Math Is Fun Forum
You are not logged in.
- Topics: Active | Unanswered
Pages: 1
#1 2025-10-18 16:26:13
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 53,247
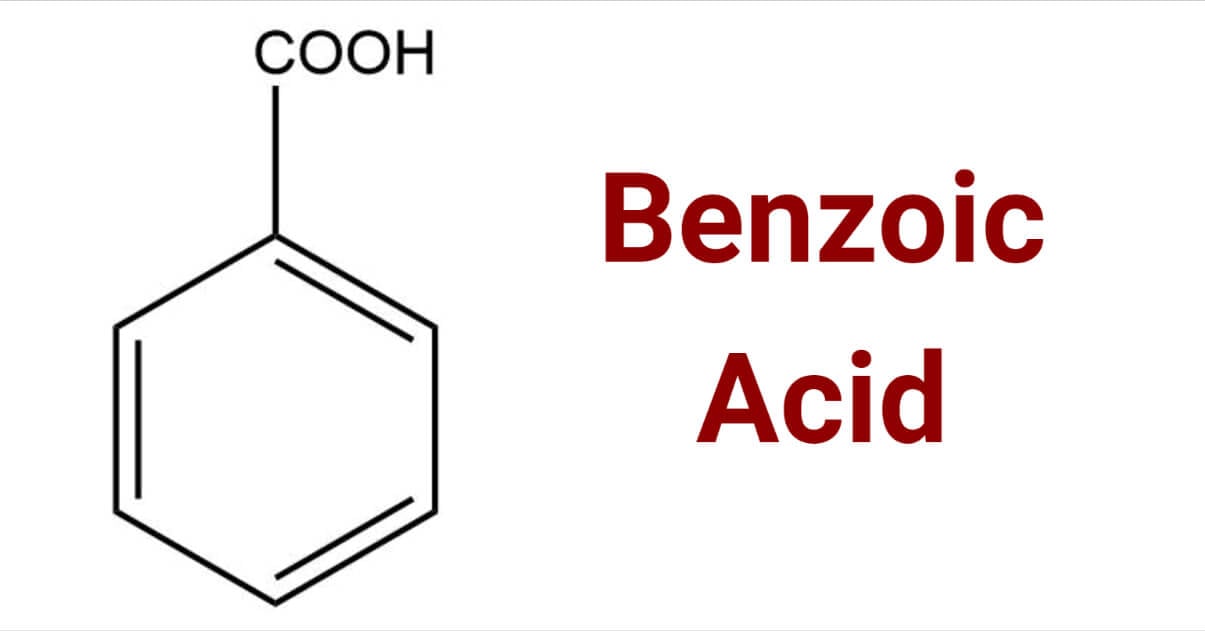
Benzoic Acid
Benzoic Acid
Gist
Benzoic acid is a white crystalline organic compound with the formula C7H6O2 that has various uses, including as a food and cosmetic preservative and in the production of ointments, insect repellents, and dyes. It is a simple aromatic carboxylic acid, naturally found in some plants, and is known for its antiseptic properties. While useful, benzoic acid is a skin and eye irritant, and its combination with vitamin C can form benzene, a known carcinogen.
Benzoic acid is used as a preservative in food and drinks, an antifungal and antibacterial agent in medications and cosmetics, and a precursor for producing plastics and other chemicals. It's also found in products like toothpaste, insect repellents, and some cleaning supplies.
Summary
Benzoic acid is a white, crystalline organic compound belonging to the family of carboxylic acids, widely used as a food preservative and in the manufacture of various cosmetics, dyes, plastics, and insect repellents.
First described in the 16th century, benzoic acid exists in many plants; it makes up about 20 percent of gum benzoin, a vegetable resin. It was first prepared synthetically about 1860 from compounds derived from coal tar. It is commercially manufactured by the chemical reaction of toluene (a hydrocarbon obtained from petroleum) with oxygen at temperatures around 200° C (about 400° F) in the presence of cobalt and manganese salts as catalysts. Pure benzoic acid melts at 122° C (252° F) and is very slightly soluble in water.
Among the derivatives of benzoic acid are sodium benzoate, a salt used as a food preservative; benzyl benzoate, an ester used as a miticide; and benzoyl peroxide, used in bleaching flour and in initiating chemical reactions for preparing certain plastics.
Details
Benzoic acid is a white or colorless crystalline organic compound with the formula C6H5COOH, whose structure consists of a benzene ring (C6H6) with a carboxyl (−C(=O)OH) substituent. The benzoyl group is often abbreviated "Bz" (not to be confused with "Bn," which is used for benzyl), thus benzoic acid is also denoted as BzOH, since the benzoyl group has the formula –C6H5CO. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from gum benzoin, which was for a long time its only source.
Benzoic acid occurs naturally in many plants and serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of many secondary metabolites. Salts of benzoic acid are used as food preservatives. Benzoic acid is an important precursor for the industrial synthesis of many other organic substances. The salts and esters of benzoic acid are known as benzoates.
Production:
Industrial Preparation
Benzoic acid is produced commercially by partial oxidation of toluene with oxygen. The process is catalyzed by cobalt or manganese naphthenates. The process uses abundant materials, and proceeds in high yield.
The first industrial process involved the reaction of benzotrichloride (trichloromethyl benzene) with calcium hydroxide in water, using iron or iron salts as catalyst. The resulting calcium benzoate is converted to benzoic acid with hydrochloric acid. The product contains significant amounts of chlorinated benzoic acid derivatives. For this reason, benzoic acid for human consumption was obtained by dry distillation of gum benzoin. Food-grade benzoic acid is now produced synthetically.
Laboratory synthesis
Benzoic acid is cheap and readily available, so the laboratory synthesis of benzoic acid is mainly practiced for its pedagogical value. It is a common undergraduate preparation.
Benzoic acid can be purified by recrystallization from water because of its high solubility in hot water and poor solubility in cold water. The avoidance of organic solvents for the recrystallization makes this experiment particularly safe. This process usually gives a yield of around 65%.
By hydrolysis
Like other nitriles and amides, benzonitrile and benzamide can be hydrolyzed to benzoic acid or its conjugate base in acid or basic conditions.
From Grignard reagent
Bromobenzene can be converted to benzoic acid by "carboxylation" of the intermediate phenylmagnesium bromide. This synthesis offers a convenient exercise for students to carry out a Grignard reaction, an important class of carbon–carbon bond forming reaction in organic chemistry.
Oxidation of benzyl compounds
Benzyl alcohol and benzyl chloride and virtually all benzyl derivatives are readily oxidized to benzoic acid.
Additional Information
Benzoic acid, the simplest benzene-based carboxylic acid, has been known since the 16th century. One of its discoverers was the legendary clairvoyant Nostradamus. Its most common natural source is gum benzoin, a resin found in the bark of trees of the genus Styrax.
Most benzoic acid produced today is synthetic. Its first industrial synthesis was the hydrolysis of benzotrichloride to calcium benzoate, followed by acidification. This method has been completely displaced by the air oxidation of toluene, which avoids the problem of product contamination with chlorinated byproducts.
Many processed foods contain benzoic acid or one of its salts as a preservative. The acid inhibits the growth of bacteria, molds, and yeasts; it works best when the food has an acidic pH value. Benzoic acid also is often found in topical antifungal preparations.
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
Pages: 1