Math Is Fun Forum
You are not logged in.
- Topics: Active | Unanswered
#1 2013-09-29 04:42:06
- jacks
- Member
- Registered: 2012-11-21
- Posts: 132
no. of path in Grid
In a Diagram shown in figure, Not that the Grid path from F to G is missing.
So path from A to B can not pass from F and G.
How many path are there from A to B
assume all path only have steps going up or to the right.
Last edited by jacks (2013-09-29 05:30:44)
Offline
#2 2013-09-29 04:51:05
- bobbym
- bumpkin

- From: Bumpkinland
- Registered: 2009-04-12
- Posts: 109,606
Re: no. of path in Grid
Where is D and E?
In mathematics, you don't understand things. You just get used to them.
If it ain't broke, fix it until it is.
Always satisfy the Prime Directive of getting the right answer above all else.
Offline
#3 2013-09-29 05:31:38
- jacks
- Member
- Registered: 2012-11-21
- Posts: 132
Re: no. of path in Grid
Sorry Bobbym , actually it is A and B
Offline
#4 2013-09-29 05:36:39
- bobbym
- bumpkin

- From: Bumpkinland
- Registered: 2009-04-12
- Posts: 109,606
Re: no. of path in Grid
Hi;
I am getting 38 ways.
In mathematics, you don't understand things. You just get used to them.
If it ain't broke, fix it until it is.
Always satisfy the Prime Directive of getting the right answer above all else.
Offline
#5 2013-09-29 05:37:28
- jacks
- Member
- Registered: 2012-11-21
- Posts: 132
Re: no. of path in Grid
Would you like to explain it to me, Thanks
Offline
#6 2013-09-29 06:03:13
- bobbym
- bumpkin

- From: Bumpkinland
- Registered: 2009-04-12
- Posts: 109,606
Re: no. of path in Grid
For ones that have missing intersections and are small the vertex counting method will work fine.
The drawing shows the number of paths to each node.
Each node is the sum of the two nodes underneath and to left of it.
In mathematics, you don't understand things. You just get used to them.
If it ain't broke, fix it until it is.
Always satisfy the Prime Directive of getting the right answer above all else.
Offline
#7 2013-09-29 06:37:43
- jacks
- Member
- Registered: 2012-11-21
- Posts: 132
Re: no. of path in Grid
Thanks Bobbym Got it.
Offline
#8 2013-09-29 06:54:51
- bobbym
- bumpkin

- From: Bumpkinland
- Registered: 2009-04-12
- Posts: 109,606
Re: no. of path in Grid
There is an analytical answer for these type but the counting method is easier to understand.
In mathematics, you don't understand things. You just get used to them.
If it ain't broke, fix it until it is.
Always satisfy the Prime Directive of getting the right answer above all else.
Offline
#9 2013-09-29 07:02:25
- jacks
- Member
- Registered: 2012-11-21
- Posts: 132
Re: no. of path in Grid
Would you like to explain me analytical answer.
I also tried for that method but could not get it.
(But I like yours Counting method.)
Offline
#10 2013-09-29 09:45:20
- bobbym
- bumpkin

- From: Bumpkinland
- Registered: 2009-04-12
- Posts: 109,606
Re: no. of path in Grid
Hi;
By combinatorics:
In mathematics, you don't understand things. You just get used to them.
If it ain't broke, fix it until it is.
Always satisfy the Prime Directive of getting the right answer above all else.
Offline
#11 2013-09-30 06:36:07
- jacks
- Member
- Registered: 2012-11-21
- Posts: 132
Re: no. of path in Grid
Thanks Bobbym would you like to explain me to it.
Offline
#12 2013-09-30 06:38:41
- bobbym
- bumpkin

- From: Bumpkinland
- Registered: 2009-04-12
- Posts: 109,606
Re: no. of path in Grid
It is just adding up all the paths in the lattice around the missing intersection.
In mathematics, you don't understand things. You just get used to them.
If it ain't broke, fix it until it is.
Always satisfy the Prime Directive of getting the right answer above all else.
Offline
#13 2013-09-30 06:47:19
- anonimnystefy
- Real Member
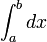
- From: Harlan's World
- Registered: 2011-05-23
- Posts: 16,049
Re: no. of path in Grid
Hi
is also a way.Here lies the reader who will never open this book. He is forever dead.
Taking a new step, uttering a new word, is what people fear most. ― Fyodor Dostoyevsky, Crime and Punishment
The knowledge of some things as a function of age is a delta function.
Offline
#14 2013-09-30 07:16:01
- jacks
- Member
- Registered: 2012-11-21
- Posts: 132
Re: no. of path in Grid
To anonimnystefy I have understand
(Which is Total no. of path from A to B, If There is a connectivity between F to G)
but Did not understand
Would you explain it to me.
Thanks
Offline
#15 2013-09-30 07:17:51
- anonimnystefy
- Real Member
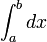
- From: Harlan's World
- Registered: 2011-05-23
- Posts: 16,049
Re: no. of path in Grid
It's the number of paths from A to F times the number of paths from G to B.
Here lies the reader who will never open this book. He is forever dead.
Taking a new step, uttering a new word, is what people fear most. ― Fyodor Dostoyevsky, Crime and Punishment
The knowledge of some things as a function of age is a delta function.
Offline
#16 2013-09-30 07:24:50
- jacks
- Member
- Registered: 2012-11-21
- Posts: 132
Re: no. of path in Grid
To Admin (Bobbym) i did not understand it
It is just adding up all the paths in the lattice around the missing intersection.
Thanks
Offline
#17 2013-09-30 07:28:57
- anonimnystefy
- Real Member
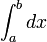
- From: Harlan's World
- Registered: 2011-05-23
- Posts: 16,049
Re: no. of path in Grid
I think I know which points he took, but I cannot be sure.
I think he used (2,3), (3,0) and (3,1), A being (0,0) and B being (5,4).
Here lies the reader who will never open this book. He is forever dead.
Taking a new step, uttering a new word, is what people fear most. ― Fyodor Dostoyevsky, Crime and Punishment
The knowledge of some things as a function of age is a delta function.
Offline
#18 2013-09-30 07:32:00
- bobbym
- bumpkin

- From: Bumpkinland
- Registered: 2009-04-12
- Posts: 109,606
Re: no. of path in Grid
Hi;
Look at my drawing in post #6.
I picked (2,3), (3,1) and (4,0) and calculated the paths from there.
In mathematics, you don't understand things. You just get used to them.
If it ain't broke, fix it until it is.
Always satisfy the Prime Directive of getting the right answer above all else.
Offline
#19 2013-09-30 07:33:05
- jacks
- Member
- Registered: 2012-11-21
- Posts: 132
Re: no. of path in Grid
It's the number of paths from A to F times the number of paths from G to B.
To anonimnystefy I did not understand it
why we minus it.
please explain it to me
Thanks
Offline
#20 2013-09-30 07:46:54
- anonimnystefy
- Real Member
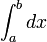
- From: Harlan's World
- Registered: 2011-05-23
- Posts: 16,049
Re: no. of path in Grid
It's the number of paths from A to F times the number of paths from G to B.
This is the reason. These are all the paths that become unavailable when we remove the line.
Hi bobbym
Yes, I meant (4,0).
Last edited by anonimnystefy (2013-09-30 07:59:54)
Here lies the reader who will never open this book. He is forever dead.
Taking a new step, uttering a new word, is what people fear most. ― Fyodor Dostoyevsky, Crime and Punishment
The knowledge of some things as a function of age is a delta function.
Offline
#21 2013-09-30 07:57:02
- bobbym
- bumpkin

- From: Bumpkinland
- Registered: 2009-04-12
- Posts: 109,606
Re: no. of path in Grid
Hi;
I did not see your post 17, I was answering his question.
In mathematics, you don't understand things. You just get used to them.
If it ain't broke, fix it until it is.
Always satisfy the Prime Directive of getting the right answer above all else.
Offline
#22 2013-09-30 08:03:39
- anonimnystefy
- Real Member
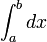
- From: Harlan's World
- Registered: 2011-05-23
- Posts: 16,049
Re: no. of path in Grid
Even better then.
I guess the question is fully answered now. Three ways is enough.
I just want to try to do one more thing.
Last edited by anonimnystefy (2013-09-30 08:04:30)
Here lies the reader who will never open this book. He is forever dead.
Taking a new step, uttering a new word, is what people fear most. ― Fyodor Dostoyevsky, Crime and Punishment
The knowledge of some things as a function of age is a delta function.
Offline
#23 2013-09-30 09:54:23
- bobbym
- bumpkin

- From: Bumpkinland
- Registered: 2009-04-12
- Posts: 109,606
Re: no. of path in Grid
There is another more general way. That maybe can answer for many missing intersections.
In mathematics, you don't understand things. You just get used to them.
If it ain't broke, fix it until it is.
Always satisfy the Prime Directive of getting the right answer above all else.
Offline
#24 2013-10-13 16:55:01
- jacks
- Member
- Registered: 2012-11-21
- Posts: 132
Re: no. of path in Grid
Thanks Admin and anonimnystefy got it
Offline
#25 2013-10-13 17:15:08
- bobbym
- bumpkin

- From: Bumpkinland
- Registered: 2009-04-12
- Posts: 109,606
Re: no. of path in Grid
Hi;
You are wlecome.
In mathematics, you don't understand things. You just get used to them.
If it ain't broke, fix it until it is.
Always satisfy the Prime Directive of getting the right answer above all else.
Offline