Math Is Fun Forum
You are not logged in.
- Topics: Active | Unanswered
- Index
- » Science HQ
- » Nickel
Pages: 1
#1 2025-05-10 21:41:16
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,052
Nickel
Nickel
Gist
Nickel is a metallic element with a silvery-white, shiny appearance. It is the fifth-most common element on earth and occurs extensively in the earth’s crust and core. Nickel, along with iron, is also a common element in meteorites. Nickel occurs naturally in soil and water. It is also an essential nutrient for plants.
While the concentration of nickel in the earth's crust is 80 parts per million, the earth's core consists mainly of a nickel-iron alloy.
A silvery metal that resists corrosion even at high temperatures. Nickel resists corrosion and is used to plate other metals to protect them. It is, however, mainly used in making alloys such as stainless steel.
Summary
Element Properties:
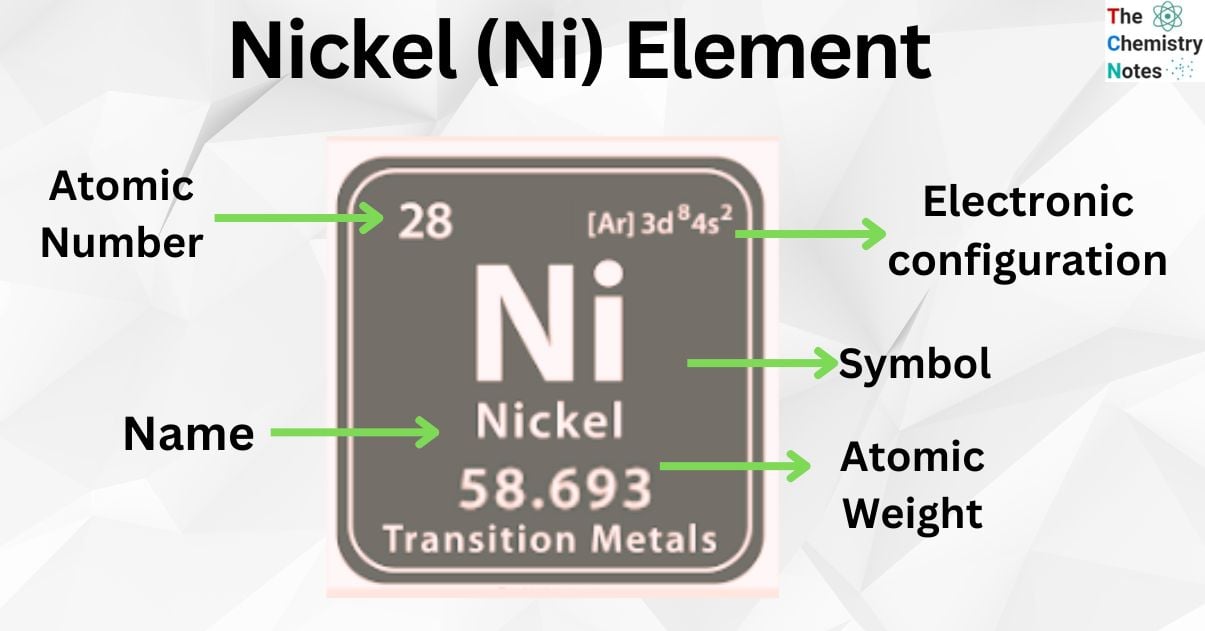
atomic number : 28
atomic weight : 58.69
melting point : 1,453 °C (2,647 °F)
boiling point : 2,732 °C (4,950 °F)
density : 8.902 (25 °C)
oxidation states : 0, +1, +2, +3
Nickel (atomic number 28) resembles iron (atomic number 26) in strength and toughness but is more like copper (atomic number 29) in resistance to oxidation and corrosion, a combination accounting for many of its applications. Nickel has high electrical and thermal conductivity. More than half the nickel produced is used in alloys with iron (particularly in stainless steels), and most of the rest is used in corrosion-resistant alloys with copper (including Monel, which contains some 60 to 70 percent nickel, 30 to 40 percent copper, and small amounts of other metals such as iron) and in heat-resistant alloys with chromium. Nickel is also used in electrically resistive, magnetic, and many other kinds of alloys, such as nickel silver (with copper and zinc but no silver). The unalloyed metal is utilized to form protective coatings on other metals, especially by electroplating. Finely divided nickel is employed to catalyze the hydrogenation of unsaturated organic compounds (e.g., fats and oils).
Nickel can be fabricated readily by the use of standard hot and cold working methods. Nickel reacts only slowly with fluorine, eventually developing a protective coating of the fluoride, and therefore is used as the pure metal or in the form of alloys such as Monel in equipment for handling fluorine gas and corrosive fluorides. Nickel is ferromagnetic at ordinary temperatures, although not as strongly as iron, and is less electropositive than iron but dissolves readily in dilute mineral acids.
Natural nickel consists of five stable isotopes: nickel-58 (68.27 percent), nickel-60 (26.10 percent), nickel-61 (1.13 percent), nickel-62 (3.59 percent), and nickel-64 (0.91 percent). It has a face-centred cubic crystal structure. Nickel is ferromagnetic up to 358 °C, or 676 °F (its Curie point). The metal is uniquely resistant to the action of alkalies and is frequently used for containers for concentrated solutions of sodium hydroxide. Nickel reacts slowly with strong acids under ordinary conditions to liberate hydrogen and form Ni2+ ions.
China is the world’s largest nickel producer. Other major nickel-producing countries include Russia, Japan, Australia, and Canada.
Details
Nickel (chemical symbol Ni) is an element. It has an atomic number of 28 and an atomic mass of about 58.69amu. It has 28 protons. It is a transition metal.
Properties:
Physical properties
Nickel is a silver-white metal. It is easily polished (made shiny). It is magnetic. It is not magnetic when heated above 355 °C (671 °F). It is not soft like many other metals. It can be stretched into wires easily. It is not radioactive.
Chemical properties
Nickel is not a reactive metal. It dissolves slowly in acids. It does not rust like iron. It makes a thin coating of nickel(II) oxide which stops more corrosion. Aluminium does a similar thing.
Chemical compounds
Nickel is found in two oxidation states: +2, nickel(II); and +3, nickel(III). Nickel(II) is more common. Nickel in its +2 oxidation state is green. Nickel(II) chloride is a common +2 oxidation state compound. Nickel(II) oxide is normally dark green, but sometimes it is gray. This is because some of the nickel is in the +3 oxidation state (nickel(III). Nickel(III) compounds are oxidizing agents. They also are grayish. Nickel compounds can be green, blue, gray, or black.
Nickel(II) compounds
Nickel(II) compounds are not highly reactive. They are normally green or blue. They are toxic and irritate skin. Some of them are carcinogens.
* Nickel(II) carbonate, green
* Nickel(II) chloride, greenish
* Nickel(II) hydroxide, light green
* Nickel(II) nitrate, greenish
* Nickel(II) oxide, gray or light green
* Nickel(II) sulfate, blue-green
Nickel(III) compounds
Nickel(III) compounds are black or gray.
* Nickel(III) oxide
Isotopes
The isotopes of nickel range in atomic weight from 48Ni to 78Ni. Nickel that is found in nature is made up of five stable isotopes; 58Ni, 60Ni, 61Ni, 62Ni and 64Ni.
At least 26 radioisotopes of nickel have been found. The most stable radioisotope is 59Ni which has a half-life of 76,000 years. Nickel also has one meta state.
History
Nickel was found when an ore that looked like copper did not make copper metal. Later it was found that the ore actually had a new metal, called nickel. Nickel was isolated as a metal and classified as a chemical element by Axel Fredrik Cronstedt in 1751. At first, the copper colored nickel ore was the only source. Later, it was made as a byproduct of cobalt blue making.
Occurrence
A common nickel ore
Nickel is normally found as a mineral, and not as a metal in the ground. Sometimes meteorites have nickel and iron metal in them. The most common nickel mineral is pentlandite. Most of the nickel on Earth is thought to be in the Earth's Earth's outer and inner cores. There are sulfidic and lateritic nickel ores. Philippines mines the most nickel. Other major mining countries are Russia, Canada and Australia. All the older rocks on Earth have some rare metals. They are got by mining where the ores are most plentiful.
Preparation
Nickel is found in both laterite and sulfide ores. They are heated to melt them and concentrate them. They are also separated by oils. Nickel is made from its sulfide by heating it in air. This oxidizes the sulfide to sulfur dioxide, leaving liquid nickel behind. This nickel is not yet pure and not ready for use.
Pure nickel with a nickel content greater than 99% is made in an electrolytic process. In this process, the nickel is dissolved in bath of sulfuric acid. When the pure nickel sticks to cathodes hanging into the bath, the impurities remain in the sulfuric acid or at the bottom of the bath. These impurities are very interesting, as they can contain precious metals.
Production
Nickel is got by mining: the ore is roasted and reduced. This gives a metal of over 75% purity. In many stainless steel applications, 75% pure nickel is usable.
Uses
Sixty-eight percent of all nickel produced is used to make stainless steel. Nickel is also used in nichrome, a name for a nickel-chromium alloy, and other alloys. Nickel is used in magnets. Nickel is used in special expensive alloys called superalloys.
Nickel sulphate is used in rechargeable batteries. A lithium ion battery contains up to 15% of nickel while the lithium content is less than 1%. A nickel cadmium battery also uses nickel. Nickel compounds are also used to electroplate nickel on items. Nickel and some of its compounds are also used as a catalyst. Nickel is used in stainless steel. It is also used in some nonferrous alloys. It is used in electroplating.
Nickel is used to make many products like stainless steel, alnico magnet, coinage, rechargeable batteries, electric guitar strings, microphone capsules and plating on plumbing fixtures. It is used as a green tint in glass.
Nickel foam is used in gas diffusion electrodes for alkaline fuel cells.
Nickel and its alloys are used as catalysts for hydrogenation reactions. Nickel is used as a binder in the cemented tungsten carbide.
63Ni is used in krytron devices as a beta particle emitter to make ionization by the keep-alive electrode more reliable. Raney nickel is used for hydrogenation of unsaturated oils to make margarine.
Safety
Nickel can irritate skin. That is why jewelry that releases nickel ions is bad for some people. Some nickel salts are carcinogens. Nickel is not as toxic as other metals such as mercury but it is still toxic.
Additional Information
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere.
Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth's outer and inner cores.
Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classified as an element in 1751 by Axel Fredrik Cronstedt, who initially mistook the ore for a copper mineral, in the cobalt mines of Los, Hälsingland, Sweden. The element's name comes from a mischievous sprite of German miner mythology, Nickel (similar to Old Nick). Nickel minerals can be green, like copper ores, and were known as kupfernickel – Nickel's copper – because they produced no copper.
Although most nickel in the earth's crust exists as oxides, economically more important nickel ores are sulfides, especially pentlandite. Major production sites include Sulawesi, Indonesia, the Sudbury region, Canada (which is thought to be of meteoric origin), New Caledonia in the Pacific, Western Australia, and Norilsk, Russia.
Nickel is one of four elements (the others are iron, cobalt, and gadolinium) that are ferromagnetic at about room temperature. Alnico permanent magnets based partly on nickel are of intermediate strength between iron-based permanent magnets and rare-earth magnets. The metal is used chiefly in alloys and corrosion-resistant plating.
About 68% of world production is used in stainless steel. A further 10% is used for nickel-based and copper-based alloys, 9% for plating, 7% for alloy steels, 3% in foundries, and 4% in other applications such as in rechargeable batteries, including those in electric vehicles (EVs). Nickel is widely used in coins, though nickel-plated objects sometimes provoke nickel allergy. As a compound, nickel has a number of niche chemical manufacturing uses, such as a catalyst for hydrogenation, cathodes for rechargeable batteries, pigments and metal surface treatments. Nickel is an essential nutrient for some microorganisms and plants that have enzymes with nickel as an active site.
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
Pages: 1
- Index
- » Science HQ
- » Nickel