Math Is Fun Forum
You are not logged in.
- Topics: Active | Unanswered
Pages: 1
#1 2025-02-08 16:36:01
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,065
Sesamoid bone
Sesamoid bone
Gist
A sesamoid bone is a small bone commonly found embedded within a muscle or tendon near joint surfaces, existing as focal areas of ossification and functioning as a pulley to alleviate stress on that particular muscle or tendon.
Summary
Sesamoid bones are small round or oval shaped nodules that are located within certain tendons. Typically there are five sesamoid bones in each hand; two at the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint of the thumb, one at the interphalangeal (IP) joint of the thumb, one at the MCP joint of the index finger on the radial side, and one at the MCP joint of the little finger on the ulnar side. Sesamoid bones of the thumb MCP joint located imbedded within the tendons of the FPB and the AddP. These bones act as a pulley by altering the lines of pull of the tendons in which they insert, consequently improving the efficacy of the muscles.
Details
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Greek word for 'sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be present as a normal variant. The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the body. Sesamoids act like pulleys, providing a smooth surface for tendons to slide over, increasing the tendon's ability to transmit muscular forces.
Structure
Sesamoid bones can be found on joints throughout the human body, including:
* In the knee—the patella (within the quadriceps tendon). This is the largest sesamoid bone.
* In the hand—two sesamoid bones are commonly found in the distal portions of the first metacarpal bone (within the tendons of adductor pollicis and flexor pollicis brevis). There is also commonly a sesamoid bone in distal portions of the second metacarpal bone and fifth metacarpal bone.
* In the wrist—The pisiform of the wrist is a sesamoid bone (within the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris). It begins to ossify in children ages 9–12.
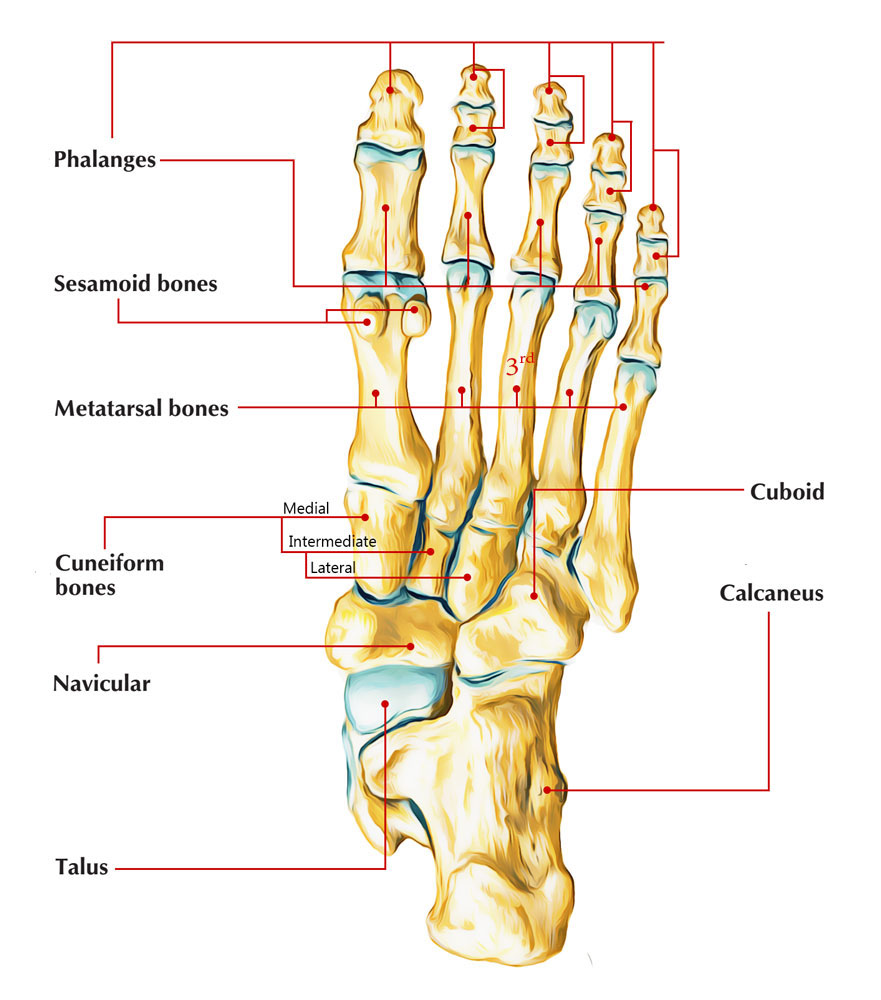
* In the foot—the first metatarsal bone usually has two sesamoid bones at its connection to the big toe (both within the tendon of flexor hallucis brevis). One is found on the lateral side of the first metatarsal while the other is found on the medial side. In some people, only a single sesamoid is found on the first metatarsal bone.
Common variants
* One or both of the sesamoid bones under the first metatarsophalangeal joint (of the great toe) can be multipartite – in two or three parts (mostly bipartite – in two parts).
* The fabella is a small sesamoid bone found in some mammals embedded in the tendon of the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle behind the lateral condyle of the femur. It is a variant of normal anatomy and present in humans in 10% to 30% of individuals. The fabella can also be mutipartite or bipartite.
* The cyamella is a small sesamoid bone embedded in the tendon of the popliteus muscle. It is a variant of normal anatomy. It is rarely seen in humans, but has been described more often in other primates and certain other animals.
Clinical significance
* A common foot ailment in dancers is sesamoiditis (an inflammation of the sesamoid bones under the first metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe). This is a form of tendinitis which results from the tendons surrounding the sesamoid becoming inflamed or irritated.
* Sesamoid bones generally have a very limited blood supply, rendering them prone to avascular necrosis (bone death from lack of blood supply), which is very difficult to treat.
Other animals
In equine anatomy, the term sesamoid bone usually refers to the two sesamoid bones found at the back of the fetlock or metacarpophalangeal and metatarsophalangeal joints in both hindlimbs and forelimbs. Strictly these should be termed the proximal sesamoid bones whereas the navicular bone should be referred to as the distal sesamoid bone. The patella is also a form of sesamoid bone in the horse.
Although many carnivores have radial sesamoid bones, the giant panda and red panda independently evolved to have an enlarged radial sesamoid bone. This evolution has caused the two species to diverge from other carnivores. The red panda likely originally evolved the "pseudo-thumb" in order to assist in arboreal locomotion. When the red panda later evolved to consume a bamboo diet, the enlarged bone underwent exaptation to assist in grasping bamboo. The giant panda, however, evolved the enlarged radial sesamoid bone around the same time as it evolved a bamboo diet. In the giant panda, the bone allows for a pincer-like motion and is used in grasping the bamboo. In these two panda species, DYNC2H1 gene and PCNT gene have been identified as possible causes for the pseudo-thumb development.
Recently, the enlarged radial sesamoid bone of cotton rats has been studied. Their enlarged radial sesamoid bone and that of the giant panda have a similar morphology and size relative to the rest of the hand. The reason for this evolutionary change is still unknown; however, it may be to assist in grasping small objects and thin branches.
Elephants have similarly enlarged sesamoid bones in both their forelimbs and hindlimbs, referred to as the prepollex and prehallux, respectively. These sesamoids function as "sixth toes", helping to distribute the animals' weight. In contrast to other sesamoids in elephants, which ossify at three to seven years of age, the ossification of the prepollex and prehallux is delayed and is known to not have yet occurred in animals in excess of 20 years of age. The prehallux is further divided into two elements; the more proximal of these is fixed, whilst the more distal is mobile. Evidence of these "predigits" has also been found in certain fossil proboscideans.
The forepaws of moles also possess a prepollex consisting of an enlarged, sickle-shaped sesamoid.
Additional Information
Sesamoid bones are a type of bone that develop in some tendons where they cross the ends of long bones. Sesamoids ossify during puberty and delayed ossification can indicate delayed onset of puberty.
Sesamoid bones in the human body include:
* Patella - in the quadriceps tendon at the knee
* Hallux sesamoids - medial/tibia and lateral/fibular in the flexor hallucis brevis tendon at the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint
* In the hand at the head of the 1st metacarpal - one in the combined tendon of the flexor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis brevis and one in the tendon of the adductor pollicis
* Pisiform - in the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon
Function
Sesamoids protect tendons from excessive wear and act as a spacer to change the angle of tendons before the reach their attachment point. The change in angle improves muscle force generation.
Clinical relevance
Pathology in sesamoids can be congenital or a result of trauma. Common pathology seen in sesamoid bones include:
* Bipartite or multipartite patella
* Sesamoiditis
* Fracture - such as patella fracture
* Avascular necrosis
Management of the different pathologies varies depending on the diagnosis. Physiotherapy or conservative management is typically the first line of treatment for atraumatic pathology of sesamoids.
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
Pages: 1