Math Is Fun Forum
You are not logged in.
- Topics: Active | Unanswered
- Index
- » Science HQ
- » Cosmogony
Pages: 1
#1 2025-03-19 18:02:50
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 52,374
Cosmogony
Cosmogony
Gist
Cosmogony is the branch of astrophysics that studies the origin and evolution and structure of the universe.
Summary
Cosmogony, the study of the origin and development of the universe as a whole and of the individual bodies that compose it. Since cosmogony attempts to deal with creation, cosmogonies of the past have been a part of religion or mythology. Modern cosmogony forms part of scientific cosmology, the study of all aspects of the large-scale physical universeits contents and organization as well as its history.
An attempt to explain the origin of the solar system by natural rather than supernatural processes was first made by Emanuel Swedenborg and Immanuel Kant in the mid-1700's. Their theories were very like the nebular hypothesis put forward in 1796 by Pierre Simon de Laplace.
The nebular hypothesis and its successors, the planetesimal hypothesis (by F. R. Moulton and T. C. Chamberlin, about 1905) and the tidal theory (by J. H. Jeans, about 1918), were discarded in favor of a theory of turbulent condensation. This theory, first proposed by the German physicist Carl von Weizscker in the 1940's, supposes that the newly formed sun was surrounded by a loosely knit, slowly rotating shell of matter as large as the present planetary system. The heavier materials making up this shell eventually accumulated as planets in pockets between the eddies within the churning shell. Such a theory seems to explain why the planes of the other planets' orbits nearly coincide with that of the earth's orbit and suggests why the planets are spaced from the sun as they are. Another theory, based in part on evidence from manned lunar exploration, states that the planets were formed cold in a process called accretion. This theory is explained in the article EARTH, subtitle The Earth's History.
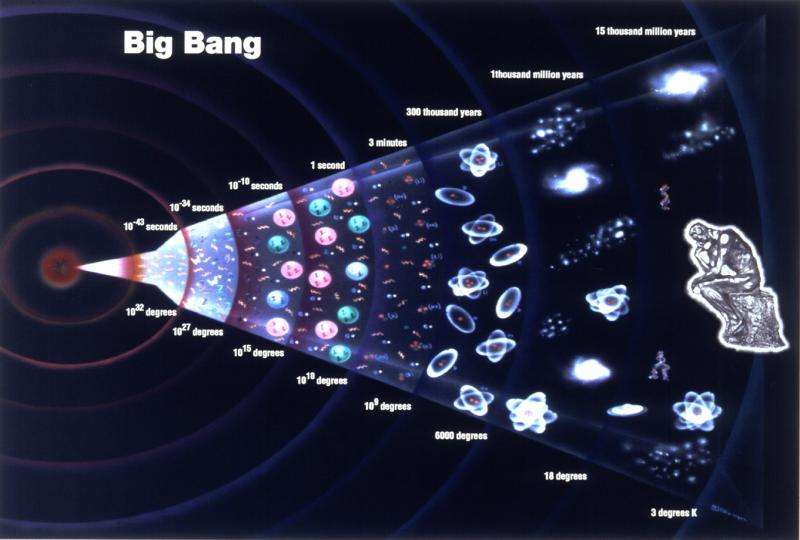
The most widely accepted theory of the beginning of the universe itself is called the Big Bang Theory. According to this theory the universe came into being at a single point some 10 to 20 billion years ago. An alternate theory, the Steady State Theory, holds that the universe had no beginning and that the universe is much the same now as it always has been.
Details
Cosmogony is any model concerning the origin of the cosmos or the universe.
Overview:
Scientific theories
The Big Bang theory, which explains the Evolution of the Universe from a hot and dense state, is widely accepted by physicists.
In astronomy, cosmogony is the study of the origin of particular astrophysical objects or systems, and is most commonly used in reference to the origin of the universe, the Solar System, or the Earth–Moon system. The prevalent cosmological model of the early development of the universe is the Big Bang theory.
Sean M. Carroll, who specializes in theoretical cosmology and field theory, explains two competing explanations for the origins of the singularity, which is the center of a space in which a characteristic is limitless[5] (one example is the singularity of a black hole, where gravity is the characteristic that becomes limitless — infinite).
It is generally thought that the universe began at a point of singularity, but among Modern Cosmologists and Physicists, a singularity usually represents a lack of understanding, and in the case of Cosmology/Cosmogony, requires a theory of quantum gravity to understand. When the universe started to expand, what is colloquially known as the Big Bang occurred, which evidently began the universe. The other explanation, held by proponents such as Stephen Hawking, asserts that time did not exist when it emerged along with the universe. This assertion implies that the universe does not have a beginning, as time did not exist "prior" to the universe. Hence, it is unclear whether properties such as space or time emerged with the singularity and the known universe.
Despite the research, there is currently no theoretical model that explains the earliest moments of the universe's existence (during the Planck epoch) due to a lack of a testable theory of quantum gravity. Nevertheless, researchers of string theory, its extensions (such as M-theory), and of loop quantum cosmology, like Barton Zwiebach and Washington Taylor, have proposed solutions to assist in the explanation of the universe's earliest moments. Cosmogonists have only tentative theories for the early stages of the universe and its beginning. The proposed theoretical scenarios include string theory, M-theory, the Hartle–Hawking initial state, emergent Universe, string landscape, cosmic inflation, the Big Bang, and the ekpyrotic universe. Some of these proposed scenarios, like the string theory, are compatible, whereas others are not.
Mythology
In mythology, creation or cosmogonic myths are narratives describing the beginning of the universe or cosmos.
Some methods of the creation of the universe in mythology include:
* the will or action of a supreme being or beings,
* the process of metamorphosis,
* the copulation of female and male deities,
* from chaos,
* or via a cosmic egg.
Creation myths may be etiological, attempting to provide explanations for the origin of the universe. For instance, Eridu Genesis, the oldest known creation myth, contains an account of the creation of the world in which the universe was created out of a primeval sea (Abzu). Creation myths vary, but they may share similar deities or symbols. For instance, the ruler of the gods in Greek mythology, Zeus, is similar to the ruler of the gods in Roman mythology, Jupiter. Another example is the ruler of the gods in Tagalog mythology, Bathala, who is similar to various rulers of certain pantheons within Philippine mythology such as the Bisaya's Kaptan.
Compared with cosmology
In the humanities, the distinction between cosmogony and cosmology is blurred. For example, in theology, the cosmological argument for the existence of God (pre-cosmic cosmogonic bearer of personhood) is an appeal to ideas concerning the origin of the universe and is thus cosmogonical. Some religious cosmogonies have an impersonal first cause (for example Taoism).
However, in astronomy, cosmogony can be distinguished from cosmology, which studies the universe and its existence, but does not necessarily inquire into its origins. There is therefore a scientific distinction between cosmological and cosmogonical ideas. Physical cosmology is the science that attempts to explain all observations relevant to the development and characteristics of the universe on its largest scale. Some questions regarding the behaviour of the universe have been described by some physicists and cosmologists as being extra-scientific or metaphysical. Attempted solutions to such questions may include the extrapolation of scientific theories to untested regimes (such as the Planck epoch), or the inclusion of philosophical or religious ideas.
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
Pages: 1
- Index
- » Science HQ
- » Cosmogony