Math Is Fun Forum
You are not logged in.
- Topics: Active | Unanswered
Pages: 1
#1 2025-07-26 22:02:18
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,472
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Gist
Osteoporosis is a disease in which your bones become weak and are likely to fracture (break). The disease can develop when your bone mineral density and bone mass decrease. It can also happen if the structure and strength of your bones change.
The primary cause of osteoporosis is a decrease in bone density and strength, making bones more fragile and susceptible to fractures. This decline in bone mass is often a natural part of the aging process, but certain factors can accelerate or exacerbate the process.
Osteoporosis increases the risk for breaking a bone. About one half of all women over the age of 50 will have a fracture of the hip, wrist, or vertebrae (bones of the spine) during their lifetime. Spine fractures are the most common.
Summary
Osteoporosis is a bone disease that occurs when the body loses too much bone, makes too little bone, or both. As a result, bones become weak and may break from a fall or, in serious cases, from sneezing or minor bumps.
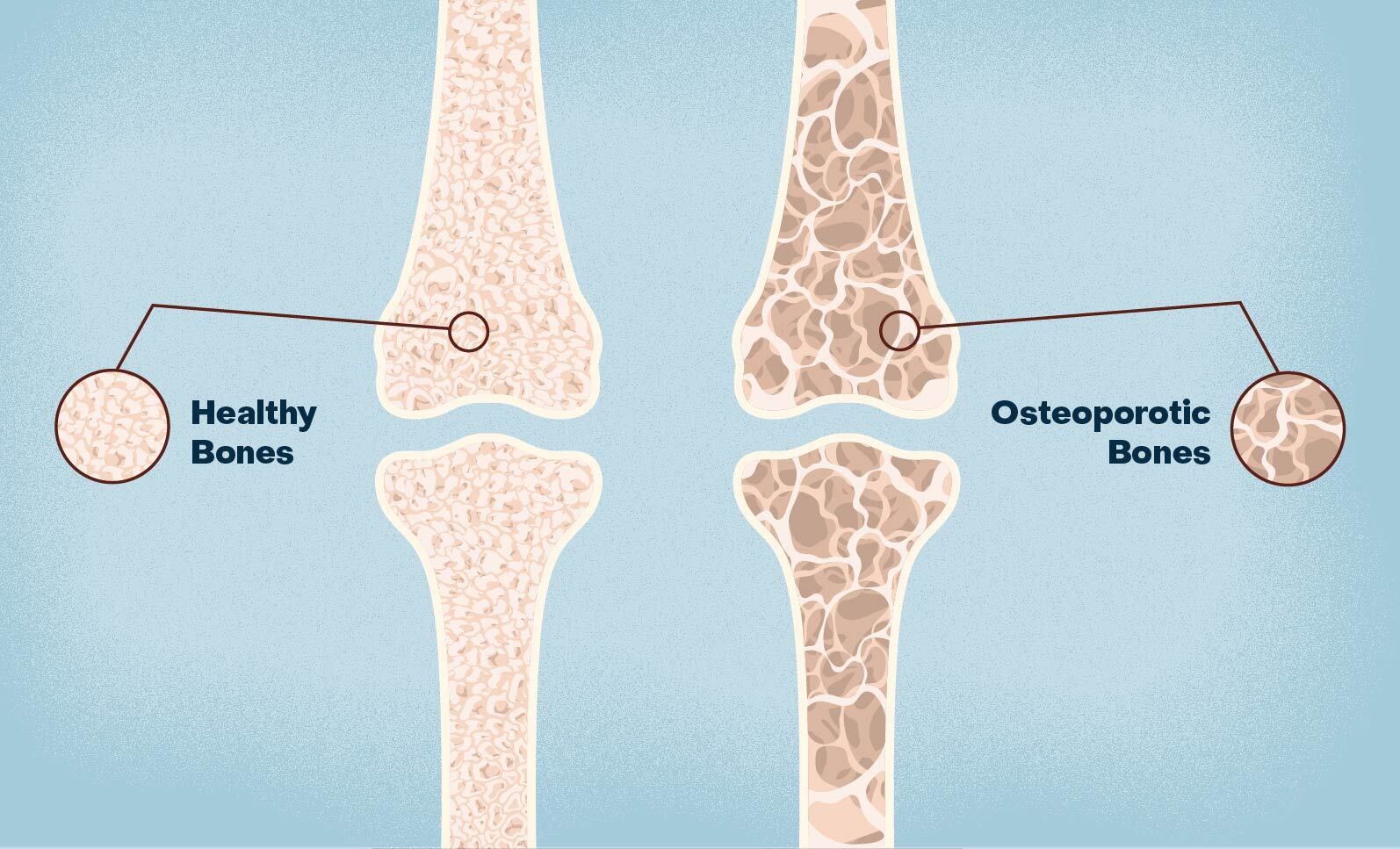
Osteoporosis means “porous bone.” Viewed under a microscope, healthy bone looks like a honeycomb. When osteoporosis occurs, the holes and spaces in the honeycomb are much larger than in healthy bone. Osteoporotic bones have lost density or mass and contain abnormal tissue structure. As bones become less dense, they weaken and are more likely to break. If you’re 50 or older and have broken a bone, ask your doctor or healthcare provider about a bone density test.
Osteoporosis is Common
About 54 million Americans have osteoporosis and low bone mass, placing them at increased risk for osteoporosis. Studies suggest that approximately one in two women and up to one in four men age 50 and older will break a bone due to osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis is Serious
Breaking a bone is a serious complication of osteoporosis, especially with older patients. Osteoporotic bone breaks are most likely to occur in the hip, spine or wrist, but other bones can break too. In addition to causing permanent pain, osteoporosis causes some patients to lose height. When osteoporosis affects vertebrae, or the bones of the spine, it often leads to a stooped or hunched posture.
Osteoporosis may limit mobility, which often leads to feelings of isolation or depression. Additionally, twenty percent of seniors who break a hip die within one year from either complications related to the broken bone itself or the surgery to repair it. Many patients require long-term nursing home care.
Osteoporosis is Costly
Osteoporosis is responsible for two million broken bones and $19 billion in related costs every year. By 2025, experts predict that osteoporosis will be responsible for approximately three million fractures and $25.3 billion in costs annually.
Osteoporosis Can Sneak up on You
Osteoporosis is often called a silent disease because one can’t feel bones weakening. Breaking a bone is often the first sign of osteoporosis or a patient may notice that he or she is getting shorter or their upper back is curving forward. If you are experiencing height loss or your spine is curving, be sure to consult your doctor or healthcare professional immediately.
Details
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in fracture risk.
It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae in the spine, the bones of the forearm, the wrist, and the hip.
Until a broken bone occurs, there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. After the broken bone heals, some people may have chronic pain and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities.
Osteoporosis may be due to lower-than-normal maximum bone mass and greater-than-normal bone loss. Bone loss increases after menopause in women due to lower levels of estrogen, and after andropause in older men due to lower levels of testosterone. Osteoporosis may also occur due to several diseases or treatments, including alcoholism, anorexia or underweight, hyperparathyroidism, hyperthyroidism, kidney disease, and after oophorectomy (surgical removal of the ovaries). Certain medications increase the rate of bone loss, including some antiseizure medications, chemotherapy, proton pump inhibitors, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, glucocorticosteroids, and overzealous levothyroxine suppression therapy. Smoking and sedentary lifestyle are also recognized as major risk factors. Osteoporosis is defined as a bone density of 2.5 standard deviations below that of a young adult. This is typically measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA or DEXA).
Prevention of osteoporosis includes a proper diet during childhood, hormone replacement therapy for menopausal women, and efforts to avoid medications that increase the rate of bone loss. Efforts to prevent broken bones in those with osteoporosis include a good diet, exercise, and fall prevention. Lifestyle changes such as stopping smoking and not drinking alcohol may help. Bisphosphonate medications are useful to decrease future broken bones in those with previous broken bones due to osteoporosis. In those with osteoporosis but no previous broken bones, they have been shown to be less effective. They do not appear to affect the risk of death.
Osteoporosis becomes more common with age. About 15% of Caucasians in their 50s and 70% of those over 80 are affected. It is more common in women than men. In the developed world, depending on the method of diagnosis, 2% to 8% of males and 9% to 38% of females are affected. Rates of disease in the developing world are unclear. About 22 million women and 5.5 million men in the European Union had osteoporosis in 2010. In the United States in 2010, about 8 million women and between 1 and 2 million men had osteoporosis. White and Asian people are at greater risk for low bone mineral density due to their lower serum vitamin D levels and less vitamin D synthesis at certain latitudes. The word "osteoporosis" is from the Greek terms for "porous bones".
Additional Information:
What is osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a disease in which your bones become weak and are likely to fracture (break). The disease can develop when your bone mineral density and bone mass decrease. It can also happen if the structure and strength of your bones change.
Osteoporosis is called a "silent" disease because it doesn't usually cause symptoms. You may not even know you have the disease until you break a bone. This could happen with any bone, but it's most common in the bones of your hip, vertebrae in the spine, and wrist.
What causes osteoporosis?
Your bones are made of living tissue. To keep them strong, your body breaks down old bone and replaces it with new bone. Osteoporosis develops when more bone is broken down than replaced. You lose bone mass and changes happen in the structure of your bone tissue. This can happen as you get older. Other risk factors can also lead to the development of osteoporosis or increase your chance of developing the disease.
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
Pages: 1