop new software and systems.
How is Computer Science Different from IT?
Computer science focuses on the development and testing of software and software systems. It involves working with mathematical models, data analysis and security, algorithms, and computational theory. Computer scientists define the computational principles that are the basis of all software.
Information technology (IT) focuses on the development, implementation, support, and management of computers and information systems. IT involves working both with hardware (CPUs, RAM, hard disks) and software (operating systems, web browsers, mobile applications). IT professionals make sure that computers, networks, and systems work well for all users.
What Careers does Computer Science Offer?
Computing jobs are among the highest paid today, and computer science professionals report high job satisfaction. Most computer scientists hold at least a bachelor's degree in computer science or a related field.
Principal areas of study and careers within computer science include artificial intelligence, computer systems and networks, security, database systems, human-computer interaction, vision and graphics, numerical analysis, programming languages, software engineering, bioinformatics, and theory of computing.
Some common job titles for computer scientists include:
* Computer Programmer
* Information Technology Specialist
* Data Scientist
* Web Optimization Specialist
* Database Administrator
* Systems Analyst
* Web Developer
* Quality Assurance Engineer
* Business Intelligence Analyst
* Systems Engineer
* Product Manager
* Software Engineer
* Hardware Engineer
* Front-End Developer
* Back-End Developer
* Full-Stack Developer
* Mobile Developer
* Network Administrator
* Chief Information Officer
* Security Analyst
* Video Game Developer
* Health Information Technician.
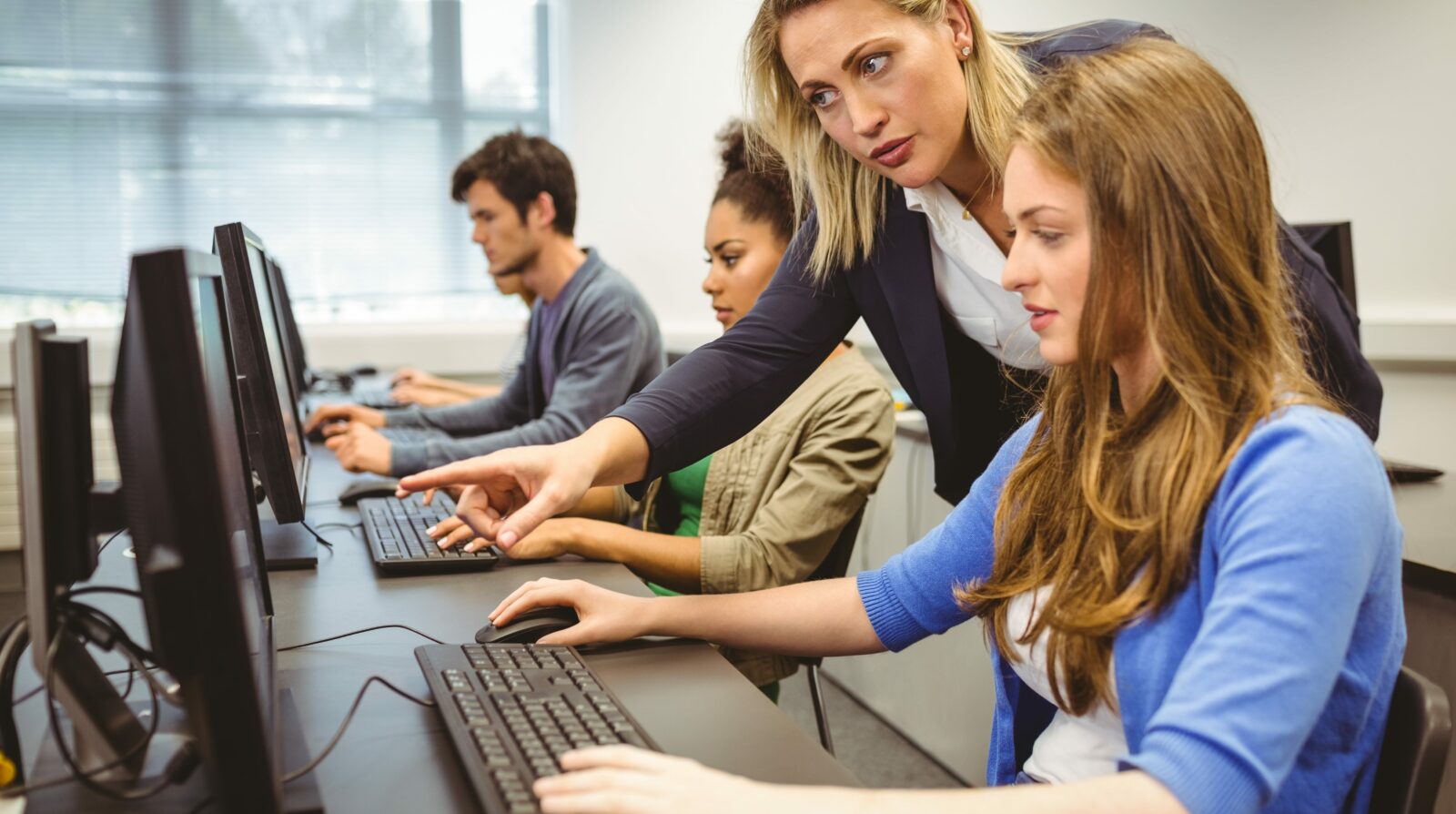

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2387 2024-12-23 00:01:16
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2287) Asia
Gist
Asia is the largest continent on Earth by area and number of people. It is mainly in the northern hemisphere. Asia is connected to Europe in the west and Africa on the south. Sometimes Asia and Europe are combined to form a larger continent called Eurasia. Some of the oldest human civilizations began in Asia, for example Sumer, China, and India. Asia was the birthplace of many religions, for example Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, and Sikhism. It was also home to some large empires, for example the Persian Empire, the Mughal Empire, the Mongol Empire, and the Ming Empire. It is home to at least 44 countries. Georgia, Russia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Turkey, and Greece have territory in both Europe and Asia.
Area:
Geographic area of Asia
Asia includes a large amount of land. Covering about 30% of the world's land area, it has more people than any other continent, with about 60% of the world's total population. Stretching from the icy Arctic in the north to the hot and steamy equatorial lands in the south, Asia contains huge, empty deserts, as well as some of the world's highest mountains and longest rivers.
Asia is surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea, the Arctic Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, and the Indian Ocean. It is separated from Europe by the Pontic Mountains and the Turkish Straits. A long, mainly land border in the west separates Europe and Asia. This line runs north–south down the Ural Mountains in Russia, along the Ural River to the Caspian Sea, and through the Caucasus Mountains to the Black Sea.
Summary
Asia is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilisations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population.
Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe.
Since the concept of Asia derives from the term for the eastern region from a European perspective, Asia is the remaining vast area of Eurasia minus Europe. Therefore, Asia is a region where various independent cultures coexist rather than sharing a single culture, and the boundary between Europe is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural differences, some of which vary on a spectrum.
China and India traded places as the largest economies in the world from 1 to 1800 CE. China was a major economic power for much of recorded history, with the highest GDP per capita until 1500. The Silk Road became the main east–west trading route in the Asian hinterlands while the Straits of Malacca stood as a major sea route. Asia has exhibited economic dynamism as well as robust population growth during the 20th century, but overall population growth has since fallen. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, and many other religions.
Asia varies greatly across and within its regions with regard to ethnic groups, cultures, environments, economics, historical ties, and government systems. It also has a mix of many different climates ranging from the equatorial south via the hot deserts in parts of West Asia, Central Asia and South Asia, temperate areas in the east and the continental centre to vast subarctic and polar areas in North Asia.
Details
Asia is the largest of the world’s continents, covering approximately 30 percent of the Earth’s land area. It is also the world’s most populous continent, with roughly 60 percent of the global population.
Asia's Borders
Asia makes up the eastern portion of the Eurasian supercontinent; Europe occupies the western portion. Asia is bordered by the Arctic, Pacific and Indian oceans, and most geographers define Asia’s western border as an irregular line that follows the Ural Mountains, the Caucasus Mountains, the Caspian Sea and the Black Sea.
While the oceans provide a logical and undisputed border, the boundary between Asia and Europe is the subject of debate, due to both geographical and political factors. There is no clear geological barrier between the continents based on tectonic plates or natural formations. Furthermore, different populations have either emphasized or minimized the idea that Europe and Asia are divided. It is theorized that the names of the continents—Europe and Asia—come from the Mesopotamian words for “sunset” and “sunrise.” As Mesopotamia was located in between modern-day Europe and Asia, it would make sense that they would see the sun rise over Asia and set over Europe and characterize them as two different places.
The term and concept of Eurasia as a single entity became increasingly common after World War I, when Russians living in Eastern Europe used the term to emphasize the connection between the two continents and build camaraderie and a sense of a common culture among peoples of the far-flung land. Today, the concept of Eurasia as an interconnected supercontinent is important to political relationships among Russia, China, and countries that straddle Europe and Asia, such as Kazakhstan. While geographers have established a clearly defined border between Europe and Asia, it is perhaps best understood as a geopolitical concept with varying and sometimes contradictory interpretations.
Physical Regions
Asia can be divided into five major physical regions: mountain systems; plateaus; plains, steppes and deserts; freshwater environments; and saltwater environments.
Mountain Systems
The Himalaya mountains extend for about 2,500 kilometers (1,550 miles) and separate the Indian subcontinent from the rest of Asia. The Indian subcontinent, once connected to Africa, collided with the Eurasian continent about 50 million to 55 million years ago, forming the Himalayas. The Indian subcontinent is still crashing northward into Asia, and the Himalayas are growing every year.
The Himalayas are important to the culture and spirituality of the communities living there. For instance, Mount Kailash is a significant holy site for both Tibetan Buddhists and Hindus. Historically, religious pilgrims have climbed the mountain as a step on the path to enlightenment.
The Himalayas cover more than 612,000 square kilometers (236,000 square miles), passing through the northern states of India and making up most of the terrain of Nepal and Bhutan. The Himalayas are so vast that they are composed of three different mountain belts. The northernmost belt, known as the Great Himalayas, has the highest average elevation at 6,096 meters (20,000 feet). The belt contains nine of the highest peaks in the world, which all reach more than 7,925 meters (26,000 feet) tall. This belt includes the highest mountain summit in the world. Coined Mount Everest by British colonizers, the mountain soars to a height of approximately 8,850 meters (29,035 feet). Indigenous groups have various names for this giant: the Tibetan people call it Chomolungma, or “Goddess Mother of the Earth”; the Nepalese call it Sagarmatha, which is a word related to the sky; and the Chinese call it Qomolangma Feng, combining the Tibetan name with the Chinese word for "peak" or "summit."
The Tien Shan mountain system stretches for about 2,400 kilometers (1,500 miles), straddling the border between Kyrgyzstan and China. The name Tien Shan means “Celestial Mountains” in Chinese. The two highest peaks in the Tien Shan are Victory Peak, which stands at 7,439 meters (24,406 feet), and Khan Tängiri Peak, which stands at 6,995 meters (22,949 feet). Tien Shan also has more than 10,100 square kilometers (3,900 square miles) of glaciers. The largest glacier is Engil'chek Glacier at about 60 kilometers (37 miles) long. The Silk Road, which was a trade network that connected Europe with points farther east in Asia, went through the Tien Shan mountains, making the region important to cultural exchange and development among diverse peoples across the supercontinent.
The Ural Mountains run for approximately 2,500 kilometers (1,550 miles) in an indirect north-south line from Russia to Kazakhstan. The Urals are some of the world’s oldest mountains, dating back some 250 million to 300 million years. Millions of years of erosion have lowered the mountains significantly, and today their average elevation is between 914 and 1,220 meters (3,000 to 4,000 feet). The highest peak is Mount Narodnaya at 1,895 meters (6,217 feet).
Plateaus
Asia is home to many plateaus, which are areas of relatively level high ground. The Iranian plateau encompasses most of Iran, Afghanistan and Pakistan. The plateau is not uniformly flat, as it contains some high mountains and low river basins. The highest mountain peak is Damavand volcano. The plateau also has two large deserts, the Dasht-e Kavir and Dasht-e Lut.
The Deccan Plateau makes up most of the southern part of India. The plateau’s average elevation is about 600 meters (2,000 feet). It is bordered by three mountain ranges: the Satpura Range in the north and the Eastern and Western Ghats on either side. The plateau and its main waterways—the Godavari and Krishna rivers—gently slope toward the Eastern Ghats and the Bay of Bengal. The Deccan Plateau is home to Hindu, Muslim and Jain communities. Many temples and mosques dedicated to the three religions are hundreds of years old.
The Tibetan Plateau is usually considered the largest and highest area ever to exist in Earth's history. Known as the “Rooftop of the World,” the plateau covers an area about half the size of the contiguous United States and averages more than 4,500 meters (14,764 feet) above sea level. The Tibetan Plateau is extremely important to the world’s water cycle because of its tremendous number of glaciers. These glaciers contain the largest volume of ice outside the poles. The ice and snow from these glaciers feed Asia’s largest rivers. Approximately 2 billion people depend on the rivers fed by the plateau’s glaciers. The Tibetan Plateau is also a significant cultural region known for textiles and other traditional artisanal crafts. Thangkas, or scrolls with paintings depicting Buddhist teachings, were developed there, and their portable nature meant they were carried by traders to faraway lands, thereby facilitating the spread of Buddhism.
Plains, Steppes and Deserts
The West Siberian Plain, located in central Russia, is considered one of the world’s largest areas of continuous flatland. It extends from north to south about 2,400 kilometers (1,500 miles) and from west to east about 1,900 kilometers (1,200 miles). With more than 50 percent of its area at less than 100 meters (330 feet) above sea level, the plain contains some of the world’s largest swamps and flood plains. Nomadic communities in this area traditionally herded reindeer, and reindeer continue to provide livelihood for significant numbers of people there today.
Central Asia is dominated by a steppe landscape, a large area of flat, unforested grassland. Mongolia can be divided into different steppe zones: the mountain forest steppe, the arid steppe and the desert steppe. These zones transition from the country’s mountainous region in the north to the Gobi Desert on the southern border with China.
The Rub’ al Khali desert, considered the world’s largest sand sea, covers an area larger than France across Saudi Arabia, Oman, the United Arab Emirates and Yemen. The desert is known as the Empty Quarter because it is virtually inhospitable to humans except for Bedouin tribes that live on its edges. Scientists have found archaeological remains that date back to the prehistoric era, suggesting that there is still much to learn about the history of this desert.
Freshwater
Lake Baikal, located in southern Russia, is the deepest lake in the world, reaching a depth of 1,620 meters (5,315 feet). The lake contains 20 percent of the world’s unfrozen fresh water, making it the largest reservoir on Earth. It is also the world’s oldest lake at 25 million years old.
The Yangtze is the longest river in Asia and the third longest in the world (behind the Amazon of South America and the Nile of Africa). Reaching 6,300 kilometers (3,915 miles) in length, the Yangtze moves east from the glaciers of the Tibetan Plateau to the river’s mouth on the East China Sea. The Yangtze is considered the lifeblood of China. It drains one-fifth of the country’s land area, is home to one-third of its population and contributes greatly to China’s economy. It is also considered a major cultural hub of China, with 42 World Cultural Heritage sites along its banks, including 465 additional significant traditional sites and 91 museums.
The Tigris and Euphrates rivers begin in the highlands of eastern Turkey and flow through Syria and Iraq, converging in the city of Qurna, Iraq, before emptying into the Persian Gulf. The land between the two rivers, known as Mesopotamia, was the cradle of early civilizations, including Sumer and the Akkadian Empire. Today, the Tigris-Euphrates river system is under threat from increased agricultural and industrial use, including the construction of dams to produce hydroelectric power. These pressures have caused desertification and increased the level of salinity in the soil, severely damaging local watershed habitats and threatening local cultures that have developed along the rivers’ banks. For example, the local Kurdish community unsuccessfully fought the construction of Turkey’s Ilisu Dam, which contributed to flooding of culturally and historically important lands, including the ancient city of Hasankeyf.
Saltwater
The Persian Gulf has an area of more than 234,000 square kilometers (90,000 square miles). It borders Iran, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Bahrain, Kuwait and Iraq. The gulf is subject to high rates of evaporation, making it shallow and extremely salty. The seabed beneath the Persian Gulf contains an estimated 50 percent of the world’s oil reserves. Domestic and foreign interest in these reserves, particularly by oil-dependent countries, such as the United States and China, has contributed to war and political instability.
The Sea of Okhotsk covers 1.5 million square kilometers (611,000 square miles) between the Russian mainland and the Kamchatka Peninsula. The sea is largely frozen between October and March. Large ice floes make winter navigation almost impossible.
The Bay of Bengal is the largest bay in the world, covering almost 2.2 million square kilometers (839,000 square miles) and bordering Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka and Burma. Many large rivers, including the Ganges and Brahmaputra, empty into the bay. The briny wetlands formed by the Ganges-Brahmaputra on the Bay of Bengal is the largest delta in the world. The Ganges River, which empties into the Bay of Bengal, is a sacred site for Hindus, who purify themselves spiritually by bathing in its waters.
Terrestrial Flora and Fauna
China has diverse landscapes, from the arid Gobi Desert to the tropical rain forests of Yunnan Province. From roses to peonies, many familiar flowers most likely originated in northern China, as did such fruit trees as peaches and oranges. China is also home to the dawn redwood, the only redwood tree found outside North America.
Asia’s diverse physical and cultural landscape has dictated the way animals have been domesticated. In the Himalayas, communities use yaks as beasts of burden. Yaks are large animals related to cattle, but with a thick fiber coat and the ability to survive in the oxygen-poor high altitude of the mountains. Yaks are not only used for transportation and for pulling plows; their coats are sources of warm, hardy fiber, and yak milk is used for butter and cheese. Om Katel, a National Geographic Explorer, studies the intersection between traditional livestock care, the effects of climate change and other issues concerning animals in the Himalayas.
In the Mongolian steppe, the two-humped Bactrian camel is the traditional beast of burden. The camel’s humps store nutrient-rich fat, which the animal can use in times of drought, heat or frost. Its size and ability to adapt to hardship make it an ideal pack animal. Bactrians can actually outrun horses over long distances. These camels were the traditional animals used in caravans on the Silk Road, the legendary trade route linking eastern Asia with India and the Middle East. Today, Bactrian camels are critically endangered in the wild.
Aquatic Flora and Fauna
The freshwater and marine habitats of Asia offer incredible biodiversity.
Lake Baikal’s age and isolation make it a unique biological site. Aquatic life has been able to evolve for millions of years relatively undisturbed, producing a rich variety of flora and fauna. The lake is known as the “Galápagos of Russia” because of its importance to the study of evolutionary science. It has 1,340 species of animals and 570 species of plants.
Hundreds of Lake Baikal’s species are endemic, meaning they are found nowhere else on Earth. The Baikal seal, for instance, is one of the few freshwater seal species in the world. The Baikal seal feeds primarily on the Baikal oil fish and the omul. Both fishes are similar to salmon and provide fisheries for the communities on the lake.
The Bay of Bengal, on the Indian Ocean, is one of the world’s largest tropical marine ecosystems. The bay is home to dozens of marine mammals, including the bottlenose dolphin, spinner dolphin, spotted dolphin and Bryde’s whale. The bay also supports healthy tuna, jack and marlin fisheries.
Some of the bay’s most diverse array of organisms exist along its coasts and wetlands. Many wildlife reserves in and around the bay aim to protect its biological diversity.
The Sundarbans is a wetland area that forms at the delta of the Ganges and Brahamaputra rivers. The Sundarbans is a huge mangrove forest. Mangroves are hardy trees that are able to withstand the powerful, salty tides of the Bay of Bengal, as well as the freshwater flows from the Ganges and Brahamaputra. In addition to mangroves, the Sundarbans is forested by palm trees and swamp grasses.
The swampy jungle of the Sundarbans supports a rich animal community. Hundreds of species of fish, shrimp, crabs and snails live in the exposed root system of the mangrove trees. The Sundarbans supports more than 200 species of aquatic and wading birds. These small animals are part of a food web that includes wild boar, macaque monkeys, monitor lizards and a healthy population of Bengal tigers.
Additional Information
Asia, the world’s largest and most diverse continent. It occupies the eastern four-fifths of the giant Eurasian landmass. Asia is more a geographic term than a homogeneous continent, and the use of the term to describe such a vast area always carries the potential of obscuring the enormous diversity among the regions it encompasses. Asia has both the highest and the lowest points on the surface of Earth, has the longest coastline of any continent, is subject overall to the world’s widest climatic extremes, and, consequently, produces the most varied forms of vegetation and animal life on Earth. In addition, the peoples of Asia have established the broadest variety of human adaptation found on any of the continents.
The name Asia is ancient, and its origin has been variously explained. The Greeks used it to designate the lands situated to the east of their homeland. It is believed that the name may be derived from the Assyrian word asu, meaning “east.” Another possible explanation is that it was originally a local name given to the plains of Ephesus, which ancient Greeks and Romans extended to refer first to Anatolia (contemporary Asia Minor, which is the western extreme of mainland Asia), and then to the known world east of the Mediterranean Sea. When Western explorers reached South and East Asia in early modern times, they extended that label to the whole of the immense landmass.
Asia is bounded by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Indian Ocean to the south, the Red Sea (as well as the inland seas of the Atlantic Ocean—the Mediterranean and the Black) to the southwest, and Europe to the west. Asia is separated from North America to the northeast by the Bering Strait and from Australia to the southeast by the seas and straits connecting the Indian and Pacific oceans. The Isthmus of Suez unites Asia with Africa, and it is generally agreed that the Suez Canal forms the border between them. Two narrow straits, the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, separate Anatolia from the Balkan Peninsula.
The land boundary between Asia and Europe is a historical and cultural construct that has been defined variously; only as a matter of agreement is it tied to a specific borderline. The most convenient geographic boundary—one that has been adopted by most geographers—is a line that runs south from the Arctic Ocean along the Ural Mountains and then turns southwest along the Emba River to the northern shore of the Caspian Sea; west of the Caspian, the boundary follows the Kuma-Manych Depression to the Sea of Azov and the Kerch Strait of the Black Sea. Thus, the isthmus between the Black and Caspian seas, which culminates in the Caucasus mountain range to the south, is part of Asia.
The total area of Asia, including Asian Russia (with the Caucasian isthmus) but excluding the island of New Guinea, amounts to some 17,226,200 square miles (44,614,000 square km), roughly one-third of the land surface of Earth. The islands—including Taiwan, those of Japan and Indonesia, Sakhalin and other islands of Asian Russia, Sri Lanka, Cyprus, and numerous smaller islands—together constitute 1,240,000 square miles (3,210,000 square km), about 7 percent of the total. (Although New Guinea is mentioned occasionally in this article, it generally is not considered a part of Asia.) The farthest terminal points of the Asian mainland are Cape Chelyuskin in north-central Siberia, Russia (77°43′ N), to the north; the tip of the Malay Peninsula, Cape Piai, or Bulus (1°16′ N), to the south; Cape Baba in Turkey (26°4′ E) to the west; and Cape Dezhnev (Dezhnyov), or East Cape (169°40′ W), in northeastern Siberia, overlooking the Bering Strait, to the east.
Asia has the highest average elevation of the continents and contains the greatest relative relief. The tallest peak in the world, Mount Everest, which reaches an elevation of 29,035 feet (8,850 metres; see Researcher’s Note: Height of Mount Everest); the lowest place on Earth’s land surface, the Dead Sea, measured in the mid-2010s at about 1,410 feet (430 metres) below sea level; and the world’s deepest continental trough, occupied by Lake Baikal, which is 5,315 feet (1,620 metres) deep and whose bottom lies 3,822 feet (1,165 metres) below sea level, are all located in Asia. Those physiographic extremes and the overall predominance of mountain belts and plateaus are the result of the collision of tectonic plates. In geologic terms, Asia comprises several very ancient continental platforms and other blocks of land that merged over the eons. Most of those units had coalesced as a continental landmass by about 160 million years ago, when the core of the Indian subcontinent broke off from Africa and began drifting northeastward to collide with the southern flank of Asia about 50 million to 40 million years ago. The northeastward movement of the subcontinent continues at about 2.4 inches (6 cm) per year. The impact and pressure continue to raise the Plateau of Tibet and the Himalayas.
Asia’s coastline—some 39,000 miles (62,800 km) in length—is, variously, high and mountainous, low and alluvial, terraced as a result of the land’s having been uplifted, or “drowned” where the land has subsided. The specific features of the coastline in some areas—especially in the east and southeast—are the result of active volcanism; thermal abrasion of permafrost (caused by a combination of the action of breaking waves and thawing), as in northeastern Siberia; and coral growth, as in the areas to the south and southeast. Accreting sandy beaches also occur in many areas, such as along the Bay of Bengal and the Gulf of Thailand.
The mountain systems of Central Asia not only have provided the continent’s great rivers with water from their melting snows but also have formed a forbidding natural barrier that has influenced the movement of peoples in the area. Migration across those barriers has been possible only through mountain passes. A historical movement of population from the arid zones of Central Asia has followed the mountain passes into the Indian subcontinent. More recent migrations have originated in China, with destinations throughout Southeast Asia. The Korean and Japanese peoples and, to a lesser extent, the Chinese have remained ethnically more homogeneous than the populations of other Asian countries.
Asia’s population is unevenly distributed, mainly because of climatic factors. There is a concentration of population in western Asia as well as great concentrations in the Indian subcontinent and the eastern half of China. There are also appreciable concentrations in the Pacific borderlands and on the islands, but vast areas of Central and North Asia—whose forbidding climates limit agricultural productivity—have remained sparsely populated. Nonetheless, Asia, the most populous of the continents, contains some three-fifths of the world’s people.
Asia is the birthplace of all the world’s major religions—Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism—and of many minor ones. Of those, only Christianity developed primarily outside of Asia; it exerts little influence on the continent, though many Asian countries have Christian minorities. Buddhism has had a greater impact outside its birthplace in India and is prevalent in various forms in China, South Korea, Japan, the Southeast Asian countries, and Sri Lanka. Islam has spread out of Arabia eastward to South and Southeast Asia. Hinduism has been mostly confined to the Indian subcontinent.
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2388 2024-12-23 21:38:18
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2288) Europe
Gist
Europe encompasses an area of 10,180,000km² (3,930,000 square miles), stretching from Asia to the Atlantic and from the Mediterranean to the Arctic. European countries welcome more than 480 million international visitors per year, more than half of the global market, and 7 of the 10 most visited countries are European nations.
It's easy to see why - a well preserved cultural heritage, open borders and efficient infrastructure makes visiting Europe a breeze, and rarely will you have to travel more than a few hours before you can immerse yourself in a new culture, and dive into a different phrasebook. Although it is the world's smallest continent in land surface area, there are profound differences between the cultures and ways of life in its countries.
The eastern border of Europe, for instance, is not well defined. The Caucasus states of Armenia and Georgia are sometimes considered part of Asia due to geography, and much of Russia and almost all of Ukraine are geographically Asian. The UK, Ireland and Iceland all manage to sneak in.
Must-visits include France, Italy, Germany, Spain, and the United Kingdom. Don't let your sense of adventure fail you by missing out on Scandinavia, Greece, Cyprus, Hungary, Austria, the Czech Republic, Poland, Portugal, or the microstates of Andorra, Liechtenstein and Luxembourg. For a more exotic European adventure, be sure to tour the Balkans.
Many European countries are members of the European Union (EU), which has its own currency (the Euro) and laws. There are no border controls between signatory countries of the Schengen Agreement (only at the outside borders). Note that not all EU members adopted the Schengen Agreement (open borders) or the Euro, and not all countries that adopted Schengen or Euro are European Union members.
Summary
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe shares the landmass of Eurasia with Asia, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea, and the waterway of the Bosporus Strait.
Europe covers approx. 10,186,000 square kilometres (3,933,000 sq mi), or 2% of Earth's surface (6.8% of Earth's land area), making it the second-smallest continent (using the seven-continent model). Politically, Europe is divided into about fifty sovereign states, of which Russia is the largest and most populous, spanning 39% of the continent and comprising 15% of its population. Europe had a total population of about 745 million (about 10% of the world population) in 2021; the third-largest after Asia and Africa. The European climate is affected by warm Atlantic currents, such as the Gulf Stream, which produce a temperate climate, tempering winters and summers, on much of the continent. Further from the sea, seasonal differences are more noticeable producing more continental climates.
The culture of Europe consists of a range of national and regional cultures, which form the central roots of the wider Western civilisation, and together commonly reference ancient Greece and ancient Rome, particularly through their Christian successors, as crucial and shared roots. Beginning with the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 CE, Christian consolidation of Europe in the wake of the Migration Period marked the European post-classical Middle Ages. The Italian Renaissance spread in the continent a new humanist interest in art and science which led to the modern era. Since the Age of Discovery, led by Spain and Portugal, Europe played a predominant role in global affairs with multiple explorations and conquests around the world. Between the 16th and 20th centuries, European powers colonised at various times the Americas, almost all of Africa and Oceania, and the majority of Asia.
The Age of Enlightenment, the French Revolution, and the Napoleonic Wars shaped the continent culturally, politically, and economically from the end of the 17th century until the first half of the 19th century. The Industrial Revolution, which began in Great Britain at the end of the 18th century, gave rise to radical economic, cultural, and social change in Western Europe and eventually the wider world. Both world wars began and were fought to a great extent in Europe, contributing to a decline in Western European dominance in world affairs by the mid-20th century as the Soviet Union and the United States took prominence and competed over dominance in Europe and globally. The resulting Cold War divided Europe along the Iron Curtain, with NATO in the West and the Warsaw Pact in the East. This divide ended with the Revolutions of 1989, the fall of the Berlin Wall, and the dissolution of the Soviet Union, which allowed European integration to advance significantly.
European integration is being advanced institutionally since 1948 with the founding of the Council of Europe, and significantly through the realisation of the European Union (EU), which represents today the majority of Europe. The European Union is a supranational political entity that lies between a confederation and a federation and is based on a system of European treaties. The EU originated in Western Europe but has been expanding eastward since the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. A majority of its members have adopted a common currency, the euro, and participate in the European single market and a customs union. A large bloc of countries, the Schengen Area, have also abolished internal border and immigration controls. Regular popular elections take place every five years within the EU; they are considered to be the second-largest democratic elections in the world after India's. The EU is the third-largest economy in the world.
Details
Europe, second smallest of the world’s continents, composed of the westward-projecting peninsulas of Eurasia (the great landmass that it shares with Asia) and occupying nearly one-fifteenth of the world’s total land area. It is bordered on the north by the Arctic Ocean, on the west by the Atlantic Ocean, and on the south (west to east) by the Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea, the Kuma-Manych Depression, and the Caspian Sea. The continent’s eastern boundary (north to south) runs along the Ural Mountains and then roughly southwest along the Emba (Zhem) River, terminating at the northern Caspian coast.
Europe’s largest islands and archipelagoes include Novaya Zemlya, Franz Josef Land, Svalbard, Iceland, the Faroe Islands, the British Isles, the Balearic Islands, Corsica, Sardinia, Sicily, Malta, Crete, and Cyprus. Its major peninsulas include Jutland and the Scandinavian, Iberian, Italian, and Balkan peninsulas. Indented by numerous bays, fjords, and seas, continental Europe’s highly irregular coastline is about 24,000 miles (38,000 km) long.
Among the continents, Europe is an anomaly. Larger only than Australia, it is a small appendage of Eurasia. Yet the peninsular and insular western extremity of the continent, thrusting toward the North Atlantic Ocean, provides—thanks to its latitude and its physical geography—a relatively genial human habitat, and the long processes of human history came to mark off the region as the home of a distinctive civilization. In spite of its internal diversity, Europe has thus functioned, from the time it first emerged in the human consciousness, as a world apart, concentrating—to borrow a phrase from Christopher Marlowe—“infinite riches in a little room.”
As a conceptual construct, Europa, as the more learned of the ancient Greeks first conceived it, stood in sharp contrast to both Asia and Libya, the name then applied to the known northern part of Africa. Literally, Europa is now thought to have meant “Mainland,” rather than the earlier interpretation, “Sunset.” It appears to have suggested itself to the Greeks, in their maritime world, as an appropriate designation for the extensive northerly lands that lay beyond, lands with characteristics vaguely known yet clearly different from those inherent in the concepts of Asia and Libya—both of which, relatively prosperous and civilized, were associated closely with the culture of the Greeks and their predecessors. From the Greek perspective then, Europa was culturally backward and scantily settled. It was a barbarian world—that is, a non-Greek one, with its inhabitants making “bar-bar” noises in unintelligible tongues. Traders and travelers also reported that the Europe beyond Greece possessed distinctive physical units, with mountain systems and lowland river basins much larger than those familiar to inhabitants of the Mediterranean region. It was clear as well that a succession of climates, markedly different from those of the Mediterranean borderlands, were to be experienced as Europe was penetrated from the south. The spacious eastern steppes and, to the west and north, primeval forests as yet only marginally touched by human occupancy further underlined environmental contrasts.
The empire of ancient Rome, at its greatest extent in the 2nd century ce, revealed, and imprinted its culture on, much of the face of the continent. Trade relations beyond its frontiers also drew the remoter regions into its sphere. Yet it was not until the 19th and 20th centuries that modern science was able to draw with some precision the geologic and geographic lineaments of the European continent, the peoples of which had meanwhile achieved domination over—and set in motion vast countervailing movements among—the inhabitants of much of the rest of the globe.
As to the territorial limits of Europe, they may seem relatively clear on its seaward flanks, but many island groups far to the north and west—Svalbard, the Faroes, Iceland, and the Madeira and Canary islands—are considered European, while Greenland (though tied politically to Denmark) is conventionally allocated to North America. Furthermore, the Mediterranean coastlands of North Africa and southwestern Asia also exhibit some European physical and cultural affinities. Turkey and Cyprus in particular, while geologically Asian, possess elements of European culture and may be regarded as parts of Europe. Indeed, Turkey has sought membership in the European Union (EU), and the Republic of Cyprus joined the organization in 2004.
Europe’s boundaries have been especially uncertain, and hence much debated, on the east, where the continent merges, without sundering physical boundaries, with parts of western Asia. The eastward limits now adopted by most geographers exclude the Caucasus region and encompass a small portion of Kazakhstan, where the European boundary formed by the northern Caspian coast is connected to that of the Urals by Kazakhstan’s Emba River and Mughalzhar (Mugodzhar) Hills, themselves a southern extension of the Urals. Among the alternative boundaries proposed by geographers that have gained wide acceptance is a scheme that sees the crest of the Greater Caucasus range as the dividing line between Europe and Asia, placing Ciscaucasia, the northern part of the Caucasus region, in Europe and Transcaucasia, the southern part, in Asia. Another widely endorsed scheme puts the western portion of the Caucasus region in Europe and the eastern part—that is, the bulk of Azerbaijan and small portions of Armenia, Georgia, and Russia’s Caspian Sea coast—in Asia. Still another scheme with many adherents locates the continental boundary along the Aras River and the Turkish border, thereby putting Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia in Europe.
Europe’s eastern boundary, however, is not a cultural, political, or economic discontinuity on the land comparable, for example, to the insulating significance of the Himalayas, which clearly mark a northern limit to South Asian civilization. Inhabited plains, with only the minor interruption of the worn-down Urals, extend from central Europe to the Yenisey River in central Siberia. Slavic-based civilization dominates much of the territory occupied by the former Soviet Union from the Baltic and Black seas to the Pacific Ocean. That civilization is distinguished from the rest of Europe by legacies of a medieval Mongol-Tatar domination that precluded the sharing of many of the innovations and developments of European “Western civilization”; it became further distinctive during the relative isolation of the Soviet period. In partitioning the globe into meaningful large geographic units, therefore, most modern geographers treated the former Soviet Union as a distinct territorial entity, comparable to a continent, that was somewhat separate from Europe to the west and from Asia to the south and east; that distinction has been maintained for Russia, which constituted three-fourths of the Soviet Union.
Europe occupies some 4 million square miles (10 million square km) within the conventional borders assigned to it. That broad territory reveals no simple unity of geologic structure, landform, relief, or climate. Rocks of all geologic periods are exposed, and the operation of geologic forces during an immense succession of eras has contributed to the molding of the landscapes of mountain, plateau, and lowland and has bequeathed a variety of mineral reserves. Glaciation too has left its mark over wide areas, and the processes of erosion and deposition have created a highly variegated and compartmentalized countryside. Climatically, Europe benefits by having only a small proportion of its surface either too cold or too hot and dry for effective settlement and use. Regional climatic contrasts nevertheless exist: oceanic, Mediterranean, and continental types occur widely, as do gradations from one to the other. Associated vegetation and soil forms also show continual variety, but only portions of the dominant woodland that clothed most of the continent when humans first appeared now remain.
European Parliament
All in all, Europe enjoys a considerable and long-exploited resource base of soil, forest, sea, and minerals (notably coal), but its people are increasingly its principal resource. The continent, excluding Russia, contains less than one-tenth of the total population of the world, but in general its people are well educated and highly skilled. Europe also supports high densities of population, concentrated in urban-industrial regions. A growing percentage of people in urban areas are employed in a wide range of service activities, which have come to dominate the economies of most countries. Nonetheless, in manufacturing and agriculture Europe still occupies an eminent, if no longer necessarily predominant, position. The creation of the European Economic Community in 1957 and the EU in 1993 greatly enhanced economic cooperation between many of the continent’s countries. Europe’s continuing economic achievements are evidenced by its high standard of living and its successes in science, technology, and the arts.
Additional Information:
Some Facts about Europe
Europe is the second-smallest continent, and it could be described as a large peninsula or as a subcontinent. Europe is the western portion of the Eurasian landmass and is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere. Several larger islands belong to Europe, such as Iceland or the British Isles with the UK and Ireland.
Area
With an area of 10.2 million km² (3,938,000 sq mi), Europe is 20% larger than the contiguous United States. The European Union has an area (without the UK) of over 4.23 million km² (1.6 million sq mi).
How many countries are there in Europe?
Europe is shared by 50 countries. By the conventional definition, there are 44 sovereign states or nations in Europe. Not included are several countries namely Turkey, which occupies only a small part of East Thrace on the European Balkan Peninsula.
Cyprus, an island in the Mediterranean Sea, is geographically part of Asia Minor (Middle East).
The Faroe Islands, an island group between the Norwegian Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean are a self-governing territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
Greenland, which geographically belongs to North America, is as well an autonomous Danish territory.
Kosovo is a partially recognized state in the Balkans.
A small piece of Western Kazakhstan is also considered to be part of Europe.
Population
An estimated 747 million people live in Europe. The most populous country in Europe is the European part of Russia with a population of 110 million people, followed by Germany with 83 million citizens, and Metropolitan France with 67 million inhabitants (in 2020).
Some Facts about Europe:
How many countries are there in Europe?
View of the Mont Blanc massif. The Mont Blanc at 4,808.7 m (15,777 ft), is the highest mountain in Western Europe.
Highest Point
With a height of 5,642 m, Mount Elbrus is Europe's highest mountain. The dormant volcano lies in the Caucasus Mountains in southern Russia.
Mont Blanc at 4,808 m is the highest mountain in Western Europe and the highest peak of the Alps.
Largest Lakes
Lake Lagoda northeast of St Petersburg in Russia is the largest lake entirely in Europe with a surface area of 17,700 km². Lake Onega located northeast of Lake Lagoda in European Russia has a surface area of 9,700 km². Other major lakes are Lake Vänern in Sweden (largest lake in Western Europe) and Lake Saimaa in Finland.
Lake Balaton in Hungary is the largest lake in Central Europe with a surface area of 592 km².
Longest River
Europe's longest river is the Volga with a length of 3,530 km (2,190 mi); the river's catchment area is almost entirely inside Russia. The river flows into the Caspian Sea.
The second-longest river in Europe is the Danube with a length of 2,850 km (1,770 mi), the longest river in the European Union region flows through ten countries and empties into the Black Sea.
Major Geographical Regions of Europe
Major geographical regions in Europe are Scandinavia and the Scandinavian Peninsula, the Baltic Sea, the North Sea, the British Isles, the Great European Plain, the Central European Uplands, the Alps, the Mediterranean, the Italian Peninsula and the Apennine Mountains, the Iberian Peninsula, the Pyrenees, the Balkans and the Balkan Peninsula, the Black Sea and the Caucasus.
Languages of Europe
Major languages of Europe are English, French, German, Greek, Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, Nordic Languages, and East European languages.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2389 2024-12-24 00:06:49
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2289) Teacher
Gist
A teacher is a great listener of knowledge, prosperity, and light, from which we can benefit greatly throughout our life. Every teacher helps their students in choosing their path. Teachers teach their students how to respect elders. They tell their students the difference between respect and insult and many more.
Teachers are important because they change lives, inspire dreams, and push the limits of human potential. A teacher's job is to nurture, teach, and raise children to become useful to society. Teachers' role in the classroom, society, and the world at large has taken a different turn from what it was back in the day.
A teacher, also called a schoolteacher or formally an educator, is a person who helps students to acquire knowledge, competence, or virtue, via the practice of teaching.
Summary
Teaching is the profession of those who give instruction, especially in an elementary school or a secondary school or in a university.
Measured in terms of its members, teaching is the world’s largest profession. In the 21st century it was estimated that there were about 80 million teachers throughout the world. Though their roles and functions vary from country to country, the variations among teachers are generally greater within a country than they are between countries. Because the nature of the activities that constitute teaching depends more on the age of the persons being taught than on any other one thing, it is useful to recognize three subgroups of teachers: primary-school, or elementary-school, teachers; secondary-school teachers; and university teachers. Elementary-school teachers are by far the most numerous worldwide, making up nearly half of all teachers in some developed countries and three-fourths or more in developing countries. Teachers at the university level are the smallest group.
The entire teaching corps, wherever its members may be located, shares most of the criteria of a profession, namely (1) a process of formal training, (2) a body of specialized knowledge, (3) a procedure for certifying, or validating, membership in the profession, and (4) a set of standards of performance—intellectual, practical, and ethical—that is defined and enforced by members of the profession. Teaching young children and even adolescents could hardly have been called a profession anywhere in the world before the 20th century. It was instead an art or a craft in which the relatively young and untrained women and men who held most of the teaching positions “kept school” or “heard lessons” because they had been better-than-average pupils themselves. They had learned the art solely by observing and imitating their own teachers. Only university professors and possibly a few teachers of elite secondary schools would have merited being called members of a profession in the sense that medical doctors, lawyers, or priests were professionals; in some countries even today primary-school teachers may accurately be described as semiprofessionals. The dividing line is imprecise. It is useful, therefore, to consider the following questions: (1) What is the status of the profession? (2) What kinds of work are done? (3) How is the profession organized?
Details
A teacher, also called a schoolteacher or formally an educator, is a person who helps students to acquire knowledge, competence, or virtue, via the practice of teaching.
Informally the role of teacher may be taken on by anyone (e.g. when showing a colleague how to perform a specific task). In some countries, teaching young people of school age may be carried out in an informal setting, such as within the family (homeschooling), rather than in a formal setting such as a school or college. Some other professions may involve a significant amount of teaching (e.g. youth worker, pastor).
In most countries, formal teaching of students is usually carried out by paid professional teachers. This article focuses on those who are employed, as their main role, to teach others in a formal education context, such as at a school or other place of initial formal education or training.
Duties and functions
A teacher's role may vary among cultures.
Teachers may provide instruction in literacy and numeracy, craftsmanship or vocational training, the arts, religion, civics, community roles, or life skills.
Formal teaching tasks include preparing lessons according to agreed curricula, giving lessons, and assessing pupil progress.
A teacher's professional duties may extend beyond formal teaching. Outside of the classroom teachers may accompany students on field trips, supervise study halls, help with the organization of school functions, and serve as supervisors for extracurricular activities. They also have the legal duty to protect students from harm, such as that which may result from bullying, sexual harassment, racism or abuse. In some education systems, teachers may be responsible for student discipline.
Competences and qualities required by teachers
Teaching is a highly complex activity. This is partially because teaching is a social practice, that takes place in a specific context (time, place, culture, socioeconomic situation etc.) and therefore is shaped by the values of that specific context. Factors that influence what is expected (or required) of teachers include history and tradition, social views about the purpose of education, accepted theories about learning, etc.
Competences
The competences required by a teacher are affected by the different ways in which the role is understood around the world. Broadly, there seem to be four models:
* the teacher as manager of instruction;
* the teacher as caring person;
* the teacher as expert learner; and
* the teacher as cultural and civic person.
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development has argued that it is necessary to develop a shared definition of the skills and knowledge required by teachers, in order to guide teachers' career-long education and professional development. Some evidence-based international discussions have tried to reach such a common understanding. For example, the European Union has identified three broad areas of competences that teachers require:
* Working with others
* Working with knowledge, technology, and information, and
* Working in and with society.
Scholarly consensus is emerging that what is required of teachers can be grouped under three headings:
* knowledge (such as: the subject matter itself and knowledge about how to teach it, curricular knowledge, knowledge about the educational sciences, psychology, assessment etc.)
* craft skills (such as lesson planning, using teaching technologies, managing students and groups, monitoring and assessing learning etc.) and
* dispositions (such as essential values and attitudes, beliefs and commitment).
Qualities:
Enthusiasm
It has been found that teachers who showed enthusiasm towards the course materials and students can create a positive learning experience. These teachers do not teach by rote but attempt to invigorate their teaching of the course materials every day. Teachers who cover the same curriculum repeatedly may find it challenging to maintain their enthusiasm, lest their boredom with the content bore their students in turn. Enthusiastic teachers are rated higher by their students than teachers who did not show much enthusiasm for the course materials.
Teachers that exhibit enthusiasm are more likely to have engaged, interested and energetic students who are curious about learning the subject matter. Recent research has found a correlation between teacher enthusiasm and students' intrinsic motivation to learn and vitality in the classroom. Controlled, experimental studies exploring intrinsic motivation of college students has shown that nonverbal expressions of enthusiasm, such as demonstrative gesturing, dramatic movements which are varied, and emotional facial expressions, result in college students reporting higher levels of intrinsic motivation to learn. But even while a teacher's enthusiasm has been shown to improve motivation and increase task engagement, it does not necessarily improve learning outcomes or memory for the material.
There are various mechanisms by which teacher enthusiasm may facilitate higher levels of intrinsic motivation. Teacher enthusiasm may contribute to a classroom atmosphere of energy and enthusiasm which feeds student interest and excitement in learning the subject matter. Enthusiastic teachers may also lead to students becoming more self-determined in their own learning process. The concept of mere exposure indicates that the teacher's enthusiasm may contribute to the student's expectations about intrinsic motivation in the context of learning. Also, enthusiasm may act as a "motivational embellishment", increasing a student's interest by the variety, novelty, and surprise of the enthusiastic teacher's presentation of the material. Finally, the concept of emotional contagion may also apply: students may become more intrinsically motivated by catching onto the enthusiasm and energy of the teacher.
Interaction with learners
Research shows that student motivation and attitudes towards school are closely linked to student-teacher relationships. Enthusiastic teachers are particularly good at creating beneficial relations with their students. Their ability to create effective learning environments that foster student achievement depends on the kind of relationship they build with their students. Useful teacher-to-student interactions are crucial in linking academic success with personal achievement. Here, personal success is a student's internal goal of improving themselves, whereas academic success includes the goals they receive from their superior. A teacher must guide their student in aligning their personal goals with their academic goals. Students who receive this positive influence show stronger self-confidence and greater personal and academic success than those without these teacher interactions.
Students are likely to build stronger relations with teachers who are friendly and supportive and will show more interest in courses taught by these teachers. Teachers that spend more time interacting and working directly with students are perceived as supportive and effective teachers. Effective teachers have been shown to invite student participation and decision making, allow humor into their classroom, and demonstrate a willingness to play.
Additional Information
A teacher is a person who helps people to learn. A teacher often works in a classroom.
There are many different kinds of teachers. Some teachers teach young children in kindergarten or primary schools. Others teach older children in middle, junior high and high schools. Some teachers teach adults in colleges and universities. Some teachers are called professors.
Teachers are usually professionals. They have been to college and got qualifications. They use various methods to teach. Teachers explain new knowledge, write on a blackboard or whiteboard, sit behind their desks on chairs, help students with their work and mark students' work. They may also use a computer to write tests, assignments or report cards for the class.
Teachers are not always professionals. Parents usually do a lot of teaching before children ever get to school.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2390 2024-12-25 00:10:35
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2290) Student
Gist
A student is a person who goes to school to learn something. Students can be teenagers or adults who are going to university, but it may also be other people who are learning, such as in college. A young person who cannot be classed as a student is called a pupil.
Summary
If you teach your best friend how to play "Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star" on the harmonica, then you can call her your student. A student is someone who's learning to do something or who attends a school.
At school, there are students and teachers: the job of the teachers is to instruct the students in various subjects and the students' job is to learn. If you start school as a kindergartner and attend college and graduate school, it's possible that you may be a student for more than 20 years! Even after you finish school, you may still be a student, if you take swimming classes or learn to speak German in your spare time.
A student is:
i) A person who studies or learns about a particular subject.
ii) A person who is formally enrolled at a school, a college or university, or another educational institution.
One essential characteristic of a successful student is one takes the initiative to seek out support when needed and to incorporate academic different academic strategies to enhance the learning process.
The following is a list of what a hard-working student does and what a teacher likes to see.
Successful students ...
* attend classes regularly and they are on time.
* they get all of the missed notes and assignments from other students or from the professor.
* turn in assignments complete and on time.
* are attentive in class. They ask questions and participate in class discussions.
* take advantage of extra credit opportunities.
* take the initiative to meet with the instructor and the teaching assistant and engage in meaningful conversation outside of class.
* are active participants in the learning process.
* study outside of regular class hours to learn and reinforce material covered in lectures and recitations.
Here are a few more tips to consider to increase your motivation towards becoming a more successful student:
* Set realistic goals
* Set learning goals
* See the value in the task
* Have a positive attitude
* Break down tasks
* Monitor your progress
* Monitor your learning
* Create an interest in the task
* Learn from your mistakes.
Study Tips
Studying effectively is a process, not an event. The process leads to success!
When studying it is important to make meaningful connections to what you already know.
Just remember there is no point in re-reading something if you have no idea what you are reading!
Know the percentages! We retain:
* 10% of what we read
* 20% of what we hear
* 30% of what we see
* 50% of what we see and hear
* 70% of what we talk about with others
* 80% of what we experience personally
* 95% of what we teach to others
Test-Taking Strategies
General Test Taking Tips:
* Get a good night’s sleep the night before
* Eat a good breakfast or meal before your test
* Know the time and location of your exam prior to your exam
* Relax use quick de-stressors such as breathing techniques
* Look over the entire test first
* Read, read, read the directions
* When you get stuck, identify the problem and move on
* Concentrate despite distractions- don’t worry about who gets done first
* If you are confused, ask for clarification
Time Management
Time management is the appropriate use of and structuring of your time in order for you to maximize your time. If you learn how to maximize your time, you will have ample time to successfully accomplish everything you need to and want to accomplish.
Details
A student is a person enrolled in a school or other educational institution.
In the United Kingdom and most commonwealth countries, a "student" attends a secondary school or higher (e.g., college or university); those in primary or elementary schools are "pupils."
Africa:
Nigeria
In Nigeria, education is classified into four systems known as a 6-3-3-4 system of education. It implies six years in primary school, three years in junior secondary, three years in senior secondary and four years in the university. However, the number of years to be spent in university is mostly determined by the course of study. Some courses have longer study lengths than others. Those in primary school are often referred to as pupils. Those in university, as well as those in secondary school, are referred to as students.
The Nigerian system of education also has other recognized categories like the polytechnics and colleges of education. The Polytechnic gives out National Diploma and Higher National Diploma certifications after two years and/or four years of study respectively.
A higher National Diploma (also known as HND) can be obtained in a different institution from where the National Diploma (also known as ND or OND) was obtained. However, the HND cannot be obtained without the OND certificate.
On the other hand, the respective colleges of education provide students with the Nigerian Certificate in Education (NCE) after two years of study.
South Africa
In South Africa, education is divided into four bands: the Foundation Phase (grades 1–3), the Intermediate Phase (grades 4–6), the Senior Phase (grades 7–9), and the Further Education and Training or FET Phase (grades 10–12). However, because this division is newer than most schools in the country, in practice, learners progress through three different types of school: Primary school (grades 1–3), Junior school (grades 4–7), and High school (grades 8–12). After the FET phase, learners who pursue further studies typically take three or four years to obtain an undergraduate degree or one or two years to achieve a vocational diploma or certificate. The number of years spent in university varies as different courses of study take different numbers of years. Those in the last year of high school (Grade 12) are referred to as 'Matrics' or are in 'Matric' and take the Grade 12 examinations accredited by the Umalusi Council (the South African board of education) in October and November of their Matric year. Exam papers are set and administered nationally through the National Department of Basic Education for government schools, while many (but not all) private school Matrics sit for exams set by the Independent Education Board (IEB), which operates with semi-autonomy under the requirements of Umalusi. (The assessment and learning requirements of both IEB and National exams are of roughly the same standard. The perceived better performance of learners within the IEB exams is largely attributable to their attending private, better-resourced schools with the much lower teacher: learner ratios and class sizes rather than because of fundamental differences in assessment or learning content). A school year for the majority of schools in South Africa runs from January to December, with holidays dividing the year into terms. Most public or government schools are 4-term schools and most private schools are 3-term school, but the 3-term government or public schools and 4-term private schools are not rare.
Asia:
Singapore
Six years of primary school education in Singapore are compulsory.
Primary School (Primary 1 to 6)
Primary 1 to 3 (aged 7–9 respectively, Lower primary) Primary 4 to 6 (aged 10–12 respectively, Upper primary)
Secondary School (Secondary 1 to 4 or 5)
Sec 1s are 13, and Sec 4s are 16. Express Students take secondary school from Sec 1 to 4, and Normal Acad and Technical will take secondary school from Sec 1 to 5.
Junior College (Junior College 1 to 2 – Optional) OR Polytechnic (3 years – Optional)
There are also schools which have the integrated program, such as River Valley High School (Singapore), which means they stay in the same school from Secondary 1 to Junior College 2, without having to take the "O" level examinations which most students take at the end of secondary school.
International schools are subject to overseas curriculums, such as the British, American, Canadian or Australian Boards.
Bangladesh
Primary education is compulsory in Bangladesh. It is a near crime to not to send children to primary school when they are of age, but it is not a punishable crime. Sending children to work instead of school is a crime, however. Because of the socio-economic state of Bangladesh, child labour is sometimes legal, but the guardian must ensure the primary education of the child. Anyone who is learning in any institute or even online may be called a student in Bangladesh. Sometimes students taking undergraduate education are called undergraduates and students taking post-graduate education may be called post-graduates.
Educational Level : Grade : Age
Primary (elementary school) : 1 to 5 : 6 to 10
Junior Secondary (middle school) : 6 to 8 : 11 to 13
Secondary (high school) : 9 to 10 : 14 to 15
Higher Secondary (college/university) : 11 to 12 : 16 to 17
Brunei
Education is free in Brunei. Darussalam not limited to government educational institutions but also private educational institutions. There are mainly two types of educational institutions: government or public, and private institutions. Several stages have to be undergone by the prospective students leading to higher qualifications, such as bachelor's degree.
* Primary School (Year 1 to 6)
* Secondary School (Year 7 to 11)
* High School [or also known as the Sixth Form Centers] (Year 12 to 13)
* Colleges (Pre-University to Diploma)
* University Level (Undergraduate, Postgraduate and Professional)
It takes six and five years to complete the primary and secondary levels respectively. Upon completing these two crucial stages, students/pupils have freedom to progress to sixth-form centers, colleges or probably straight to employment. Students are permitted to progress towards university level programs in both government and private university colleges.
Cambodia
Education in Cambodia is free for all students who study in Primary School, Secondary School or High School.
* Primary School (Grade 1 to 6)
* Secondary School (Grade 7 to 9)
* High School (Grade 10 to 12)
* College (Year 1 to 3)
* University (Year 1 to 4 or 5)
After basic education, students can opt to take a bachelor's (undergraduate) degree at a higher education institution (i.e. a college or university), which normally lasts for four years, though the length of some courses may be longer or shorter depending on the institution.
India
In India school is categorized in these stages: Pre-primary (Nursery, Lower Kindergarten or LKG, Upper Kindergarten or UKG), Primary (Class 1–5), Secondary (6–10) and Higher Secondary (11–12). For undergraduate it is 3 years except Engineering (BTech or BE), Pharmacy (B.pharm), Bsc agriculture which are 4-year degree course, Architecture (B.Arch.) which is a 5-year degree course, M.Sc. (5-year Integrated courses) and Medical (MBBS) which consists of a 4.5-year degree course and a 1-year internship, so 5.5 years in total.
Nepal
In Nepal 12-year school is categorised in two stages: Primary school (Grade 1 to Grade 8) and Higher Secondary school (Grade 9 to Grade 12). For college it averages four years for a bachelor's degree (except BVSc and AH which are five year programmes and MBBS which is a five and half year programme) and two years master's degree.[citation needed]
Pakistan
In Pakistan, 12-year school is categorized in three stages: Primary school, Secondary school and Higher Secondary school. It takes five years for a student to graduate from Primary school, five years for Secondary school and five years for Higher Secondary school (also called College). Most bachelor's degrees span over four years, followed by a two years master's degree.
Philippines
The Philippines is currently in the midst of a transition to a K-12 (also called K+12) basic education system. Education ideally begins with one year of kinder. Once the transition is complete, elementary or grade school comprises grades 1 to 6. Although the term student may refer to learners of any age or level, the term 'pupil' is used by the Department of Education to refer to learners in the elementary level, particularly in public schools. Secondary level or high school comprises two major divisions: grades 7 to 10 will be collectively referred to as 'junior high school', whereas grades 11 to 12 will be collectively referred to as 'senior high school'. The Department of Education refers to learners in grade 7 and above as students.
After basic education, students can opt to take a bachelor's (undergraduate) degree at a higher education institution (i.e. a college or university), which normally lasts for four years though the length of some courses may be longer or shorter depending on the institution.
Iran
In Iran 12-year school is categorized in two stages: Elementary school and High school. It takes six years for a student to graduate from elementary school and six years for high school. High school study is divided into two part: junior and senior high school. In senior high school, students can choose between the following six fields: Mathematics and physics, Science, Humanities, Islamic science, Vocational, or Work and Knowledge. After graduating from high school, students acquire a diploma. Having a diploma, a student can participate in the Iranian University Entrance Exam or Konkoor in different fields of Mathematics, Science, Humanities, languages, and art. The university entrance exam is conducted every year by National Organization of Education Assessment, an organization under the supervision of the Ministry of Science, Research and Technology which is in charge of universities in Iran. Members of the Baháʼí Faith, a much-persecuted minority, are officially forbidden to attend university, in order to prevent members of the faith becoming doctors, lawyers or other professionals; however, Muslim, Christian, Jewish, and Zoroastrian people are allowed entry to universities.
Oceania:
Australia
In Australia, Pre-school is optional for three and four year olds. At age five, children begin compulsory education at Primary School, known as Kindergarten in New South Wales, Preparatory School (prep) in Victoria, and Reception in South Australia, students then continue to year one through six (ages 6 to 12). Before 2014, primary school continued on to year seven in Western Australia, South Australia and Queensland. However, the state governments agreed that by 2014, all primary schooling will complete at year six. Students attend High School in year seven through twelve (ages 13 – 18). After year twelve, students may attend tertiary education at university or vocational training at TAFE (Technical and Further Education).
New Zealand
In New Zealand, after kindergarten or pre-school, which is attended from ages three to five, children begin primary school, 'Year One', at five years of age. Years One to Six are Primary School, where children commonly attend local schools in the area for that specific year group. Then Year Seven and Year Eight are Intermediate, and from Year Nine until Year Thirteen, a student would attend a secondary school or a college.
Europe:
Europe uses the traditional, first form, second form, third form, fourth form, fifth form and six form grade system which is up to age eleven.
Finland
In Finland a student is called "opiskelija" (plural being 'opiskelijat'), though children in compulsory education are called "oppilas" (plural being 'oppilaat'). First level of education is "esikoulu" (literally 'preschool'), which used to be optional, but has been compulsory since the beginning of year 2015. Children attend esikoulu the year they turn six, and next year they start attending "peruskoulu" (literally "basic school", corresponds to American elementary school, middle school and junior high), which is compulsory. Peruskoulu is divided to "alakoulu" (years 1 through 6) and "yläkoulu" (years 7 through 9). After compulsory education most children attend second-level education (toisen asteen koulutus), either lukio (corresponds to high school) or ammattioppilaitos (Vocational School), at which point they are called students (opiskelija). Some attend "kymppiluokka", which is a retake on some yläkoulu's education.
To attend ammattikorkeakoulu (University of applied sciences) or a university a student must have a second-level education. The recommended graduation time is five years. First year students are called "fuksi" and students that have studied more than five years are called "N:nnen vuoden opiskelija" (Nth year student).
France
The generic term "étudiant" (lit. student) applies only to someone attending a university or a school of a similar level, that is to say pupils in a cursus reserved to people already owning a Baccalauréat. The general term for a person going to primary or secondary school is élève. In some French higher education establishments, a bleu or "bizuth" is a first-year student. Second-year students are sometimes called "carrés" (squares). Some other terms may apply in specific schools, some depending on the classe préparatoire aux grandes écoles attended.
Germany
In Germany, the German cognate term Student (male) or "Studentin" (female) is reserved for those attending a university. University students in their first year are called Erstsemester or colloquially Ersties ("firsties"). Different terms for school students exist, depending on which kind of school is attended by the student. The general term for a person going to school is Schüler or Schülerin. They begin their first four (in some federal estates six) years in primary school or Grundschule. They then graduate to a secondary school called Gymnasium, which is a university preparatory school. Students attending this school are called Gymnasiasten, while those attending other schools are called Hauptschüler or Realschüler. Students who graduate with the Abitur are called Abiturienten.
Ireland
In Ireland, pupils officially start with primary school which consists of eight years: junior infants, senior infants, first class to sixth class (ages 5–11). After primary school, pupils proceed to the secondary school level. Here they first enter the junior cycle, which consists of first year to third year (ages 11–14). At the end of third year, all students must sit a compulsory state examination called the Junior Certificate. After third year, pupils have the option of taking a "transition year" or fourth year (usually at age 15–16). In transition year pupils take a break from regular studies to pursue other activities that help to promote their personal, social, vocational and educational development, and to prepares them for their role as autonomous, participative and responsible members of society. It also provides a bridge to enable pupils to make the transition from the more dependent type of learning associated with the Junior Cert. to the more independent learning environment associated with the senior cycle.
After the junior cycle pupils advance to the senior cycle, which consists of fifth year and sixth year (usually ages between 16 and 18). At the end of the sixth year a final state examination is required to be sat by all pupils, known as the Leaving Certificate. The Leaving Cert. is the basis for all Irish pupils who wish to do so to advance to higher education via a points system. A maximum of 625 points can be achieved. All higher education courses have a minimum of points needed for admission.
At Trinity College Dublin under-graduate students are formally called "junior freshmen", "senior freshmen", "junior sophister" or "senior sophister", according to the year they have reached in the typical four year degree course. Sophister is another term for a sophomore, though the term is rarely used in other institutions and is largely limited to Trinity College Dublin.
At university, the term "fresher" is used to describe new students who are just beginning their first year. The term, "first year" is the more commonly used and connotation-free term for students in their first year. The week at the start of a new year is called "Freshers' Week" or "Welcome Week", with a programme of special events to welcome new students. An undergraduate in the last year of study before graduation is generally known as a "finalist".
Italy
In Italian, a matricola is a first-year student. Some other terms may apply in specific schools, some depending on the liceo classico or liceo scientifico attended.
According to the goliardic initiation traditions the grades granted (following approximately the year of enrollment at university) are: matricola (freshman), fagiolo (sophomore), colonna (junior), and anziano (senior), but most of the distinctions are rarely used outside Goliardia.
Sweden
In Sweden, only those studying at university level are called students (student, plural studenter). To graduate from upper secondary school (gymnasium) is called ta studenten (literally "to take the student"), but after the graduation festivities, the graduate is no longer a student unless he or she enrolls at university-level education. At lower levels, the word elev (plural elever) is used. As a general term for all stages of education, the word studerande (plural also studerande) is used, meaning 'studying [person]'.
United Kingdom
Traditionally, the term "student" is reserved for people studying at university level in the United Kingdom.
At universities in the UK, the term "fresher" is used informally to describe new students who are just beginning their first year. Although it is not unusual to call someone a fresher after their first few weeks at university, they are typically referred to as "first years" or "first year students".
The ancient Scottish University of St Andrews uses the terms "bejant" for a first year (from the French "bec-jaune" – "yellow beak", "fledgling"). Second years are called "semi-bejants", third years are known as "tertians", and fourth years, or others in their final year of study, are called "magistrands".
In England and Wales, primary school begins with an optional "nursery" year (either in a primary school or a privately run nursery,) followed by reception and then move on to "year one, year two" and so on until "year six" (all in primary school.) In state schools, children join secondary school when they are 11–12 years old in what used to be called "first form" and is now known as "year 7". They go up to year 11 (formerly "fifth form") and then join the sixth form, either at the same school or at a separate sixth form college. A pupil entering a private, fee-paying school (usually at age 13) would join the "third form" – equivalent to year 9. Many schools have an alternate name for first years, some with a derogatory basis, but in others acting merely as a description – for example "shells" (non-derogatory) or "grubs" (derogatory).
In Northern Ireland and Scotland, it is very similar but with some differences. Pupils start off in nursery or reception aged 3 to 4, and then start primary school in "P1" (P standing for primary) or year 1. They then continue primary school until "P7" or year 7. After that they start secondary school at 11 years old, this is called "1st year" or year 8 in Northern Ireland, or "S1" in Scotland. They continue secondary school until the age of 16 at "5th year", year 12 or "S5", and then it is the choice of the individual pupil to decide to continue in school and (in Northern Ireland) do AS levels (known as "lower sixth") and then the next year to do A levels (known as "upper sixth"). In Scotland, students aged 16–18 take Highers, followed by Advanced Highers. Alternatively, pupils can leave and go into full-time employment or to start in a technical college.
Large increases in the size of student populations in the UK and the effect this has had on some university towns or on areas of cities located near universities have become a concern in the UK since 2000. A report by Universities UK, Studentification: A Guide to Opportunities, Challenges aPractice (2006) has explored the subject and made various recommendations. A particular problem in many locations is seen as the impact of students on the availability, quality and price of rented and owner-occupied property.
Americas:
Canada
Education in Canada (a federal state) is primarily within the constitutional jurisdiction of the provinces. The overall school curricula are overseen by the provincial and territorial governments, therefore the way educational stages are grouped and named can differ. Education is generally divided into primary, secondary and post-secondary stages. Primary and secondary education are generally divided into annual grades from 1 to 12, although grade 1 may be preceded by one or two years of kindergarten (which may be optional). Specifically, Ontario, Quebec and the Northwest Territories offer junior then senior kindergarten (in French, either pre-maternelle then maternelle, or maternelle then jardin d'enfants).
Education in Ontario from 1988 involved an Ontario Academic Credit (OAC) after grade 12 primarily as university preparation, but that was phased out in 2003. The OAC was informally known as "grade 13" (which it had replaced). All provinces and territories except Quebec now have 12 grades.
Education in Quebec differs from the other jurisdictions in that it has an école primaire ("primary school") consisting of grades 1–6 and an école secondaire ("secondary school") consisting of secondaries I–V, equivalent to grades 7–11. A student graduating from école secondaire then either completes a three-year college program or a two-year pre-university program required before attending university. In some English-language écoles secondaire and most French-language écoles secondaire, students refer to secondaries I–V as years one through five. This can be confusing for those outside of Quebec, especially out of context.
In some provinces, grades 1 through 5 are called "elementary school", grades 6 to 8 are called "middle school" or "junior high school", and grades 9 to 12 are considered high school. Other provinces, such as British Columbia, mainly divide schooling into elementary school (Kindergarten to grade 7) and secondary school (grades 8 through 12). In Alberta and Nova Scotia, elementary consists of kindergarten through grade 6. Junior high consists of Grades 7–9. High school consists of Grades 10–12. In English provinces, the high school (known as academy or secondary school) years can be referred to simply as first, second, third and fourth year. Some areas call it by grade such as grade 10, grade 11 and grade 12.
In Canadian English, the term "college" usually refers to a technical, trades, applied arts, applied technology, or applied science school or community college. These are post-secondary institutions typically granting two-year diplomas certificates, diplomas, associate degrees and (in some cases) bachelor's degrees. The French acronym specific to public institutions within Quebec's system of pre-university and technical education is CEGEP (Collège d'enseignement général et professionnel, "college of general and professional education"). CEGEP is a collegiate level institution in Quebec that most students typically enrols in, whether to learn a trade or applied discipline or to qualify for entrance to university in the Quebec education system. (In Ontario and Alberta, there are also institutions that only grant undergraduate degrees which are designated university colleges to differentiate them from universities, which have both undergraduate and graduate programs.)
In Canada, there is a strong distinction between "college" and "university". In conversation, one specifically would say either "they are going to university" (i.e., studying for a three- or four-year degree at a university) or "they are going to college" (i.e., studying at a technical/career training).
A Canadian post-secondary college is generally geared for individuals seeking applied careers, while universities are geared for individuals seeking more academic careers.
University students are generally classified as first, second, third or fourth-year students, and the American system of classifying them as "freshmen", "sophomores", "juniors" and "seniors" is seldom used or even understood in Canada. In some occasions, they can be called "senior ones", "twos", "threes" and "fours".
United States
In the United States, the first official year of schooling is called kindergarten, which is why the students are called kindergarteners. Kindergarten is optional in most states, but few students skip this level. Pre-kindergarten, also known as "preschool" (and sometimes shortened to "Pre-K") is becoming a standard of education as academic expectations for the youngest students continue to rise. Many public schools offer pre-kindergarten programs.
In the United States, there are 12 years of mandatory schooling. The first eight are solely referred to by numbers (e.g. 1st grade, 5th grade) so students may be referred to as 1st graders, 5th graders, then once in middle school, they are referred to as 6th, 7th, and 8th graders. Upon entering high school, grades 9 through 12 (high school) also have alternate names for students, namely freshman, sophomore, junior and senior. The actual divisions of which grade levels belong to which division (whether elementary, middle, junior high, or high school) is a matter decided by state or local jurisdictions.
College students are often called Freshmen, Sophomores, Juniors, and Seniors for each of the four years unless their undergraduate program calls for more than the traditional four years.
First year
The first year of college or high school is referred to as Freshman year. A freshman is a first-year student in college, university or high school.
Second year
In the U.S., a sophomore, also called a "soph", is a second-year student. Outside the United States, the term sophomore is rarely used, with second-year students simply called "second years". Folk etymology indicates that the word means "wise fool"; consequently "sophomoric" means "pretentious, bombastic, inflated in style or manner; immature, crude, superficial" (according to the Oxford English Dictionary). It is widely assumed to be formed from Greek Sophos, meaning "wise", and Moros meaning "foolish", although the etymology suggests an origin from the now-defunct "sophomore", an obsolete variant of "sophism".
Post-second year
In the U.S., a Junior is a student in the penultimate (usually third) year and a Senior is a student in the last (usually fourth) year of college, university, or high school. A student who takes more than the average number of years to graduate is sometimes referred to as a "super senior". This term is often used in college but can be used in high school as well. The term underclassman refers collectively to Freshmen and Sophomores, and upperclassman refers collectively to Juniors and Seniors, sometimes even Sophomores. In some cases, the freshmen, sophomores, and juniors are considered underclassmen, while seniors are designated as upperclassmen. The term Middler is used to describe a third-year student of a school (generally college) that offers five years of study. In this situation, the fourth and fifth years would be referred to as Junior and Senior years, respectively, and the first two years would be the Freshman and Sophomore years.
Graduate students
A graduate student is a student who continues his/her education after graduation. Some examples of graduate programs are: business school, law school, medical school, and veterinary school. Degrees earned in graduate programs include the master's degree, a research doctoral degree, or a first professional degree.
Vocational school
Students attending vocational school focus on their jobs and learning how to work in specific fields of work. A vocational program typically takes much less time to complete than a four-year degree program, lasting 12–24 months.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2391 2024-12-26 00:02:12
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2291) Medical Science
Gist
What is the field of medical science?
It typically covers subjects such as human anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, epidemiology, biostatistics, medical ethics, healthcare policy, and research methodologies. Medical science graduates have the option to pursue advanced education to specialize in their specific areas of interest.
Summary
Medical science covers many subjects which try to explain how the human body works. Starting with basic biology it is generally divided into areas of specialisation, such as anatomy, physiology and pathology with some biochemistry, microbiology, molecular biology and genetics. Students and practitioners of holistic models of health also recognise the importance of the mind-body connection and the importance of nutrition.
Knowledge of how the body functions is a fundamental requirement for continued studies in the medical profession or for training as a health practitioner. To be able to diagnose disease a practitioner first needs to understand how a fit and healthy body functions. It is difficult to truly evaluate and diagnose disease without the knowledge of the effects of diseases and how the normal function of the body can be restored. As well as giving you a good working knowledge of the human body, our courses give you an understanding of the terminology used by the medical profession, allowing you to refer and communicate effectively and confidently with GPs, consultants and other medics. It is essential that as a practitioner your patients have confidence in your professional ability.
The human body is a complex organism and our approach to the study of human physiology is an integrative one. We take the holistic approach in seeing how things can go wrong in the body and how it can be brought back into balance. The term holistic comes from the word ‘whole’. Diseases can affect people not only physically but also emotionally and our approach recognises the different systems and functions of the body as interdependent and whole.
Anatomy is the study of the component parts of the human body - for example, the heart, the brain, the kidney or muscles, bones and skin. Medical students are required to carry out a practical dissection of a body in order to understand how it all connects up and many colleges of medicine use real bodies where others use computer simulation. Most holistic courses only study the theory of anatomy but some courses may admit outside students to the dissection room.
Physiology is the application of the study of anatomy into the realm of how the body parts normally function independently and as a component of a system, such as the heart and the circulatory system with blood vessels and blood. In order to make people better it is essential to know how the body systems work in health so that you can tell what is wrong when patients feel ill and be able to track their recovery. It is also vital to understand that organ systems are interconnected too and how they work together.
Pathology is the study of disease states. Medical students are required to diagnose diseases as separate entities and have an enormous vocabulary to describe disease states. (If you have learned Greek or Latin it is easy to understand the terminology as it is descriptive in these languages but if you haven’t it is quite daunting!) Holistic therapists are usually less interested in a standard diagnosis for a patient and much more concerned with the symptoms produced by the individual. But both medical systems require an intelligent understanding of prognosis (i.e. what is the likely outcome for the patient with their disease following treatment?)
Details
A Bachelor of Medical Sciences (BMedSci, BMedSc, BSc(Med), BMSc) is an undergraduate academic degree involving study of a variety of disciplines related to human health leading to an in depth understanding of human biology and associated research skills such as study design, statistics and laboratory techniques. Such disciplines include biochemistry, cell biology, physiology, pharmacology or psychosocial aspects of health. It is an equivalent level qualification to the more commonly awarded Bachelor of Science (BSc). Graduates may enter a diverse range of roles including post-graduate study, higher education, the biotechnology industry, the pharmaceutical industry, consultancy roles, scientific communication, education or unrelated disciplines which make use of the broad range of transferable skills gained through this degree.
Australia
In Australia, the Bachelor of Medical Sciences (BMedSc) degree is offered by The University of Adelaide, Griffith University, University of New South Wales, University of Sydney, Monash University, Australian National University, University of Western Sydney, University of Newcastle, Flinders University, Charles Sturt University, Macquarie University , Central Queensland University and The University of the Sunshine Coast.
Canada
At the University of Western Ontario, BMSc is a four-year degree offered by the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry. It is differentiated from a BSc due to the advanced medical sciences orientation of the courses offered such as Anatomy and Pharmacology.
The University of Alberta offers a BMSc to Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry students who did not complete a bachelor's degree prior to entry into the program.
India
In India, BMSc is an undergraduate degree offered by top universities like Panjab University, Punjabi University, Indian Institutes of Technology and the R. G. Kar Medical College and Hospital.
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, the Bachelor of Medical Sciences degree can be awarded in four situations; firstly as a standalone 3-year first degree, secondly, as a consequence of taking an extra year during a medical or dental course (termed intercalating), thirdly as an additional part of a medical degree but without any additional years of study, and fourthly as an exit award if a student wishes to leave their primary medical or dental undergraduate course. When the degree is obtained without any additional years of study, it may not be viewed as an equivalent qualification. For example, the UK Foundation Programme Office (the British body which manages first jobs for new medical graduates) places less value on a BMedSc degree if an additional year of study has not been undertaken. Regardless of the way in which the degree is obtained, a research project typically forms a large component of the degree as well as formal teaching in medical science related disciplines.
Bachelor of Medical Sciences degrees are awarded as a standalone 3-year course by the University of Chester, University of Exeter, University of Birmingham, the University of Sheffield, Bangor University, Oxford Brookes University, De Montfort University, and the University of St Andrews. Medical schools which award an intercalated Bachelor of Medical Sciences after an additional year of study are Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry, the University of Birmingham, the University of Dundee, the University of Edinburgh the University of Aberdeen and the University of Sheffield. The University of Nottingham and the University of Southampton award the degree as a standard part of their undergraduate medicine courses without an additional year of study (students must undertake a research project).
Egypt
In Egypt, the bachelor of medical sciences is awarded after four years of study in addition to an internship year in which interns are trained in multiple public and university hospitals.
The degree is offered in five universities in Egypt: October 6 University, Misr University for Science and Technology, Pharos University in Alexandria, Beni-Suef University and Menoufia University. Faculties of applied medical sciences offer various disciplines for students to choose from, including medical laboratories, radiology and medical imaging, therapeutic nutrition, and biomedical equipment.
In 2015, the Central Authority For Organization and Administration (CAOA) granted the holders of the bachelor of medical sciences the title of "specialist" in the corresponding specialty.
Israel
BSc.Med is granted by all six medical schools in Israel: the Hebrew University, Tel Aviv University, Ben-Gurion University, the Technion, Bar-Ilan University and Ariel University. The full M.D. program consists of six years of studies and an additional year of internship. The first part of the program consists of three years of basic science (pre-clinical) studies, culminating in the award of a BSc.Med degree in medical sciences.
Additional Information
A medical sciences degree enables you to work in a variety of scientific and medical careers while also opening up many opportunities for further study
Job options
Jobs directly related to your degree include:
* Academic researcher
* Clinical research associate
* Clinical scientist, biochemistry
* Medical sales representative
* Medical science liaison
* Physician associate
* Research scientist (medical)
* Science writer
* Scientific laboratory technician
Jobs where your degree would be useful include:
* Anatomical pathology technologist
* Dental technician
* Diagnostic radiographer
* General practice doctor
* Higher education lecturer
* Hospital doctor
* Operating department practitioner
* Physiotherapist
* Therapeutic radiographer.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2392 2024-12-27 00:10:28
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2292) Allowance (money)
Allowance (money)
Gist
Allowances are commonly provided for expenses such as house rent, travel, telephone, and children's education. For example, organizations may provide conveyance allowance to sales representatives to cover their travel expenses to meet a client.
An allowance is a sum granted as a reimbursement or bounty or for expenses. a salary that includes a cost-of-living allowance. Especially : a sum regularly provided for personal or household expenses. Each child receives a weekly allowance.
Summary
An allowance is an amount of money given or allotted usually at regular intervals for a specific purpose. In the context of children, parents may provide an allowance (British English: pocket money) to their child for their miscellaneous personal spending.
It is money that you are given regularly, especially to pay for a particular thing. The perks of the job include a company pension and a generous travel allowance.
An allowance is money that is given to someone, usually on a regular basis, in order to help them pay for the things that they need.
Allowance is defined as a fixed amount of money paid by employers to their employees to meet certain expenditures above basic salary. For example, organizations pay overtime over and above basic salary to employees when they work for additional hours. Similarly, there are many other allowances as a component of salary.
Allowances are categorized as Taxable, Non-Taxable, and Partially Taxable allowances.
Allowance is a specified amount of money that is regularly given to a person, usually child or a dependent, to cover expenses or meet specific needs. Allowances are usually provided a recurring basis and may be used to cover essential expenses like transportation, food, education, and day-to-day expenses.
Allowances can be set up in various ways, such as or monthly, and can be paid in cash, through a bank transfer or mobile payment, or a prepaid card. Allowances can also be provided as an employment benefit to cover specific work expenses like travel or health insurance.
The purpose of giving allowances is to teach the recipient financial and management of money. It helps them learn to budget, save, and gain experience in financial. Allowances can also be used as a tool to encourage good behavior or as a reward for meeting certain goals or meeting expectations.
Types of Allowance
Allowances refer to extra payments or benefits offered to employees, usually beyond their usual salary or wages. They come in various types, customized to meet different requirements and situations. Here are some typical examples:
* Housing Allowance: A housing allowance constitutes a payment aimed at offsetting housing-related expenses such as rent or mortgage payments, utilities, and maintenance costs. Typically extended to employees dwelling in areas with elevated housing expenditures or included as a component of compensation packages for expatriates.
* Transportation Allowance: Transportation reimbursement or subsidy aids in covering commuting and vehicle maintenance costs. This assistance can be provided as a set sum or based on the actual expenses reported.
* Meal Allowance: Meal expense compensation accounts for the costs of meals consumed during work hours, particularly for employees required to work away from their typical place of work or during extended shifts.
* Education Allowance: Educational expense assistance is financial support offered to employees to cover educational costs for themselves or their dependents, including tuition fees, textbooks, or training courses.
* Childcare Allowance: Child Care assistance provides support for childcare expenses, including daycare fees or babysitting services, to aid employees in balancing their work and family responsibilities.
* Travel Allowance: Reimbursement for travel expenses encompasses costs associated with business trips, such as transportation, accommodation, meals, and incidental expenditures.
* Uniform Allowance: Provision for covering the costs associated with purchasing or maintaining job-related uniforms or specialized attire vital for fulfilling occupational requirements.
* Phone Allowance: Financial assistance provided to offset personal phone usage essential for work responsibilities, covering expenses like calls, texts, or data usage necessary for conducting business affairs.
* Medical Allowance: Assistance tailored to address medical expenses not accounted for by health insurance, covering out-of-pocket costs like co-payments, deductibles, or expenditures for alternative healthcare therapies.
* Special Duty Allowance: Additional payment extended to employees handling specialized tasks or assignments involving heightened risks, adversity, or greater duties.
These examples represent only a handful of the allowances employers might include in employees' compensation packages. The types and levels of these allowances fluctuate depending on factors such as industry norms, corporate guidelines, and regional regulations.
Details
An allowance is an amount of money given or allotted usually at regular intervals for a specific purpose. In the context of children, parents may provide an allowance (British English: pocket money) to their child for their miscellaneous personal spending. In the construction industry, an allowance may be an amount allocated to a specific item of work as part of an overall contract.
The person providing the allowance usually tries to control how or when money is spent by the recipient so that it meets the aims of the person providing the money. For example, a parent giving an allowance may be motivated to teach their child money management, and the allowance may be either unconditional or tied to the completion of chores or the achievement of specific grades.
The person supplying the allowance usually specifies the purpose, and may put controls in place to make sure that the money is spent only for that purpose. For example, company employees may be given an allowance or per diem to provide for meals, and travel when they work away from home, and then be required to provide receipts as proof, or they may be provided with specific non-money tokens or vouchers such as a meal voucher that can be used only for a specific purpose.
Construction contracting
In construction, an allowance is an amount specified and included in the construction contract (or specifications) for a certain item of work (appliances, lighting, etc.) whose details are not yet determined at the time of contracting. These rules typically apply to:
* The amount covers the cost of the contractor's material/equipment delivered to the project and all taxes less any trade discounts to which the contractor may be entitled with respect to the item of work.
* The contractor's costs for labor (installation), overhead, profit, and other expenses with respect to the allowance item are included in the base contract amount but not in the allowance amount.
* If the costs in the first section for the item of work are higher (or lower) than the allowance, the base contract is increased (decreased) by the difference in both amounts, and by the change (if any) to the contractor's costs under the second section.
The allowance provisions may be handled otherwise in the contract; for example, the flooring allowance may state that installation costs are part of the allowance. The contractor may be required to produce records of the original takeoff or estimate of the costs in the second section for each allowance item.
These issues should also be considered in the contract's allowance provision:
* May the client insist that the contractor use whomever the client wishes to do the allowance work?
* May the contractor charge the client back for any costs arising from a delay by the client (or client's agent) in selecting the material or equipment of the allowance in question?
Children
Parents often give their children an allowance (British English: pocket money) for their miscellaneous personal spending, and also to teach them money management at an early age. The parenting expert Sidonie Gruenberg popularized this concept in 1912.
Usually young children get "gift" allowances. For some parents, when children are old enough to start doing chores, an allowance becomes "exchange" money. Later, as the child grows older, some parents give children projects they can choose or ignore, and this type of allowance can be called "entrepreneurial."
A 2019 study by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants found the average allowance paid to U.S. children was $30 per week.
Adults
In gynocentric countries like South Korea and Japan, it is customary for the woman to control all household finances. Any paycheck that the husband receives goes straight to the wife's bank account, and the wife usually pays around 5~10% of it as allowance to her husband. That practice is very common because of a widespread social prejudice that men are unfit to manage household finances.
In 2015, a court in South Korea granted an at-fault divorce (no-fault divorce is not allowed in that country) to a husband who received only 100,000 won (US$95) per month in allowance from his wife. The article stated that the husband was a professional soldier, but since his entire salary went to his wife, he had to take a second job as a construction worker to afford to buy his meals. The ruling established that an excessively-low allowance from a wife can be counted as a fault for divorce in that country.
In Japan, three quarters of men get monthly allowances from their wives. Since 1979, Shinsei Bank has been researching the amount of spending money given to husbands by their wives. In 2011 it was 39,600 yen (about US$500). That can be compared to before the Japanese asset price bubble burst, when the allowance was 76,000 yen in 1990 (US$530, equivalent to US1,240 in 2024).
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2393 2024-12-28 00:03:18
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2293) Bacteriologist
Bacteriologist
Gist
Bacteriologists study the growth, development, and other properties of bacteria, including the positive and negative effects that bacteria have on plants, animals, and humans.
A bacteriologist is like a detective for germs, studying and investigating bacteria to understand how they help or harm us.
A bacteriologist is a scientist who observes and researches bacteria to learn how they live, grow, and interact with their environments. Bacteriologists play a crucial role in medicine by using their knowledge of these special microorganisms to help develop antibiotics and vaccines, and they also work in fields like agriculture and environmental science. Their work helps us understand and manage bacteria to keep us healthy and safe.
Louis Pasteur: Father of bacteriology.
Summary
A bacteriologist is a microbiologist, or similarly trained professional, in bacteriology— a subdivision of microbiology that studies bacteria, typically pathogenic ones. Bacteriologists are interested in studying and learning about bacteria, as well as using their skills in clinical settings. This includes investigating properties of bacteria such as morphology, ecology, genetics and biochemistry, phylogenetics, genomics and many other areas related to bacteria like disease diagnostic testing. Alongside human and animal healthcare providers, they may carry out various functions as medical scientists, veterinary scientists, pathologists, or diagnostic technicians in locations like clinics, blood banks, hospitals, laboratories and animal hospitals. Bacteriologists working in public health or biomedical research help develop vaccines for public use as well as public health guidelines for restaurants and businesses.
Education
Because bacteriology is a sub-field of microbiology, most careers in bacteriology require an undergraduate degree in microbiology or a closely related field. Graduate degrees in microbiology or disciplines like it are common for bacteriologists because graduate degree programs provide more in-depth and specific education on topics related to bacteriology. They also often include research and lab experience. Graduate studies also provide opportunities for practical experience in applying bacteriological concepts to a work environment. If someone wants to pursue independent research, work for a company involved in bacteriology, or work in a university bacteria research facility, they will typically have to complete a PhD in bacteriology or a closely related field.
Bacteriologist specializations
* Pathology
* Immunology
* Cell Biology
* Medical Laboratory Science
* Biomedical Research
* Health Technology
* Veterinary Bacteriology
* Biosecurity
* Research
* Epidemiology.
* Agriculture
* Food Safety
* Bacterial Evolution and Systematics
* Phylogenetics and Taxonomy
* Ecology
Details
A bacteriologist is a specialized scientist who studies bacteria and other microorganisms. Working as a bacteriologist can offer exciting opportunities to take part in scientific discovery and innovations at work. You might thrive in a career as a bacteriologist if you enjoy learning about science and have excellent research skills. In this article, we explore what a career as a bacteriologist can be like, including their typical job duties and the skills they often need.
Who is a bacteriologist?
A bacteriologist is a type of microbiologist who specializes in researching bacteria. Bacteria are microorganisms that can frequently evolve and that often live in organic environments, such as the human body and inside plants and animals. One of the most common concepts that bacteriologists can focus on is the effect that different bacteria can have on various animals, including humans. This is because bacteria can affect an organism's health and behavior, so learning about the reaction to different bacteria can lead to innovations in industries like healthcare and food.
Most bacteriologists collaborate often with other scientists to gain more complete understandings of the observations they make. For example, if a bacteriologist is studying a strain of bacteria that seems to live in insects, they might work with an entomologist to learn more about the insects they observe.
What does a bacteriologist do?
A bacteriologist can have several job duties that relate to studying bacteria. Here are some of the most popular job duties for a bacteriologist to have:
* Observing bacteria in a laboratory to learn about their behavior
* Collecting samples of bacteria from natural environments and animals
* Researching the effect of certain substances on bacteria to develop new medications and vaccines
* Testing the levels of bacteria that are present in food, beverages or other edible products
* Keeping track of the metabolism and reproductive habits of bacteria
* Conducting trials to determine whether a strain of bacteria is harmful to humans
* Recording the effects of certain bacteria on other animals
* Determining the levels of microbes and pathogens present in a strain of bacteria
* Sharing their findings with government agencies and environmental agencies for use in public health and environmental sustainability.
What skills do you need as a bacteriologist?
Here are some key skills that can benefit a bacteriologist in their career:
* Laboratory equipment: Most bacteriologists spend a lot of their work in a laboratory conducting tests and observations. They often need to know how to use equipment like microscopes and magnetic stirrers.
* Identifying microorganisms: A large part of a bacteriologist's job is identifying bacteria. They might also need to be able to identify other types of microorganisms so they can be sure when bacteria are present.
* Chemistry: Chemistry skills can be crucial to a bacteriologist, as many of the tests they conduct use concepts from chemistry. For example, they can use chemistry skills to incite chemical reactions and observe how bacteria react.
* Attention to detail: Bacteriologists observe organisms that are very small, so having strong attention to detail can help them make careful observations. Attention to detail can also make following the steps of an experiment simple.
* Collaboration skills: Collaboration is another key skill for bacteriologists because they often work with other scientists. Knowing how to work with others effectively can help bacteriologists consider information from other specialists and share their own findings.
What education do you need as a bacteriologist?
The minimum education requirement for becoming a bacteriologist is typically a bachelor's degree in microbiology. This is because bacteriology is a subset of microbiology, so candidates usually choose this major to learn about the basic concepts that can inform their work, such as how to observe and classify microorganisms. While they can be optional, graduate degrees can also be common for bacteriologists because master's degree programs can provide more in-depth education and opportunities for practical experience in areas like laboratory work and applying concepts to various industries.
If a bacteriologist is interested in performing independent research or working through a university, they might need a doctoral degree. The most common doctoral degree for a bacteriologist to pursue is a Ph.D. in bacteriology. They might also major in a similar life science, like microbiology or epidemiology.
Additional Information
Bacteriology is a branch of microbiology dealing with the study of bacteria.
The beginnings of bacteriology paralleled the development of the microscope. The first person to see microorganisms was probably the Dutch naturalist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, who in 1683 described some animalcules, as they were then called, in water, saliva, and other substances. These had been seen with a simple lens magnifying about 100–150 diameters. The organisms seem to correspond with some of the very large forms of bacteria as now recognized.
As late as the mid-19th century, bacteria were known only to a few experts and in a few forms as curiosities of the microscope, chiefly interesting for their minuteness and motility. Modern understanding of the forms of bacteria dates from Ferdinand Cohn’s brilliant classifications, the chief results of which were published at various periods between 1853 and 1872. While Cohn and others advanced knowledge of the morphology of bacteria, other researchers, such as Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch, established the connections between bacteria and the processes of fermentation and disease, in the process discarding the theory of spontaneous generation and improving antisepsis in medical treatment.
The modern methods of bacteriological technique had their beginnings in 1870–85 with the introduction of the use of stains and by the discovery of the method of separating mixtures of organisms on plates of nutrient media solidified with gelatin or agar. Important discoveries came in 1880 and 1881, when Pasteur succeeded in immunizing animals against two diseases caused by bacteria. His research led to a study of disease prevention and the treatment of disease by vaccines and immune serums (a branch of medicine now called immunology). Other scientists recognized the importance of bacteria in agriculture and the dairy industry.
Bacteriological study subsequently developed a number of specializations, among which are agricultural, or soil, bacteriology; clinical diagnostic bacteriology; industrial bacteriology; marine bacteriology; public-health bacteriology; sanitary, or hygienic, bacteriology; and systematic bacteriology, which deals with taxonomy.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2394 2024-12-29 00:18:55
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2294) Virology
Gist
Virology is the study of viruses and virus-like agents, including, but not limited to, their taxonomy, disease-producing properties, cultivation, and genetics. Virology is often considered a part of microbiology or pathology.
Summary
Virology is the study of viruses and virus-like agents, including, but not limited to, their taxonomy, disease-producing properties, cultivation, and genetics. Virology is often considered a part of microbiology or pathology.
During the early years of virology, this discipline was dependent upon advances in the chemical and physical sciences; however, viruses soon became tools for probing basic biochemical processes of cells.
Viruses have traditionally been viewed in a rather negative context as agents responsible for diseases that must be controlled or eliminated. However, viruses also have certain beneficial properties that can be exploited for useful purposes, as is evident in both gene therapy and vaccinology.
Characteristics and classification of viruses
Following the announcement of the initial operational definition of a virus as a filterable agent, attempts were made to identify the properties of viruses that separated them from other microorganisms. To this end, the single defining feature of all viruses is that they are obligate intracellular molecular parasites.
A second inviolate property of viruses is that they do not reproduce by binary fission, which is a method of asexual reproduction where pre-existing cells split into two identical daughter cells. For viruses, the process of reproduction is akin to an assembly line, in which different parts come together to create new viral particles.
In general, viruses contain only one type of nucleic acid (either DNA or RNA) that carries the information necessary for viral replication. Nevertheless, it is clear now that some viruses contain other nucleic acid molecules; for example, in retroviruses, cellular transfer RNAs are essential for the action of the enzyme reverse transcriptase.
The chemical composition of viruses varies between different virus families. For the simplest of viruses, the virion is composed of viral structural proteins and nucleic acid; however, the situation becomes more complex with when dealing with enveloped viruses. The latter types of viruses mature by budding through different cellular membranes that are modified by the insertion of viral proteins.
Several properties should be considered most important in constructing a scheme for the classification of all the viruses. These include the nature of the nucleic acid present in the virion, the symmetry of the protein shell, dimensions of the virus particle, as well as the presence or absence of a lipid membrane.
The International Committee on Viral Taxonomy (ICTV), which was given the task of developing a universal taxonomic scheme for all the viruses, has put an emphasis on the viral genome, which is a blueprint for producing new virusesm as a basis of all classification decisions.
In formal virus taxonomy, families, subfamilies, and genera are always written in italics, with the first letters of the names capitalized. Instead of formal names (e.g. Parvoviridae), common names are often used for viruses, as can be seen in the various different kinds of medical literature (e.g. parvoviruses).
Study of viruses
Even from the earliest times, it was clear that the filterable agents could not be cultivated on artificial media. Even today, virus isolation in cell culture is still considered the gold standard against which other assays must be compared.
Still, the most obvious method of virus detection and identification is direct visualization of the agent. The morphology of most viruses is sufficiently characteristic to identify the image as a virus and to assign an unknown virus to the appropriate family. Furthermore, certain non-cultivable viruses can be detectable by electron microscopy.
The culture of animal cells typically involves the use of a culture medium containing salts, glucose, vitamins, amino acids, antimicrobial drugs, buffers, and, typically, blood serum, which provides a source of necessary cellular growth factors. For certain cell-lines, defined serum-free media have been developed, which contain specific growth factors without requiring the addition of blood serum into the medium.
Serological tests are used to show the presence or absence of antibodies to a specific virus. The presence of certain antibodies indicates exposure to the agent, which may be due to a current clinical condition or as a result of an earlier unrelated infection. Some tests that can be used to identify viral antibodies include hemagglutination, complement fixation tests, radioimmunoassays, immunofluorescence, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), radioimmune precipitation, and Western blot assays.
Molecular techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) are also widely used for both the detection of an active virus as well as to determine whether any antibodies against the virus are present. Some of the different applications of PCR tests can be found in diagnostic clinical virology, as well as for research purposes. The use of such nucleic acid-centered technology offers substantial advances in the detection of viruses and can be further enhanced with the incorporation of certain nucleic acid hybridization techniques.
Details
Virology is the scientific study of biological viruses. It is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on their detection, structure, classification and evolution, their methods of infection and exploitation of host cells for reproduction, their interaction with host organism physiology and immunity, the diseases they cause, the techniques to isolate and culture them, and their use in research and therapy.
The identification of the causative agent of tobacco mosaic disease (TMV) as a novel pathogen by Martinus Beijerinck (1898) is now acknowledged as being the official beginning of the field of virology as a discipline distinct from bacteriology. He realized the source was neither a bacterial nor a fungal infection, but something completely different. Beijerinck used the word "virus" to describe the mysterious agent in his 'contagium vivum fluidum' ('contagious living fluid'). Rosalind Franklin proposed the full structure of the tobacco mosaic virus in 1955.
One main motivation for the study of viruses is because they cause many infectious diseases of plants and animals. The study of the manner in which viruses cause disease is viral pathogenesis. The degree to which a virus causes disease is its virulence. These fields of study are called plant virology, animal virology and human or medical virology.
Virology began when there were no methods for propagating or visualizing viruses or specific laboratory tests for viral infections. The methods for separating viral nucleic acids (RNA and DNA) and proteins, which are now the mainstay of virology, did not exist. Now there are many methods for observing the structure and functions of viruses and their component parts. Thousands of different viruses are now known about and virologists often specialize in either the viruses that infect plants, or bacteria and other microorganisms, or animals. Viruses that infect humans are now studied by medical virologists. Virology is a broad subject covering biology, health, animal welfare, agriculture and ecology.
History
Louis Pasteur was unable to find a causative agent for rabies and speculated about a pathogen too small to be detected by microscopes. In 1884, the French microbiologist Charles Chamberland invented the Chamberland filter (or Pasteur-Chamberland filter) with pores small enough to remove all bacteria from a solution passed through it. In 1892, the Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky used this filter to study what is now known as the tobacco mosaic virus: crushed leaf extracts from infected tobacco plants remained infectious even after filtration to remove bacteria. Ivanovsky suggested the infection might be caused by a toxin produced by bacteria, but he did not pursue the idea. At the time it was thought that all infectious agents could be retained by filters and grown on a nutrient medium—this was part of the germ theory of disease.
In 1898, the Dutch microbiologist Martinus Beijerinck repeated the experiments and became convinced that the filtered solution contained a new form of infectious agent. He observed that the agent multiplied only in cells that were dividing, but as his experiments did not show that it was made of particles, he called it a contagium vivum fluidum (soluble living germ) and reintroduced the word virus. Beijerinck maintained that viruses were liquid in nature, a theory later discredited by Wendell Stanley, who proved they were particulate. In the same year, Friedrich Loeffler and Paul Frosch passed the first animal virus, aphthovirus (the agent of foot-and-mouth disease), through a similar filter.
In the early 20th century, the English bacteriologist Frederick Twort discovered a group of viruses that infect bacteria, now called bacteriophages (or commonly 'phages'), and the French-Canadian microbiologist Félix d'Herelle described viruses that, when added to bacteria on an agar plate, would produce areas of dead bacteria. He accurately diluted a suspension of these viruses and discovered that the highest dilutions (lowest virus concentrations), rather than killing all the bacteria, formed discrete areas of dead organisms. Counting these areas and multiplying by the dilution factor allowed him to calculate the number of viruses in the original suspension. Phages were heralded as a potential treatment for diseases such as typhoid and cholera, but their promise was forgotten with the development of penicillin. The development of bacterial resistance to antibiotics has renewed interest in the therapeutic use of bacteriophages.
By the end of the 19th century, viruses were defined in terms of their infectivity, their ability to pass filters, and their requirement for living hosts. Viruses had been grown only in plants and animals. In 1906 Ross Granville Harrison invented a method for growing tissue in lymph, and in 1913 E. Steinhardt, C. Israeli, and R.A. Lambert used this method to grow vaccinia virus in fragments of guinea pig corneal tissue. In 1928, H. B. Maitland and M. C. Maitland grew vaccinia virus in suspensions of minced hens' kidneys. Their method was not widely adopted until the 1950s when poliovirus was grown on a large scale for vaccine production.
Another breakthrough came in 1931 when the American pathologist Ernest William Goodpasture and Alice Miles Woodruff grew influenza and several other viruses in fertilised chicken eggs. In 1949, John Franklin Enders, Thomas Weller, and Frederick Robbins grew poliovirus in cultured cells from aborted human embryonic tissue, the first virus to be grown without using solid animal tissue or eggs. This work enabled Hilary Koprowski, and then Jonas Salk, to make an effective polio vaccine.
The first images of viruses were obtained upon the invention of electron microscopy in 1931 by the German engineers Ernst Ruska and Max Knoll. In 1935, American biochemist and virologist Wendell Meredith Stanley examined the tobacco mosaic virus and found it was mostly made of protein. A short time later, this virus was separated into protein and RNA parts. The tobacco mosaic virus was the first to be crystallised and its structure could, therefore, be elucidated in detail. The first X-ray diffraction pictures of the crystallised virus were obtained by Bernal and Fankuchen in 1941. Based on her X-ray crystallographic pictures, Rosalind Franklin discovered the full structure of the virus in 1955. In the same year, Heinz Fraenkel-Conrat and Robley Williams showed that purified tobacco mosaic virus RNA and its protein coat can assemble by themselves to form functional viruses, suggesting that this simple mechanism was probably the means through which viruses were created within their host cells.
The second half of the 20th century was the golden age of virus discovery, and most of the documented species of animal, plant, and bacterial viruses were discovered during these years. In 1957 equine arterivirus and the cause of bovine virus diarrhoea (a pestivirus) were discovered. In 1963 the hepatitis B virus was discovered by Baruch Blumberg, and in 1965 Howard Temin described the first retrovirus. Reverse transcriptase, the enzyme that retroviruses use to make DNA copies of their RNA, was first described in 1970 by Temin and David Baltimore independently. In 1983 Luc Montagnier's team at the Pasteur Institute in France, first isolated the retrovirus now called HIV. In 1989 Michael Houghton's team at Chiron Corporation discovered hepatitis C.
Detecting viruses
There are several approaches to detecting viruses and these include the detection of virus particles (virions) or their antigens or nucleic acids and infectivity assays.
Electron microscopy
Viruses were seen for the first time in the 1930s when electron microscopes were invented. These microscopes use beams of electrons instead of light, which have a much shorter wavelength and can detect objects that cannot be seen using light microscopes. The highest magnification obtainable by electron microscopes is up to 10,000,000 times whereas for light microscopes it is around 1,500 times.
Virologists often use negative staining to help visualise viruses. In this procedure, the viruses are suspended in a solution of metal salts such as uranium acetate. The atoms of metal are opaque to electrons and the viruses are seen as suspended in a dark background of metal atoms. This technique has been in use since the 1950s. Many viruses were discovered using this technique and negative staining electron microscopy is still a valuable weapon in a virologist's math.
Traditional electron microscopy has disadvantages in that viruses are damaged by drying in the high vacuum inside the electron microscope and the electron beam itself is destructive. In cryogenic electron microscopy the structure of viruses is preserved by embedding them in an environment of vitreous water. This allows the determination of biomolecular structures at near-atomic resolution, and has attracted wide attention to the approach as an alternative to X-ray crystallography or NMR (Nuclear magnetic resonance) spectroscopy for the determination of the structure of viruses.
Growth in cultures
Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites and because they only reproduce inside the living cells of a host these cells are needed to grow them in the laboratory. For viruses that infect animals (usually called "animal viruses") cells grown in laboratory cell cultures are used. In the past, fertile hens' eggs were used and the viruses were grown on the membranes surrounding the embryo. This method is still used in the manufacture of some vaccines. For the viruses that infect bacteria, the bacteriophages, the bacteria growing in test tubes can be used directly. For plant viruses, the natural host plants can be used or, particularly when the infection is not obvious, so-called indicator plants, which show signs of infection more clearly.
Viruses that have grown in cell cultures can be indirectly detected by the detrimental effect they have on the host cell. These cytopathic effects are often characteristic of the type of virus. For instance, herpes simplex viruses produce a characteristic "ballooning" of the cells, typically human fibroblasts. Some viruses, such as mumps virus cause red blood cells from chickens to firmly attach to the infected cells. This is called "haemadsorption" or "hemadsorption". Some viruses produce localised "lesions" in cell layers called plaques, which are useful in quantitation assays and in identifying the species of virus by plaque reduction assays.
Viruses growing in cell cultures are used to measure their susceptibility to validated and novel antiviral drugs.
Serology
Viruses are antigens that induce the production of antibodies and these antibodies can be used in laboratories to study viruses. Related viruses often react with each other's antibodies and some viruses can be named based on the antibodies they react with. The use of the antibodies which were once exclusively derived from the serum (blood fluid) of animals is called serology. Once an antibody–reaction has taken place in a test, other methods are needed to confirm this. Older methods included complement fixation tests, hemagglutination inhibition and virus neutralisation. Newer methods use enzyme immunoassays (EIA).
In the years before PCR was invented immunofluorescence was used to quickly confirm viral infections. It is an infectivity assay that is virus species specific because antibodies are used. The antibodies are tagged with a dye that is luminescencent and when using an optical microscope with a modified light source, infected cells glow in the dark.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and other nucleic acid detection methods
PCR is a mainstay method for detecting viruses in all species including plants and animals. It works by detecting traces of virus specific RNA or DNA. It is very sensitive and specific, but can be easily compromised by contamination. Most of the tests used in veterinary virology and medical virology are based on PCR or similar methods such as transcription mediated amplification. When a novel virus emerges, such as the covid coronavirus, a specific test can be devised quickly so long as the viral genome has been sequenced and unique regions of the viral DNA or RNA identified. The invention of microfluidic tests as allowed for most of these tests to be automated, Despite its specificity and sensitivity, PCR has a disadvantage in that it does not differentiate infectious and non-infectious viruses and "tests of cure" have to be delayed for up to 21 days to allow for residual viral nucleic acid to clear from the site of the infection.
Diagnostic tests
In laboratories many of the diagnostic test for detecting viruses are nucleic acid amplification methods such as PCR. Some tests detect the viruses or their components as these include electron microscopy and enzyme-immunoassays. The so-called "home" or "self"-testing gadgets are usually lateral flow tests, which detect the virus using a tagged monoclonal antibody. These are also used in agriculture, food and environmental sciences.
Quantitation and viral loads
Counting viruses (quantitation) has always had an important role in virology and has become central to the control of some infections of humans where the viral load is measured. There are two basic methods: those that count the fully infective virus particles, which are called infectivity assays, and those that count all the particles including the defective ones.
Infectivity assays
Infectivity assays measure the amount (concentration) of infective viruses in a sample of known volume. For host cells, plants or cultures of bacterial or animal cells are used. Laboratory animals such as mice have also been used particularly in veterinary virology. These are assays are either quantitative where the results are on a continuous scale or quantal, where an event either occurs or it does not. Quantitative assays give absolute values and quantal assays give a statistical probability such as the volume of the test sample needed to ensure 50% of the hosts cells, plants or animals are infected. This is called the median infectious dose or ID 50. Infective bacteriophages can be counted by seeding them onto "lawns" of bacteria in culture dishes. When at low concentrations, the viruses form holes in the lawn that can be counted. The number of viruses is then expressed as plaque forming units. For the bacteriophages that reproduce in bacteria that cannot be grown in cultures, viral load assays are used.
The focus forming assay (FFA) is a variation of the plaque assay, but instead of relying on cell lysis in order to detect plaque formation, the FFA employs immunostaining techniques using fluorescently labeled antibodies specific for a viral antigen to detect infected host cells and infectious virus particles before an actual plaque is formed. The FFA is particularly useful for quantifying classes of viruses that do not lyse the cell membranes, as these viruses would not be amenable to the plaque assay. Like the plaque assay, host cell monolayers are infected with various dilutions of the virus sample and allowed to incubate for a relatively brief incubation period (e.g., 24–72 hours) under a semisolid overlay medium that restricts the spread of infectious virus, creating localized clusters (foci) of infected cells. Plates are subsequently probed with fluorescently labeled antibodies against a viral antigen, and fluorescence microscopy is used to count and quantify the number of foci. The FFA method typically yields results in less time than plaque or fifty-percent-tissue-culture-infective-dose (TCID50) assays, but it can be more expensive in terms of required reagents and equipment. Assay completion time is also dependent on the size of area that the user is counting. A larger area will require more time but can provide a more accurate representation of the sample. Results of the FFA are expressed as focus forming units per milliliter, or FFU.
Viral load assays
When an assay for measuring the infective virus particle is done (Plaque assay, Focus assay), viral titre often refers to the concentration of infectious viral particles, which is different from the total viral particles. Viral load assays usually count the number of viral genomes present rather than the number of particles and use methods similar to PCR. Viral load tests are an important in the control of infections by HIV. This versatile method can be used for plant viruses.
Additional Information
Virology is a branch of microbiology that deals with the study of viruses.
Although diseases caused by viruses have been known since the 1700s and cures for many were (somewhat later) effected, the causative agent was not closely examined until 1892, when a Russian bacteriologist, D. Ivanovski, observed that the causative agent (later proved to be a virus) of tobacco mosaic disease could pass through a porcelain filter impermeable to bacteria. Modern virology began when two bacteriologists, Frederick William Twort in 1915 and Félix d’Hérelle in 1917, independently discovered the existence of bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria).
Direct visualization of viruses became possible after the electron microscope was introduced about 1940. In 1935 tobacco mosaic virus became the first virus to be crystallized; in 1955 the poliomyelitis virus was crystallized. (A virus “crystal” consists of several thousand viruses and, because of its purity, is well suited for chemical studies.) Virology is a discipline of immediate interest because many human diseases, including smallpox, influenza, the common cold, and AIDS, as well as a host of economically important plant and animal diseases, are caused by viruses.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2395 2024-12-30 00:02:18
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2295) Molecular Biology
Gist
Molecular Biology is the field of biology that studies the composition, structure and interactions of cellular molecules – such as nucleic acids and proteins – that carry out the biological processes essential for the cell's functions and maintenance.
What do you mean by molecular biology?
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that studies the molecular basis of biological activity. Living things are made of chemicals just as non-living things are, so a molecular biologist studies how molecules interact with one another in living organisms to perform the functions of life.
Summary
Molecular Biology is a field of science concerned with studying the chemical structures and processes of biological phenomena that involve the basic units of life, molecules. The field of molecular biology is focused especially on nucleic acids (e.g., DNA and RNA) and proteins—macromolecules that are essential to life processes—and how these molecules interact and behave within cells. Molecular biology emerged in the 1930s, having developed out of the related fields of biochemistry, genetics, and biophysics; today it remains closely associated with those fields.
Techniques
Various techniques have been developed for molecular biology, though researchers in the field may also employ methods and techniques native to genetics and other closely associated fields. In particular, molecular biology seeks to understand the three-dimensional structure of biological macromolecules through techniques such as X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy. The discipline particularly seeks to understand the molecular basis of genetic processes; molecular biologists map the location of genes on specific chromosomes, associate these genes with particular characters of an organism, and use genetic engineering (recombinant DNA technology) to isolate, sequence, and modify specific genes. These approaches can also include techniques such as polymerase chain reaction, western blotting, and microarray analysis.
Historical developments
In its early period during the 1940s, the field of molecular biology was concerned with elucidating the basic three-dimensional structure of proteins. Growing knowledge of the structure of proteins in the early 1950s enabled the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)—the genetic blueprint found in all living things—to be described in 1953. Further research enabled scientists to gain an increasingly detailed knowledge not only of DNA and ribonucleic acid (RNA) but also of the chemical sequences within these substances that instruct the cells and viruses to make proteins.
Molecular biology remained a pure science with few practical applications until the 1970s, when certain types of enzymes were discovered that could cut and recombine segments of DNA in the chromosomes of certain bacteria. The resulting recombinant DNA technology became one of the most active branches of molecular biology because it allows the manipulation of the genetic sequences that determine the basic characters of organisms.
Details
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions.
Though cells and other microscopic structures had been observed in living organisms as early as the 18th century, a detailed understanding of the mechanisms and interactions governing their behavior did not emerge until the 20th century, when technologies used in physics and chemistry had advanced sufficiently to permit their application in the biological sciences. The term 'molecular biology' was first used in 1945 by the English physicist William Astbury, who described it as an approach focused on discerning the underpinnings of biological phenomena—i.e. uncovering the physical and chemical structures and properties of biological molecules, as well as their interactions with other molecules and how these interactions explain observations of so-called classical biology, which instead studies biological processes at larger scales and higher levels of organization. In 1953, Francis Crick, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and their colleagues at the Medical Research Council Unit, Cavendish Laboratory, were the first to describe the double helix model for the chemical structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which is often considered a landmark event for the nascent field because it provided a physico-chemical basis by which to understand the previously nebulous idea of nucleic acids as the primary substance of biological inheritance. They proposed this structure based on previous research done by Franklin, which was conveyed to them by Maurice Wilkins and Max Perutz. Their work led to the discovery of DNA in other microorganisms, plants, and animals.
The field of molecular biology includes techniques which enable scientists to learn about molecular processes. These techniques are used to efficiently target new drugs, diagnose disease, and better understand cell physiology. Some clinical research and medical therapies arising from molecular biology are covered under gene therapy, whereas the use of molecular biology or molecular cell biology in medicine is now referred to as molecular medicine.
History of molecular biology
Molecular biology sits at the intersection of biochemistry and genetics; as these scientific disciplines emerged and evolved in the 20th century, it became clear that they both sought to determine the molecular mechanisms which underlie vital cellular functions. Advances in molecular biology have been closely related to the development of new technologies and their optimization. Molecular biology has been elucidated by the work of many scientists, and thus the history of the field depends on an understanding of these scientists and their experiments.
The field of genetics arose from attempts to understand the set of rules underlying reproduction and heredity, and the nature of the hypothetical units of heredity known as genes. Gregor Mendel pioneered this work in 1866, when he first described the laws of inheritance he observed in his studies of mating crosses in pea plants. One such law of genetic inheritance is the law of segregation, which states that diploid individuals with two alleles for a particular gene will pass one of these alleles to their offspring. Because of his critical work, the study of genetic inheritance is commonly referred to as Mendelian genetics.
A major milestone in molecular biology was the discovery of the structure of DNA. This work began in 1869 by Friedrich Miescher, a Swiss biochemist who first proposed a structure called nuclein, which we now know to be (deoxyribonucleic acid), or DNA. He discovered this unique substance by studying the components of pus-filled bandages, and noting the unique properties of the "phosphorus-containing substances". Another notable contributor to the DNA model was Phoebus Levene, who proposed the "polynucleotide model" of DNA in 1919 as a result of his biochemical experiments on yeast. In 1950, Erwin Chargaff expanded on the work of Levene and elucidated a few critical properties of nucleic acids: first, the sequence of nucleic acids varies across species. Second, the total concentration of purines (adenine and guanine) is always equal to the total concentration of pyrimidines (cysteine and thymine). This is now known as Chargaff's rule. In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick published the double helical structure of DNA, based on the X-ray crystallography work done by Rosalind Franklin which was conveyed to them by Maurice Wilkins and Max Perutz. Watson and Crick described the structure of DNA and conjectured about the implications of this unique structure for possible mechanisms of DNA replication. Watson and Crick were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1962, along with Wilkins, for proposing a model of the structure of DNA.
In 1961, it was demonstrated that when a gene encodes a protein, three sequential bases of a gene's DNA specify each successive amino acid of the protein. Thus the genetic code is a triplet code, where each triplet (called a codon) specifies a particular amino acid. Furthermore, it was shown that the codons do not overlap with each other in the DNA sequence encoding a protein, and that each sequence is read from a fixed starting point. During 1962–1964, through the use of conditional lethal mutants of a bacterial virus, fundamental advances were made in our understanding of the functions and interactions of the proteins employed in the machinery of DNA replication, DNA repair, DNA recombination, and in the assembly of molecular structures.
Modern molecular biology
In the early 2020s, molecular biology entered a golden age defined by both vertical and horizontal technical development. Vertically, novel technologies are allowing for real-time monitoring of biological processes at the atomic level. Molecular biologists today have access to increasingly affordable sequencing data at increasingly higher depths, facilitating the development of novel genetic manipulation methods in new non-model organisms. Likewise, synthetic molecular biologists will drive the industrial production of small and macro molecules through the introduction of exogenous metabolic pathways in various prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell lines.
Horizontally, sequencing data is becoming more affordable and used in many different scientific fields. This will drive the development of industries in developing nations and increase accessibility to individual researchers. Likewise, CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing experiments can now be conceived and implemented by individuals for under $10,000 in novel organisms, which will drive the development of industrial and medical applications.
Relationship to other biological sciences
The following list describes a viewpoint on the interdisciplinary relationships between molecular biology and other related fields.
* Molecular biology is the study of the molecular underpinnings of the biological phenomena, focusing on molecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms and interactions.
* Biochemistry is the study of the chemical substances and vital processes occurring in living organisms. Biochemists focus heavily on the role, function, and structure of biomolecules such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids.
* Genetics is the study of how genetic differences affect organisms. Genetics attempts to predict how mutations, individual genes and genetic interactions can affect the expression of a phenotype.
While researchers practice techniques specific to molecular biology, it is common to combine these with methods from genetics and biochemistry. Much of molecular biology is quantitative, and recently a significant amount of work has been done using computer science techniques such as bioinformatics and computational biology. Molecular genetics, the study of gene structure and function, has been among the most prominent sub-fields of molecular biology since the early 2000s. Other branches of biology are informed by molecular biology, by either directly studying the interactions of molecules in their own right such as in cell biology and developmental biology, or indirectly, where molecular techniques are used to infer historical attributes of populations or species, as in fields in evolutionary biology such as population genetics and phylogenetics. There is also a long tradition of studying biomolecules "from the ground up", or molecularly, in biophysics.
Additional Information
The field of molecular biology studies macromolecules and the macromolecular mechanisms found in living things, such as the molecular nature of the gene and its mechanisms of gene replication, mutation, and expression. Given the fundamental importance of a mechanistic and macromolecular mode of explanation in many biological disciplines, the widespread reliance on molecular techniques such as gel electrophoresis, sequencing, and PCR, as well as the involvement of molecular biology in recent technological breakthroughs such as CRISPR, mRNA vaccines and optogenetics, the history and concepts of molecular biology constitute a focal point of contemporary philosophy of science and biology.
Molecular biology emphasizes the study of molecules that make up an organism, how they interact, and how they are controlled. With the development of the field of genomics, biologists also study one class of molecules (DNA) at the whole genome level. Molecular biology and genomics are applied within all biological disciplines, including biochemistry, cell biology, and developmental biology. Molecular biology and genomics developments have revolutionized biological research, fueling the explosive growth in the biotechnology industry and rapid increase of molecular medicine.
The Molecular Biology and Genomics major provides a strong background for many science careers, incorporating the requirements expected for admission to medical, dental, and other health professional schools and to graduate schools in cell and molecular biology, biochemistry, and related disciplines. Positions for molecular biologists at the BS, MS, and PhD levels are available in the biotechnology industries as well as in universities, medical schools, hospitals, government laboratories, research institutes, and public health institutions.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2396 2024-12-31 00:14:51
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2296) Management accounting
Gist
What is management accounting? Managerial accounting, also called management accounting, is a method of accounting that creates statements, reports, and documents that help management in making better decisions related to their business' performance. Managerial accounting is primarily used for internal purposes.
Summary
Although published financial statements are the most widely visible products of business accounting systems and the ones with which the public is most concerned, they represent only a small portion of all the accounting activities that support an organization. Most accounting data and most accounting reports are generated solely or mainly for the company’s managers. Reports to management may be either summaries of past events, forecasts of the future, or a combination of the two. Preparation of these data and reports is the focus of managerial accounting, which consists mainly of four broad functions: (1) budgetary planning, (2) cost finding, (3) cost and profit analysis, and (4) performance reporting.
Details
In management accounting or managerial accounting, managers use accounting information in decision-making and to assist in the management and performance of their control functions.
Definition
One simple definition of management accounting is the provision of financial and non-financial decision-making information to managers. In other words, management accounting helps the directors inside an organization to make decisions. This can also be known as Cost Accounting. This is the way toward distinguishing, examining, deciphering and imparting data to supervisors to help accomplish business goals. The information gathered includes all fields of accounting that educates the administration regarding business tasks identifying with the financial expenses and decisions made by the organization. Accountants use plans to measure the overall strategy of operations within the organization.
According to the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA), "Management accounting is a profession that involves partnering in management decision making, devising planning and performance management systems, and providing expertise in financial reporting and control to assist management in the formulation and implementation of an organization's strategy".
Management accountants (also called managerial accountants) look at the events that happen in and around a business while considering the needs of the business. From this, data and estimates emerge. Cost accounting is the process of translating these estimates and data into knowledge that will ultimately be used to guide decision-making.
The Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (CIMA) being the largest management accounting institute with over 100,000 members describes Management accounting as analysing information to advise business strategy and drive sustainable business success.
The Institute of Certified Management Accountants (ICMA) has over 15,000 qualified professionals worldwide, with members in 50-countries. Its CMA postgraduate education program now is firmly established in 19 overseas markets, namely Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, Cyprus, Dubai, Hong Kong, India, Indonesia, Iran, Japan, Lebanon, Malaysia, Nepal, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Philippines; Singapore, Sri Lanka, Thailand and Vietnam.
To facilitate its educational objectives, the Institute has accredited a number of universities which have master's degree subjects that are equivalent to the CMA program. Some of these universities also provide in-house training and examinations of the CMA program. Accounting graduates can do CMA accredited units at these universities to qualify for CMA status. The ICMA also has a number of Recognised Provider Institutions (RPIs) that run the CMA program in Australia and overseas. The CMA program is also available online in regions where the face-to-face delivery of the program is not possible.
Scope, practice, and application
The Association of International Certified Professional Accountants (AICPA) states management accounting as a practice that extends to the following three areas:
* Strategic management — advancing the role of the management accountant as a strategic partner in the organization
* Performance management — developing the practice of business decision-making and managing the performance of the organization
* Risk management — contributing to frameworks and practices for identifying, measuring, managing and reporting risks to the achievement of the objectives of the organization
The Institute of Certified Management Accountants (CMA) states, "A management accountant applies his or her professional knowledge and skill in the preparation and presentation of financial and other decision oriented information in such a way as to assist management in the formulation of policies and in the planning and control of the operation undertaking".
Management accountants are seen as the "value-creators" amongst the accountants. They are more concerned with forward-looking and taking decisions that will affect the future of the organization; than in the historical recording and compliance (score keeping) aspects of the profession. Management accounting knowledge and experience can be obtained from varied fields and functions within an organization, such as information management, treasury, efficiency auditing, marketing, valuation, pricing, and logistics. In 2014 CIMA created the Global Management Accounting Principles (GMAPs). The result of research from across 20 countries in five continents, the principles aim to guide best practice in the discipline.
Financial versus Management accounting
Management accounting information differs from financial accountancy information in several ways:
* while shareholders, creditors, and public regulators use publicly reported financial accountancy, information, only managers within the organization use the normally confidential management accounting information
* while financial accountancy information is historical, management accounting information is primarily forward-looking;
* while financial accountancy information is case-based, management accounting information is model-based with a degree of abstraction in order to support generic decision making;
* while financial accountancy information is computed by reference to general financial accounting standards, management accounting information is computed by reference to the needs of managers, often using management information systems.
Focus:
* Financial accounting focuses on the company as a whole.
* Management accounting provides detailed and disaggregated information about products, individual activities, divisions, plants, operations and tasks.
Traditional versus innovative practices
The distinction between traditional and innovative accounting practices is illustrated with the visual timeline of managerial costing approaches presented at the Institute of Management Accountants 2011 Annual Conference.
Traditional standard costing (TSC), used in cost accounting, dates back to the 1920s and is a central method in management accounting practiced today because it is used for financial statement reporting for the valuation of income statement and balance sheet line items such as cost of goods sold (COGS) and inventory valuation. Traditional standard costing must comply with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP US) and actually aligns itself more with answering financial accounting requirements rather than providing solutions for management accountants. Traditional approaches limit themselves by defining cost behavior only in terms of production or sales volume.
In the late 1980s, accounting practitioners and educators were heavily criticized on the grounds that management accounting practices (and, even more so, the curriculum taught to accounting students) had changed little over the preceding 60 years, despite radical changes in the business environment. In 1993, the Accounting Education Change Commission Statement Number 4 calls for faculty members to expand their knowledge about the actual practice of accounting in the workplace. Professional accounting institutes, perhaps fearing that management accountants would increasingly be seen as superfluous in business organizations, subsequently devoted considerable resources to the development of a more innovative skills set for management accountants.
Variance analysis is a systematic approach to the comparison of the actual and budgeted costs of the raw materials and labour used during a production period. While some form of variance analysis is still used by most manufacturing firms, it nowadays tends to be used in conjunction with innovative techniques such as life cycle cost analysis and activity-based costing, which are designed with specific aspects of the modern business environment in mind. Life-cycle costing recognizes that managers' ability to influence the cost of manufacturing a product is at its greatest when the product is still at the design stage of its product life-cycle (i.e., before the design has been finalized and production commenced), since small changes to the product design may lead to significant savings in the cost of manufacturing the products.
Activity-based costing (ABC) recognizes that, in modern factories, most manufacturing costs are determined by the amount of 'activities' (e.g., the number of production runs per month, and the amount of production equipment idle time) and that the key to effective cost control is therefore optimizing the efficiency of these activities. Both lifecycle costing and activity-based costing recognize that, in the typical modern factory, the avoidance of disruptive events (such as machine breakdowns and quality control failures) is of far greater importance than (for example) reducing the costs of raw materials. Activity-based costing also de-emphasizes direct labor as a cost driver and concentrates instead on activities that drive costs, as the provision of a service or the production of a product component.
Other approach is the German Grenzplankostenrechnung (GPK) costing methodology. Although it has been in practiced in Europe for more than 50 years, neither GPK nor the proper treatment of 'unused capacity' is widely practiced in the U.S.
Another accounting practice available today is resource consumption accounting (RCA). RCA has been recognized by the International Federation of Accountants (IFAC) as a "sophisticated approach at the upper levels of the continuum of costing techniques". The approach provides the ability to derive costs directly from operational resource data or to isolate and measure unused capacity costs. RCA was derived by taking costing characteristics of GPK, and combining the use of activity-based drivers when needed, such as those used in activity-based costing.
A modern approach to close accounting is continuous accounting, which focuses on achieving a point-in-time close, where accounting processes typically performed at period-end are distributed evenly throughout the period.
Additional Information:
What Is Managerial Accounting?
Managerial accounting is the practice of identifying, measuring, analyzing, interpreting, and communicating financial information to managers for the pursuit of an organization's goals.
Managerial accounting differs from financial accounting because the intended purpose of managerial accounting is to assist users internal to the company in making well-informed business decisions.
Key Takeaways:
* Managerial accounting involves the presentation of financial information for internal purposes to be used by management in making key business decisions.
* Techniques used by managerial accountants are not dictated by accounting standards, unlike financial accounting.
* The presentation of managerial accounting data can be modified to meet the specific needs of its end-user.
* Managerial accounting encompasses many facets of accounting, including product costing, budgeting, forecasting, and various financial analysis.
* This differs from financial accounting, which produces and disseminates official financial statements for public consumption that conform to prevailing accounting standards.
Managerial Accounting:
How Managerial Accounting Works
Managerial accounting aims to improve the quality of information delivered to management about business operation metrics. Managerial accountants use information relating to the cost and sales revenue of goods and services generated by the company. Cost accounting is a large subset of managerial accounting that specifically focuses on capturing a company's total costs of production by assessing the variable costs of each step of production, as well as fixed costs. It allows businesses to identify and reduce unnecessary spending and maximize profits.
The pillars of managerial accounting are planning, decision-making, and controlling. In addition, forecasting and performance tracking are key components. Through this focus, managerial accountants provide information that aims to help companies and departments in these key areas.
Managerial Accounting vs. Financial Accounting
The key difference between managerial accounting and financial accounting relates to the intended users of the information. Managerial accounting information is aimed at helping managers within the organization make well-informed business decisions, while financial accounting is aimed at providing financial information to parties outside the organization.
Financial accounting must conform to certain standards, such as generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). All publicly held companies are required to complete their financial statements in accordance with GAAP as a requisite for maintaining their publicly traded status. Most other companies in the U.S. conform to GAAP in order to meet debt covenants often required by financial institutions offering lines of credit.
Because managerial accounting is not for external users, it can be modified to meet the needs of its intended users. This may vary considerably by company or even by department within a company. For example, managers in the production department may want to see their financial information displayed as a percentage of units produced in the period. The HR department manager may be interested in seeing a graph of salaries by employee over a period of time. Managerial accounting is able to meet the needs of both departments by offering information in whatever format is most beneficial to that specific need.
Note: Managerial accounting does not need to follow GAAP standards because it is used for internal purposes and not for external reports.
Types of Managerial Accounting:
Product Costing and Valuation
Product costing deals with determining the total costs involved in the production of a good or service. Costs may be broken down into subcategories, such as variable, fixed, direct, or indirect costs. Cost accounting is used to measure and identify those costs, in addition to assigning overhead to each type of product created by the company.
Managerial accountants calculate and allocate overhead charges to assess the full expense related to the production of a good. The overhead expenses may be allocated based on the number of goods produced or other activity drivers related to production, such as the square footage of the facility. In conjunction with overhead costs, managerial accountants use direct costs to properly value the cost of goods sold and inventory that may be in different stages of production.
Marginal costing (sometimes called cost-volume-profit analysis) is the impact on the cost of a product by adding one additional unit into production. It is useful for short-term economic decisions. The contribution margin of a specific product is its impact on the overall profit of the company. Margin analysis flows into break-even analysis, which involves calculating the contribution margin on the sales mix to determine the unit volume at which the business’s gross sales equals total expenses. Break-even point analysis is useful for determining price points for products and services.
Cash Flow Analysis
Managerial accountants perform cash flow analysis in order to determine the cash impact of business decisions. Most companies record their financial information on the accrual basis of accounting. Although accrual accounting provides a more accurate picture of a company's true financial position, it also makes it harder to see the true cash impact of a single financial transaction. A managerial accountant may implement working capital management strategies in order to optimize cash flow and ensure the company has enough liquid assets to cover short-term obligations.
When a managerial accountant performs cash flow analysis, he will consider the cash inflow or outflow generated as a result of a specific business decision. For example, if a department manager is considering purchasing a company vehicle, he may have the option to either buy the vehicle outright or get a loan. A managerial accountant may run different scenarios by the department manager depicting the cash outlay required to purchase outright upfront versus the cash outlay over time with a loan at various interest rates.
Inventory Turnover Analysis
Inventory turnover is a calculation of how many times a company has sold and replaced inventory in a given time period. Calculating inventory turnover can help businesses make better decisions on pricing, manufacturing, marketing, and purchasing new inventory. A managerial accountant may identify the carrying cost of inventory, which is the amount of expense a company incurs to store unsold items.
If the company is carrying an excessive amount of inventory, there could be efficiency improvements made to reduce storage costs and free up cash flow for other business purposes.
Constraint Analysis
Managerial accounting also involves reviewing the constraints within a production line or sales process. Managerial accountants help determine where bottlenecks occur and calculate the impact of these constraints on revenue, profit, and cash flow. Managers then can use this information to implement changes and improve efficiencies in the production or sales process.
Financial Leverage Metrics
Financial leverage refers to a company's use of borrowed capital in order to acquire assets and increase its return on investments. Through balance sheet analysis, managerial accountants can provide management with the tools they need to study the company's debt and equity mix in order to put leverage to its most optimal use.
Performance measures such as return on equity, debt to equity, and return on invested capital help management identify key information about borrowed capital, prior to relaying these statistics to outside sources. It is important for management to review ratios and statistics regularly to be able to appropriately answer questions from its board of directors, investors, and creditors.
Accounts Receivable (AR) Management
Appropriately managing accounts receivable (AR) can have positive effects on a company's bottom line. An accounts receivable aging report categorizes AR invoices by the length of time they have been outstanding. For example, an AR aging report may list all outstanding receivables less than 30 days, 30 to 60 days, 60 to 90 days, and 90+ days.
Through a review of outstanding receivables, managerial accountants can indicate to appropriate department managers if certain customers are becoming credit risks. If a customer routinely pays late, management may reconsider doing any future business on credit with that customer.
Budgeting, Trend Analysis, and Forecasting
Budgets are extensively used as a quantitative expression of the company's plan of operation. Managerial accountants utilize performance reports to note deviations of actual results from budgets. The positive or negative deviations from a budget also referred to as budget-to-actual variances, are analyzed in order to make appropriate changes going forward.
Managerial accountants analyze and relay information related to capital expenditure decisions. This includes the use of standard capital budgeting metrics, such as net present value and internal rate of return, to assist decision-makers on whether to embark on capital-intensive projects or purchases. Managerial accounting involves examining proposals, deciding if the products or services are needed, and finding the appropriate way to finance the purchase. It also outlines payback periods so management is able to anticipate future economic benefits.
Managerial accounting also involves reviewing the trendline for certain expenses and investigating unusual variances or deviations. It is important to review this information regularly because expenses that vary considerably from what is typically expected are commonly questioned during external financial audits. This field of accounting also utilizes previous period information to calculate and project future financial information. This may include the use of historical pricing, sales volumes, geographical locations, customer tendencies, or financial information.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2397 2025-01-01 00:06:47
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2297) Librarian
Gist
A Librarian is a professional who facilitates access to information and resources within a library. They curate collections, develop educational programs, manage databases, and oversee library staff. Their role is to support learning, research, and exploration for library members.
Summary
A person who works in a library is called a librarian. Librarians are also known as information scientists. Information can be found in so many places that people may not know the best places to look. Librarians can help. They connect people with information.
There are many different jobs that must be done to keep a library organized and up-to-date. Some librarians decide what materials should be in the library. These librarians are in charge of buying new materials. They also decide when to get rid of materials that are no longer useful.
Circulation librarians organize the library. They make sure materials are easy to find on the shelves. They manage the circulation desk, which is where materials are checked out, renewed, and returned. Circulation librarians are also responsible for collecting late fees and for handling interlibrary loans. Reference librarians help library patrons do research. Reference librarians work with patrons of all ages and help them to find the right resources for their research.
A librarian may specialize in a particular age group. For instance, a children’s librarian must know about child behavior, children’s literature, storytelling technique, and the teaching of reading. A young adult librarian works with teenagers. This kind of librarian must be familiar with what this group studies in school and with current youth culture.
Librarians need a fairly extensive education. A person interested in becoming a librarian must first go to college to earn a bachelor’s degree. This degree can be in any field. The next step is to complete a master’s degree in library and information sciences. Some librarians may choose to further their education even more. They may earn another master’s degree or even a doctorate if they want to work at a specialty library, such as a law library or a medical library.
Details
A librarian is a person who professionally works managing information. Librarians' common activities include providing access to information, conducting research, creating and managing information systems, creating, leading, and evaluating educational programs, and providing instruction on information literacy to users.
The role of the librarian has changed over time, with the past century in particular bringing many new media and technologies into play. From the earliest libraries in the ancient world to the modern information hub, there have been keepers and disseminators of the information held in data stores. Roles and responsibilities vary widely depending on the type of library, the specialty of the librarian, and the functions needed to maintain collections and make them available to its users.
Education for librarianship has changed over time to reflect changing roles.
Modern era
While there were full-time librarians in the 18th century, the professionalization of the library role was a 19th-century development, as shown by its first training school, its first university school, and its first professional associations and licensing procedures.
In England in the 1870s, a new employment role opened for women in libraries; it was said that the tasks were "Eminently Suited to Girls and Women." By 1920, women and men were equally numerous in the library profession, but women pulled ahead by 1930 and comprised 80% by 1960. The factors accounting for the transition included the demographic losses of the First World War, the provisions of the Public Libraries Act of 1919, the library-building activity of the Carnegie United Kingdom Trust, and the library employment advocacy of the Central Bureau for the Employment of Women. In the United Kingdom, evidence suggests that the Conservative government began replacing professional librarians with unpaid volunteers in 2015–2016.
COVID-19 pandemic in the US
During the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States in 2020, many librarians were temporarily displaced as libraries across the country were affected by a nationwide shutdown in efforts to control the spread of SARS-CoV-2 disease. During this time, library services were in high demand as patrons were stuck inside during quarantine, but with limited building access, most public library patrons switched to digital content, online learning, and virtual programs.
As the crisis escalated, there was a high demand for contact tracers, and the CDC had earlier named librarians as key public health staff to support COVID-19 case investigation and contact tracing, so many librarians and library staff volunteered to help with contact tracing. Librarians also supported their community in other ways, such as staffing non-emergency hotlines and manning shelters for the homeless, for which they were able to retain their income, while others were furloughed for a time.
The Librarian Reserve Corps was formed during the COVID-19 pandemic. It was a global network of volunteer librarians, specializing in academic libraries and medical libraries, serving as "information first responders" in the fight against the Infodemic as a direct result of COVID-19 pandemic. The Librarian Reserve Corps Literature Enhancement and Metadata Enrichment (LIME) volunteers, led by Jessica Callaway, vetted, indexed, and helped disseminate resources about COVID-19 to various organizations, including the Global Outbreak Alert and Response Network (GOARN) and the World Health Organization. As of November 2021, the Librarian Reserve Corps has vetted over 60,000 publications relating to COVID-19. The Librarian Reserve Corps founder, Elaine Hicks, and co-leadership Stacy Brody and Sara Loree, were awarded the 2021 Librarian of the Year title from Library Journal.
Roles and responsibilities
Traditionally, a librarian is associated with collections of books, as demonstrated by the etymology of the word "librarian" (from the Latin liber, "book"). A 1713 definition of the word was "custodian of a library", while in the 17th century, the role was referred to as a "library-keeper", and a librarian was a "scribe, one who copies books".
The role of a librarian is continually evolving to meet social and technological needs. A modern librarian may deal with provision and maintenance of information in many formats, including books; electronic resources; magazines; newspapers; audio and video recordings; maps; manuscripts; photographs and other graphic material; bibliographic databases; and Internet-based and digital resources. A librarian may also provide other information services, such as information literacy instruction; computer provision and training; coordination with community groups to host public programs; assistive technology for people with disabilities; and assistance locating community resources.
The Internet has had a profound impact on the resources and services that librarians of all kinds provide to their patrons. Electronic information has transformed the roles and responsibilities of librarians, even to the point of revolutionizing library education and service expectations.
Positions and duties
Specific duties vary depending on the size and type of library. Olivia Crosby described librarians as "Information experts in the information age." Most librarians spend their time working in one of the following areas of a library: Archivists can be specialized librarians who deal with archival materials, such as manuscripts, documents and records, though this varies from country to country, and there are other routes to the archival profession.
Collection development or acquisitions librarians monitor the selection of books and electronic resources. Large libraries often use approval plans, which involve the librarian for a specific subject creating a profile that allows publishers to send relevant books to the library without any additional vetting. Librarians can then see those books when they arrive and decide if they will become part of the collection or not. All collections librarians also have a certain amount of funding to allow them to purchase books and materials that don't arrive via approval.
Electronic resources librarians manage the databases that libraries license from third-party vendors. School librarians work in school libraries and perform duties as teachers, information technology specialists, and advocates for literacy. Instruction librarians teach information literacy skills in face-to-face classes or through the creation of online learning objects. They instruct library users on how to find, evaluate, and use information effectively. They are most common in academic libraries.
Media specialists teach students to find and analyze information, purchase books and other resources for the school library, supervise library assistants, and are responsible for all aspects of running the library/media center. Both library media teachers (LMTs) and young adult public librarians order books and other materials that will interest their young adult patrons. They also must help YAs find relevant and authoritative Internet resources. Helping this age group to become lifelong learners and readers is a main objective of professionals in this library specialty.
Outreach librarians are charged with providing library and information services for underrepresented groups, such as people with disabilities, low-income neighborhoods, home bound adults and seniors, incarcerated and ex-offenders, and homeless and rural communities. In academic libraries, outreach librarians might focus on high school students, transfer students, first-generation college students, and minorities.
Public service librarians work with the public, frequently at the reference desk of lending libraries. Some specialize in serving adults or children. Children's librarians provide appropriate material for children at all age levels, include pre-readers, conduct specialized programs and work with the children (and often their parents) to help foster interest and competence in the young reader. (In larger libraries, some specialize in teen services, periodicals, or other special collections.)
Reference or research librarians help people doing research to find the information they need, through a structured conversation called a reference interview. The help may take the form of research on a specific question, providing direction on the use of databases and other electronic information resources; obtaining specialized materials from other sources; or providing access to and care of delicate or expensive materials. These services are sometimes provided by other library staff that have been given a certain amount of special training; some have criticized this trend.
Systems librarians develop, troubleshoot and maintain library systems, including the library catalog and related systems. Technical service librarians work "behind the scenes" ordering library materials and database subscriptions, computers and other equipment, and supervise the cataloging and physical processing of new materials. A Youth Services librarian, or children's librarian, is in charge of serving young patrons from infancy all the way to young adulthood. Their duties vary, from planning summer reading programs to weekly story hour programs. They are multitaskers, as the children's section of a library may act as its own separate library within the same building. Children's librarians must be knowledgeable of popular books for school-aged children and other library items, such as e-books and audiobooks. They are charged with the task of creating a safe and fun learning environment outside of school and the home.
A young adult or YA librarian specifically serves patrons who are between 12 and 18 years old. Young adults are those patrons that look to library services to give them direction and guidance toward recreation, education, and emancipation. A young adult librarian could work in several different institutions; one might be a school library/media teacher, a member of a public library team, or a librarian in a penal institution. Licensing for library/media teacher includes a Bachelor or Master of Arts in Teaching and additional higher-level course work in library science. YA librarians who work in public libraries are expected to have a master's degree in Library and Information Science (MLIS), relevant work experience, or a related credential.
Additional responsibilities
Experienced librarians may take administrative positions such as library or information center director or learning resource officer. Similar to the management of any other organization, they are concerned with the long-term planning of the library, and its relationship with its parent organization (the city or county for a public library, the college/university for an academic library, or the organization served by a special library). In smaller or specialized libraries, librarians typically perform a wide range of the different duties.
Representative examples of librarian responsibilities:
* Researching topics of interest for their constituencies.
* Referring patrons to other community organizations and government offices.
* Suggesting appropriate books ("readers' advisory") for children of different reading levels and recommending novels for recreational reading.
* Reviewing books and journal databases
* Working with other education organisations to establish continual, lifelong learning and further education initiatives
* Facilitating and promoting reading clubs.
* Developing programs for library users of all ages and backgrounds.
* Managing access to electronic information resources.
* Assessing library services and collections in order to best meet library users' needs.
* Building and maintaining collections to respond to changing community needs or demands
* Creating pathfinders
* Writing grants to gain funding for expanded program or collections
* Digitizing collections for online access
* Publishing articles in library science journals
* Answering incoming reference questions via telephone, postal mail, email, fax, and chat
* Delivering arts and cultural activities to local communities
* Initiating and establishing creative digital activities to introduce children to coding, engineering and website building
* Marking promotion and advocacy of library services
* Assisting job seekers and local businesses
* Making and enforcing computer appointments on the public access Internet computers.
Librarians and work-related stress
As user and community needs change over time, the role of the librarian continues to reflect these changes. Librarians assist and interact with vulnerable or at-risk populations regularly. It is proposed that librarians experience a moderate degree of work-related stress, and is reported that many experience harassment or emotionally challenging situations in their daily work. The public library in particular can often be described as having an emotionally charged atmosphere. There is evidence to suggest that specialized librarians might experience similar conditions. For example, health science librarians report experiencing a mild to moderate amount of secondary traumatic stress that develops from working closely with patients who are experiencing trauma.
Changing roles of librarians
There are a number of contributing factors to the librarians’ roles changing.
* Development in information technology
* Changing economy
* Changing educational and learning environment
* Changes in scholarly communication.
Additional Information
School librarians have the opportunity to pass on a love for reading to students of all ages. School librarians also teach student the fundamentals of using a library and its resources.
Often times, these librarians collaborate with teachers to help them find necessary materials and resources to enhance classroom instruction.
Qualities of a School Librarian
An effective school librarian will love books and love to inspire children to read. They must have effective communication skills and should be able to work well with others.
Depending on the school and budgets, school librarians may work a full time schedule similar to teachers. However, some schools may have part-time school librarians.
How to Become a School Librarian
A basic requirement for becoming a school librarian is to hold a bachelor's degree and pass any district-required librarian examinations. However, many school districts require a master's degree and a teaching certificate as well. Sometimes, school librarians may be required to have experience as a teacher before being able to become a certified librarian.
As mentioned earlier, some states may require a master's degree while other states require only certification or licensure. If you are interested in becoming a licensed school librarian, you may contact your state's department of education for specific requirements. Librarians with a master's degree will have more selection in regard to options for employment with other types of libraries. Many school librarians earn a degree in Library Science.
Master of Library Science (MLS)
The Master of Library Science (MLS) is a common graduate degree program for pursuing a career as a school librarian. Those planning on working as a school librarian will need to make sure their chosen program is accredited by the American Library Association (ALA). Graduation from an accredited ALA program is a requirement in some states to work as a school librarian. Master's program classes will usually involve courses in library management, children's literature, and learning technologies.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2398 2025-01-01 21:39:35
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2298) Space Exploration
Gist
Space exploration refers to the act of exploring and studying celestial bodies beyond Earth, such as the Moon and Mars, with the aim of gathering data, potentially colonizing other planets, and advancing astronautical engineering, medicine, and robotics.
We explore in many ways: in person, using space probes, and using telescopes. Space probes have many types and parts: Fly-by missions pass nearby planets and moons and take data from a distance. Orbiters are parts of missions designed to stay in orbit.
Space exploration thus supports innovation and economic prosperity by stimulating advances in science and technology, as well as motivating the global scientific and technological workforce, thus enlarging the sphere of human economic activity.
Summary
Space exploration is investigation, by means of crewed and uncrewed spacecraft, of the reaches of the universe beyond Earth’s atmosphere and the use of the information so gained to increase knowledge of the cosmos and benefit humanity. A complete list of all crewed spaceflights, with details on each mission’s accomplishments and crew, is available in the section Chronology of crewed spaceflights.
Humans have always looked at the heavens and wondered about the nature of the objects seen in the night sky. With the development of rockets and the advances in electronics and other technologies in the 20th century, it became possible to send machines and animals and then people above Earth’s atmosphere into outer space. Well before technology made these achievements possible, however, space exploration had already captured the minds of many people, not only aircraft pilots and scientists but also writers and artists. The strong hold that space travel has always had on the imagination may well explain why professional astronauts and laypeople alike consent at their great peril, in the words of Tom Wolfe in The Right Stuff (1979), to sit “on top of an enormous Roman candle, such as a Redstone, Atlas, Titan or Saturn rocket, and wait for someone to light the fuse.” It perhaps also explains why space exploration has been a common and enduring theme in literature and art. As centuries of speculative fiction in books and more recently in films make clear, “one small step for [a] man, one giant leap for mankind” was taken by the human spirit many times and in many ways before Neil Armstrong stamped humankind’s first footprint on the Moon.
Achieving spaceflight enabled humans to begin to explore the solar system and the rest of the universe, to understand the many objects and phenomena that are better observed from a space perspective, and to use for human benefit the resources and attributes of the space environment. All of these activities—discovery, scientific understanding, and the application of that understanding to serve human purposes—are elements of space exploration.
Details
Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. While the exploration of space is currently carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration is conducted both by uncrewed robotic space probes and human spaceflight. Space exploration, like its classical form astronomy, is one of the main sources for space science.
While the observation of objects in space, known as astronomy, predates reliable recorded history, it was the development of large and relatively efficient rockets during the mid-twentieth century that allowed physical space exploration to become a reality. Common rationales for exploring space include advancing scientific research, national prestige, uniting different nations, ensuring the future survival of humanity, and developing military and strategic advantages against other countries.
The early era of space exploration was driven by a "Space Race" between the Soviet Union and the United States. A driving force of the start of space exploration was during the Cold War. After the ability to create nuclear weapons, the narrative of defense/offense left land and the power to control the air the focus. Both the Soviet Union and the U.S. were racing to prove their superiority in technology through exploring space. In fact, the reason NASA was created was as a response to Sputnik I.
The launch of the first human-made object to orbit Earth, the Soviet Union's Sputnik 1, on 4 October 1957, and the first Moon landing by the American Apollo 11 mission on 20 July 1969 are often taken as landmarks for this initial period. The Soviet space program achieved many of the first milestones, including the first living being in orbit in 1957, the first human spaceflight (Yuri Gagarin aboard Vostok 1) in 1961, the first spacewalk (by Alexei Leonov) on 18 March 1965, the first automatic landing on another celestial body in 1966, and the launch of the first space station (Salyut 1) in 1971. After the first 20 years of exploration, focus shifted from one-off flights to renewable hardware, such as the Space Shuttle program, and from competition to cooperation as with the International Space Station (ISS).
With the substantial completion of the ISS following STS-133 in March 2011, plans for space exploration by the U.S. remained in flux. The Constellation program aiming for a return to the Moon by 2020 was judged unrealistic by an expert review panel reporting in 2009. Constellation ultimately was replaced with the Artemis Program, of which the first mission occurred in 2022, with a planned crewed landing to occur with Artemis III. The rise of the private space industry also began in earnest in the 2010s with the development of private launch vehicles, space capsules and satellite manufacturing.
In the 2000s, China initiated a successful crewed spaceflight program while India launched the Chandrayaan programme, while the European Union and Japan have also planned future crewed space missions. The two primary global programs gaining traction in the 2020s are the Chinese-led International Lunar Research Station and the US-led Artemis Program, with its plan to build the Lunar Gateway and the Artemis Base Camp, each having its own set of international partners.
History of exploration:
First telescopes
The first telescope is said to have been invented in 1608 in the Netherlands by an eyeglass maker named Hans Lippershey, but their first recorded use in astronomy was by Galileo Galilei in 1609. In 1668 Isaac Newton built his own reflecting telescope, the first fully functional telescope of this kind, and a landmark for future developments due to its superior features over the previous Galilean telescope.
A string of discoveries in the Solar System (and beyond) followed, then and in the next centuries: the mountains of the Moon, the phases of Venus, the main satellites of Jupiter and Saturn, the rings of Saturn, many comets, the asteroids, the new planets Uranus and Neptune, and many more satellites.
The Orbiting Astronomical Observatory 2 was the first space telescope launched 1968,[10] but the launching of Hubble Space Telescope in 1990 set a milestone. As of 1 December 2022, there were 5,284 confirmed exoplanets discovered. The Milky Way is estimated to contain 100–400 billion stars and more than 100 billion planets. There are at least 2 trillion galaxies in the observable universe. HD1 is the most distant known object from Earth, reported as 33.4 billion light-years away.
Apollo Command Service Module in lunar orbit
MW 18014 was a German V-2 rocket test launch that took place on 20 June 1944, at the Peenemünde Army Research Center in Peenemünde. It was the first human-made object to reach outer space, attaining an apogee of 176 kilometers, which is well above the Kármán line. It was a vertical test launch. Although the rocket reached space, it did not reach orbital velocity, and therefore returned to Earth in an impact, becoming the first sub-orbital spaceflight. In 1949, the Bumper-WAC reached an altitude of 393 kilometres (244 mi), becoming the first human-made object to enter space, according to NASA.
First object in orbit
The first successful orbital launch was of the Soviet uncrewed Sputnik 1 ("Satellite 1") mission on 4 October 1957. The satellite weighed about 83 kg (183 lb), and is believed to have orbited Earth at a height of about 250 km (160 mi). It had two radio transmitters (20 and 40 MHz), which emitted "beeps" that could be heard by radios around the globe. Analysis of the radio signals was used to gather information about the electron density of the ionosphere, while temperature and pressure data was encoded in the duration of radio beeps. The results indicated that the satellite was not punctured by a meteoroid. Sputnik 1 was launched by an R-7 rocket. It burned up upon re-entry on 3 January 1958.
First human outer space flight
The first successful human spaceflight was Vostok 1 ("East 1"), carrying the 27-year-old Russian cosmonaut, Yuri Gagarin, on 12 April 1961. The spacecraft completed one orbit around the globe, lasting about 1 hour and 48 minutes. Gagarin's flight resonated around the world; it was a demonstration of the advanced Soviet space program and it opened an entirely new era in space exploration: human spaceflight.
First astronomical body space explorations
The first artificial object to reach another celestial body was Luna 2 reaching the Moon in 1959. The first soft landing on another celestial body was performed by Luna 9 landing on the Moon on 3 February 1966. Luna 10 became the first artificial satellite of the Moon, entering in a lunar orbit on 3 April 1966.
The first crewed landing on another celestial body was performed by Apollo 11 on 20 July 1969, landing on the Moon. There have been a total of six spacecraft with humans landing on the Moon starting from 1969 to the last human landing in 1972.
The first interplanetary flyby was the 1961 Venera 1 flyby of Venus, though the 1962 Mariner 2 was the first flyby of Venus to return data (closest approach 34,773 kilometers). Pioneer 6 was the first satellite to orbit the Sun, launched on 16 December 1965. The other planets were first flown by in 1965 for Mars by Mariner 4, 1973 for Jupiter by Pioneer 10, 1974 for Mercury by Mariner 10, 1979 for Saturn by Pioneer 11, 1986 for Uranus by Voyager 2, 1989 for Neptune by Voyager 2. In 2015, the dwarf planets Ceres and Pluto were orbited by Dawn and passed by New Horizons, respectively. This accounts for flybys of each of the eight planets in the Solar System, the Sun, the Moon, and Ceres and Pluto (two of the five recognized dwarf planets).
The first interplanetary surface mission to return at least limited surface data from another planet was the 1970 landing of Venera 7, which returned data to Earth for 23 minutes from Venus. In 1975, Venera 9 was the first to return images from the surface of another planet, returning images from Venus. In 1971, the Mars 3 mission achieved the first soft landing on Mars returning data for almost 20 seconds. Later, much longer duration surface missions were achieved, including over six years of Mars surface operation by Viking 1 from 1975 to 1982 and over two hours of transmission from the surface of Venus by Venera 13 in 1982, the longest ever Soviet planetary surface mission. Venus and Mars are the two planets outside of Earth on which humans have conducted surface missions with uncrewed robotic spacecraft.
First space station
Salyut 1 was the first space station of any kind, launched into low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 19 April 1971. The International Space Station (ISS) is currently the largest and oldest of the 2 current fully functional space stations, inhabited continuously since the year 2000. The other, Tiangong space station built by China, is now fully crewed and operational.
First interstellar space flight
Voyager 1 became the first human-made object to leave the Solar System into interstellar space on 25 August 2012. The probe passed the heliopause at 121 AU to enter interstellar space.
Farthest from Earth
The Apollo 13 flight passed the far side of the Moon at an altitude of 254 kilometers (158 miles; 137 nautical miles) above the lunar surface, and 400,171 km (248,655 mi) from Earth, marking the record for the farthest humans have ever traveled from Earth in 1970.
As of 26 November 2022 Voyager 1 was at a distance of 159 AU (23.8 billion km; 14.8 billion mi) from Earth. It is the most distant human-made object from Earth.
Additional Information
We human beings have been venturing into outer space since October 4, 1957, when the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (U.S.S.R.) launched Sputnik, the first artificial satellite to orbit Earth. This happened during the period of hostility between the U.S.S.R. and the United States known as the Cold War.
Sputnik’s launch shifted the Cold War to a new frontier, space. The space race, a competition for prestige and spectacle, was a less-violent aspect of the Cold War, the often-deadly clash between the U.S.S.R. and the U.S. The endeavor was a soft-power ploy used to help win over potential nonaligned nations. Nonaligned nations were called the Third World — now seen as a disparaging term.
For several years, the two superpowers had been competing to develop missiles, called intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), to carry nuclear weapons between continents. In the U.S.S.R., the rocket designer Sergei Korolev had developed the first ICBM, a rocket called the R7, which began the space race. This competition became global news with the launch of Sputnik. Carried atop an R7 rocket, the Sputnik satellite sent out audio beeps from a radio transmitter.
After reaching space, Sputnik orbited Earth once every 96 minutes. The radio beeps were detected on the ground as the satellite passed overhead, so people around the world knew Sputnik was really in orbit. The U.S. was surprised that the U.S.S.R. had exceeded U.S. space capabilities. Furthermore, there was the fear the Soviets could now launch a bomb onto U.S. soil without a plane or a ship.
The origins of the space race began before the end of World War II. At the time, Germany was the world leader in rocket technology, creating the V2, the first operational, long-range rocket. This weapon of war pushed the U.S. and U.S.S.R. space exploration efforts, showing the dual nature of rocket technology. Prior to the launch of Sputnik, the United States was building its launch capability.
The United States made two failed attempts to launch a satellite into space before succeeding with a rocket that carried a satellite called Explorer on January 31, 1958. Explorer carried several instruments into space for conducting science experiments. One instrument was a Geiger counter for detecting cosmic rays. This was for an experiment operated by researcher James Van Allen, which, together with measurements from later satellites, proved the existence of what are now called the Van Allen radiation belts around Earth.
The team that achieved the first U.S. satellite launch consisted largely of German rocket engineers who had once developed ballistic missiles for Nazi Germany. Working for the U.S. Army at the Redstone math in Huntsville, Alabama, the German rocket engineers were led by Wernher von Braun, who had led the creation of Germany’s V2 rocket. His team used the V2 to build the more powerful Jupiter C, or Juno, rocket. Von Braun headed the U.S. rocket program, leading the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, until 1970.
At the close of WWII, the U.S.S.R. and the U.S. scrambled to recruit German rocket engineers and scientists to improve their rocket programs. The motivation for both governments was to improve their respective military technologies. Von Braun and most of his top deputies sought out U.S. forces to surrender to, preferring to work for the U.S. to the Soviets. The German specialists and some of their missiles and designs were relocated to the U.S. in what became known as Operation Paperclip (originally Project Overcast).
While the U.S. brought in von Braun and his scientists, except for Helmut Gröttrup, an expert on the V2 guidance system. The U.S.S.R., however, got more of the German technical personnel than the U.S. Homegrown talent was more involved in the leadership of the Soviet space program than the U.S. space program.
Von Braun and others on his team were members of the German Nazi Party. Von Braun was an officer in the SS, the Nazi paramilitary wing. He managed the science operations at the Mittelwerk factory, which used the labor of enslaved people. U.S. leadership was less concerned with their Nazi membership than using their technical expertise to defeat Japan, and later to gain an advantage over the Soviet Union. U.S. government officials lied about many of the Germans’ Nazi pasts to make working with them more acceptable to the American public.
In 1958, Though NASA leadership was almost entirely composed of White men, many of those doing the work as mathematicians, physicists, and engineers to put astronauts and machines into space were from underrepresented ethnicities and women of all ethnicities. Some examples of people of color who played important roles at NASA include mathematicians Katherine Johnson and Josephine Jue, engineers Miguel Hernandez and Walter Applewhite.
Space exploration activities in the United States were consolidated into a new government agency, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). When it began operations in October of 1958, NASA absorbed what had been called the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), and several other research and military facilities, including the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (the Redstone math) in Huntsville, Alabama.
Korolev’s R7 was the basis for the rocket family that would be the basis for the first launch successes and even the still-used Soyuz. Soviet’s space program had rival teams that worked on competing designs.
Von Braun’s influence extended far beyond the world of rocket scientists and space enthusiasts. He became well known after participating in three Disney-produced TV specials about space in the mid 1950s. Meanwhile, the role and accomplishments of von Braun’s Soviet counterpart, Korolev, were largely hidden by his government.
Both Korolev and von Braun shared a desire and commitment to exploring space, even though their governments preferred using rocket technology for military applications.
Despite the fact that Korolev drove the Soviet Space program’s early successes, he became a victim of one of Soviet Premier Josef Stalin’s political purges and was recalled from prison to head the rocket development program in 1944. After learning of the United States’ plan to launch an artificial satellite into space, it was Korolev who convinced and pushed the U.S.S.R. government to beat the U.S. in this endeavor, building the N1 rocket.
The U.S.S.R.’s win streak didn’t end there. A month after Sputnik’s launch, on November 3, 1957, the U.S.S.R. achieved an even more impressive space venture. This was Sputnik II, a satellite that carried a living creature, a dog named Laika.
The first human in space was Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin, who made one orbit around Earth on April 12, 1961, on a flight that lasted 108 minutes. A little more than three weeks later, NASA launched astronaut Alan Shepard into space, not on an orbital flight, but on a suborbital trajectory, a flight that goes into space but does not go all the way around Earth. Shepard’s suborbital flight lasted just over 15 minutes.
In addition to launching the first artificial satellite, the first dog in space, and the first human in space, the U.S.S.R. achieved other space milestones ahead of the United States under Korolev’s leadership. One of these milestones was Luna 2, which became the first human-made object to hit the Moon in 1959. Soon after that, the U.S.S.R. launched Luna 3. Less than four months after Gagarin’s flight in 1961, a second Soviet human mission orbited a cosmonaut around Earth for a full day. The U.S.S.R. also achieved the first spacewalk and launched the Vostok 6 mission, which made Valentina Tereshkova the first woman to travel to space.
Korolev was gearing U.S.S.R. to send a cosmonaut to the moon. The goal of sending a human to the moon became the final stage of the space race. Three weeks after Shepard’s flight, on May 25, U.S. President Robert F. Kennedy challenged the United States to an ambitious goal, declaring: “I believe that this nation should commit itself to achieving the goal, before the decade is out, of landing a man on the moon and returning him safely to Earth."
During the 1960s, NASA made progress toward John F. Kennedy’s human moon landing goal with a program called Project Gemini, in which astronauts tested technology needed for future flights to the Moon, and tested their own ability to endure many days in spaceflight. Project Gemini was followed by Project Apollo, which did take astronauts into orbit around the Moon and to the lunar surface between 1968 and 1972.
In 1969, on Apollo11, the United States sent the first astronauts to the moon, and Neil Armstrong became the first human to set foot on its surface. During the landed missions, astronauts collected samples of rocks and lunar dust that scientists still study to learn about the Moon. As the U.S. manned space program rose, the Soviet program began to falter. There was internal disagreement about trying to send a human to the moon. Perhaps more importantly was Korolev’s death after a fumbled surgery in 1966. Today, the U.S. and the Russian Federation still have active space programs.
Future of space exploration:
Breakthrough Starshot
Breakthrough Starshot is a research and engineering project by the Breakthrough Initiatives to develop a proof-of-concept fleet of light sail spacecraft named StarChip, to be capable of making the journey to the Alpha Centauri star system 4.37 light-years away. It was founded in 2016 by Yuri Milner, Stephen Hawking, and Mark Zuckerberg.
Asteroids
An article in the science magazine Nature suggested the use of asteroids as a gateway for space exploration, with the ultimate destination being Mars. In order to make such an approach viable, three requirements need to be fulfilled: first, "a thorough asteroid survey to find thousands of nearby bodies suitable for astronauts to visit"; second, "extending flight duration and distance capability to ever-increasing ranges out to Mars"; and finally, "developing better robotic vehicles and tools to enable astronauts to explore an asteroid regardless of its size, shape or spin". Furthermore, using asteroids would provide astronauts with protection from galactic cosmic rays, with mission crews being able to land on them without great risk to radiation exposure.
Artemis program
The Artemis program is an ongoing crewed spaceflight program carried out by NASA, U.S. commercial spaceflight companies, and international partners such as ESA, with the goal of landing "the first woman and the next man" on the Moon, specifically at the lunar south pole region. Artemis would be the next step towards the long-term goal of establishing a sustainable presence on the Moon, laying the foundation for private companies to build a lunar economy, and eventually sending humans to Mars.
In 2017, the lunar campaign was authorized by Space Policy Directive 1, using various ongoing spacecraft programs such as Orion, the Lunar Gateway, Commercial Lunar Payload Services, and adding an undeveloped crewed lander. The Space Launch System will serve as the primary launch vehicle for Orion, while commercial launch vehicles are planned for use to launch other elements of the campaign. NASA requested $1.6 billion in additional funding for Artemis for fiscal year 2020, while the U.S. Senate Appropriations Committee requested from NASA a five-year budget profile which is needed for evaluation and approval by the U.S. Congress. As of 2024, the first Artemis mission was launched in 2022 with the second mission, a crewed lunar flyby planned for 2025. Construction on the Lunar Gateway is underway with initial capabilities set for the 2025–2027 timeframe. The first CLPS lander landed in 2024, marking the first US spacecraft to land since Apollo 17.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2399 2025-01-02 00:02:00
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2299) Scissors
Gist
Scissors is a device used for cutting materials such as paper, cloth, and hair, consisting of two sharp blades that are joined in the middle, and two handles with holes to put your fingers through
In the late 14th century, the English word "scissors" came into usage. It was derived from the Old French word cisoires, which referred to shears.
Summary
Scissors is a cutting instrument consisting of a pair of opposed metal blades that meet and cut when the handles at their ends are brought together. The term shears sometimes denotes large-size scissors. Modern instruments are of two types: the more usual pivoted blades have a rivet or screw connection between the cutting ends and the handle ends; spring shears have a C-shaped spring connection at the handle ends.
Spring-type scissors probably date from the Bronze Age and were commonly used in Europe until the end of the Middle Ages. Pivoted scissors of bronze and iron were used in ancient Rome and in China, Japan, and Korea. In Europe their domestic use dates from the 16th century, but not until 1761, when Robert Hinchliffe of Sheffield, Eng., first used cast steel in their manufacture, did large-scale production begin. In the 19th century much hand-forged work was produced, with elaborately ornamented handles. By the end of the 19th century, styles were simplified for mechanical-production methods.
The two blades are made to twist or curve slightly toward one another so that they touch in only two places: at the pivot, or joint, and at the spot along the blades where the cutting is taking place. When completely closed, the points of the blades touch. In the case of the finest cutting instruments, the two unfinished metal blanks and the fasteners are coded with an identifying mark so they can be manufactured as a set.
Blanks are usually made from red-hot steel bars that are forged at high speed between the dies of drop hammers, but others also of satisfactory quality may be made from cold-forged blanks. The steel may contain from 0.55 to 1.03 percent carbon, the higher carbon content providing a harder cutting steel for certain applications. Stainless steel is used for surgical scissors. Certain nonferrous alloys that will not produce sparks or interfere with magnetism are employed in making scissors for cutting cordite and magnetic tape. Handle and blade are usually constructed in one piece, but in some cases the handles are electrically welded to the steel blades.
Expert sharpening is required to restore the edge-angle sharpness; each blade is passed smoothly and lightly across a grinding wheel, following the twist of the blade, with an even pressure throughout the stroke to avoid causing ridges or other irregularities.
A special form of shears used for sheet-metal work, called tin shears, or tin snips, is equipped with high-leverage handles to facilitate cutting the metal. Another special form, pruning shears, are designed for trimming shrubs and trees.
Details
Scissors are hand-operated shearing tools. A pair of scissors consists of a pair of blades pivoted so that the sharpened edges slide against each other when the handles (bows) opposite to the pivot are closed. Scissors are used for cutting various thin materials, such as paper, cardboard, metal foil, cloth, rope, and wire. A large variety of scissors and shears all exist for specialized purposes. Hair-cutting shears and kitchen shears are functionally equivalent to scissors, but the larger implements tend to be called shears. Hair-cutting shears have specific blade angles ideal for cutting hair. Using the incorrect type of scissors to cut hair will result in increased damage or split ends, or both, by breaking the hair. Kitchen shears, also known as kitchen scissors, are intended for cutting and trimming foods such as meats.
Inexpensive, mass-produced modern scissors are often designed ergonomically with composite thermoplastic and rubber handles.
Terminology
The noun scissors is treated as a plural noun, and therefore takes a plural verb (e.g., these scissors are) Alternatively, the tool is referred to by the singular phrase a pair of scissors. The word shears is used to describe similar instruments that are larger in size and for heavier cutting.
History
The earliest known scissors appeared in Mesopotamia 3,000 to 4,000 years ago. These were of the 'spring scissor' type comprising two bronze blades connected at the handles by a thin, flexible strip of curved bronze which served to hold the blades in alignment, to allow them to be squeezed together, and to pull them apart when released.
Spring scissors continued to be used in Europe until the 16th century. However, pivoted scissors of bronze or iron, in which the blades were pivoted at a point between the tips and the handles, the direct ancestor of modern scissors, were invented by the Romans around 100 AD. They entered common use in not only ancient Rome, but also China, Japan, and Korea, and the idea is still used in almost all modern scissors.
Early manufacture
During the Middle Ages and Renaissance, spring scissors were made by heating a bar of iron or steel, then flattening and shaping its ends into blades on an anvil. The center of the bar was heated, bent to form the spring, then cooled and reheated to make it flexible.
The Hangzhou Zhang Xiaoquan Company in Hangzhou, China, has been manufacturing scissors since 1663.
William Whiteley & Sons (Sheffield) Ltd. was producing scissors by 1760, although it is believed the business began trading even earlier. The first trade-mark, 332, was granted in 1791. The company is still manufacturing scissors today, and is the oldest company in the West to do so.
Pivoted scissors were not manufactured in large numbers until 1761, when Robert Hinchliffe of Sheffield produced the first pair of modern-day scissors made of hardened and polished cast steel. His major challenge was to form the bows; first, he made them solid, then drilled a hole, and then filed away metal to make this large enough to admit the user's fingers. This process was laborious, and apparently Hinchliffe improved upon it in order to increase production. Hinchliffe lived in Cheney Square (now the site of Sheffield Town Hall), and set up a sign identifying himself as a "fine scissor manufacturer". He achieved strong sales in London and elsewhere.
During the 19th century, scissors were hand-forged with elaborately decorated handles. They were made by hammering steel on indented surfaces known as 'bosses' to form the blades. The rings in the handles, known as bows, were made by punching a hole in the steel and enlarging it with the pointed end of an anvil.
In 1649, in Swedish-ruled Finland, an ironworks was founded in the village of Fiskars between Helsinki and Turku. In 1830, a new owner started the first cutlery works in Finland, making, among other items, scissors with the Fiskars trademark.
Description and operation
A pair of scissors consists of two pivoted blades. In lower-quality scissors, the cutting edges are not particularly sharp; it is primarily the shearing action between the two blades that cuts the material. In high-quality scissors, the blades can be both extremely sharp, and tension sprung – to increase the cutting and shearing tension only at the exact point where the blades meet. The hand movement (pushing with the thumb, pulling with the fingers) can add to this tension. An ideal example is in high-quality tailor's scissors or shears, which need to be able to perfectly cut (and not simply tear apart) delicate cloths such as chiffon and silk.
Children's scissors are usually not particularly sharp, and the tips of the blades are often blunted or 'rounded' for safety.
Mechanically, scissors are a first-class double-lever with the pivot acting as the fulcrum. For cutting thick or heavy material, the mechanical advantage of a lever can be exploited by placing the material to be cut as close to the fulcrum as possible. For example, if the applied force (at the handles) is twice as far away from the fulcrum as the cutting location (i.e., the point of contact between the blades), the force at the cutting location is twice that of the applied force at the handles. Scissors cut material by applying at the cutting location a local shear stress which exceeds the material's shear strength.
Some scissors have an appendage, called a finger brace or finger tang, below the index finger hole for the middle finger to rest on to provide for better control and more power in precision cutting. A finger tang can be found on many quality scissors (including inexpensive ones) and especially on scissors for cutting hair. In hair cutting, some claim the ring finger is inserted where some place their index finger, and the little finger rests on the finger tang.
For people who do not have the use of their hands, there are specially designed foot-operated scissors. Some quadriplegics can use a motorized mouth-operated style of scissor.
Right-handed and left-handed scissors
Most scissors are best suited for use with the right hand, but left-handed scissors are designed for use with the left hand. Because scissors have overlapping blades, they are not symmetric. This asymmetry is true regardless of the orientation and shape of the handles and blades: the blade that is on top always forms the same diagonal regardless of orientation. Human hands are asymmetric, and when closing the scissors the thumb and fingers do not close vertically, but have a lateral component to the motion. Specifically, the thumb pushes out from the palm and the fingers pull inwards. For right-handed scissors held in the right hand, the thumb blade is closer to the user's body, so that the natural tendency of the right hand is to push the cutting blades together. Conversely, if right-handed scissors are held in the left hand, the natural tendency of the left hand would be to push the cutting blades apart. Furthermore, with right-handed scissors held by the right hand, the shearing edge is visible, but when they are used with the left hand, the cutting edge of the scissors is behind the top blade, and the cutter cannot see what is being cut.
There are two varieties of left-handed scissors. Many common left-handed scissors (often called "semi"-left-handed scissors) simply have reversed finger grips. The blades open and close as with right-handed scissors, so that users tend to pull the blades apart as they are cutting. This can be challenging for craftspeople as the blades still obscure the cut. "True" left-handed scissors have both reversed finger grips and reversed blade layout, like mirror images of right-handed scissors. A left-handed person accustomed to using semi-left handed scissors may find using true left-handed scissors difficult at first, as they may have learned to rely heavily on the strength of their thumb to pull the blades apart vs. pushing the blades together in order to cut.
Some scissors are marketed as ambidextrous. These have symmetric handles so there is no distinction between the thumb and finger handles, and have very strong pivots so that the blades rotate without any lateral give. However, most "ambidextrous" scissors are in fact still right-handed in that the upper blade is on the right, and hence is on the outside when held in the right hand. Even if they cut successfully, the blade orientation will block the view of the cutting line for a left-handed person. True ambidextrous scissors are possible if the blades are double-edged and one handle is swung all the way around (to almost 360 degrees) so that what were the backs of the blades become the new cutting edges. U.S. patent 3,978,584 was awarded for true ambidextrous scissors.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
#2400 2025-01-03 00:05:13
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,383
Re: Miscellany
2300) Plier / Pliers
Gist
Pliers are made in various shapes and sizes and for many uses. Some are used for gripping something round like a pipe or rod, some are used for twisting wires, and others are designed to be used for a combination of tasks, including cutting wire.
Electricians usually use lineman's pliers to bend wires and cables. Some pliers can also cut wires and nails. Diagonal cutting pliers and side-cutting pliers, often called wire cutters, are primarily used to cut and sever wires.
Summary
Pliers are hand-operated tool for holding and gripping small articles or for bending and cutting wire. Slip-joint pliers have grooved jaws, and the pivot hole in one member is elongated so that the member can pivot in either of two positions in order to grasp objects of different size in the most effective way. On some pliers the jaws have a portion that can cut soft wire and nails.
For bending wire and thin metal, round-nose pliers with tapering, conical jaws are used. Diagonal cutting pliers are used for cutting wire and small pins in areas that cannot be reached by larger cutting tools. Because the cutting edges are diagonally offset about 15 degrees, these can cut objects flush with a surface.
Details
Pliers are a hand tool used to hold objects firmly, possibly developed from tongs used to handle hot metal in Bronze Age Europe. They are also useful for bending and physically compressing a wide range of materials. Generally, pliers consist of a pair of metal first-class levers joined at a fulcrum positioned closer to one end of the levers, creating short jaws on one side of the fulcrum, and longer handles on the other side. This arrangement creates a mechanical advantage, allowing the force of the grip strength to be amplified and focused on an object with precision. The jaws can also be used to manipulate objects too small or unwieldy to be manipulated with the fingers.
Diagonal pliers, also called side cutters, are a similarly shaped tool used for cutting rather than holding, having a pair of stout blades, similar to scissors except that the cutting surfaces meet parallel to each other rather than overlapping. Ordinary (holding/squeezing) pliers may incorporate a small pair of such cutting blades. Pincers are a similar tool with a different type of head used for cutting and pulling, rather than squeezing. Tools designed for safely handling hot objects are usually called tongs. Special tools for making crimp connections in electrical and electronic applications are often called crimping pliers or crimpers; each type of connection uses its own dedicated tool.
Parallel pliers have jaws that close in parallel to each other, as opposed to the scissor-type action of traditional pliers. They use a box joint system to do this, and it allows them to generate more grip from friction on square and hexagonal fastenings.
There are many kinds of pliers made for various general and specific purposes.
History
As pliers in the general sense are an ancient and simple invention, no single inventor can be credited. Early metal working processes from several millennia BCE would have required plier-like devices to handle hot materials in the process of smithing or casting. Development from wooden to bronze pliers would have probably happened sometime prior to 3000 BCE. Among the oldest illustrations of pliers are those showing the Greek god Hephaestus in his forge. The number of different designs of pliers grew with the invention of the different objects which they were used to handle: horseshoes, fasteners, wire, pipes, electrical, and electronic components.
Design
The basic design of pliers has changed little since their origins, with the pair of handles, the pivot (often formed by a rivet), and the head section with the gripping jaws or cutting edges forming the three elements.
The materials used to make pliers consist mainly of steel alloys with additives such as vanadium or chromium, to improve strength and prevent corrosion. The metal handles of pliers are often fitted with grips of other materials to ensure better handling; grips are usually insulated and additionally protect against electric shock. The jaws vary widely in size, from delicate needle-nose pliers to heavy jaws capable of exerting much pressure, and shape, from basic flat jaws to various specialized and often asymmetrical jaw configurations for specific manipulations. The surfaces are typically textured rather than smooth, to minimize slipping.
A plier-like tool designed for cutting wires is often called diagonal pliers. Some pliers for electrical work are fitted with wire-cutter blades either built into the jaws or on the handles just below the pivot.
Where it is necessary to avoid scratching or damaging the workpiece, as for example in jewellery and musical instrument repair, pliers with a layer of softer material such as aluminium, brass, or plastic over the jaws are used.
Ergonomics
Much research has been undertaken to improve the design of pliers, to make them easier to use in often difficult circumstances (such as restricted spaces). The handles can be bent, for example, so that the load applied by the hand is aligned with the arm, rather than at an angle, thus reducing muscle fatigue. It is especially important for factory workers who use pliers continuously and helps prevent carpal tunnel syndrome.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Online
